Liability insurance for owners of hazardous production facilities. Safety of dangerous objects. What applies to objects
On one of the forums dedicated to insurance issues, a question was posted: “I am a modest entrepreneur, I have a small gas station. When I say that it is “small”, it means that it is very small! I only have one fuel dispenser, and the fuel storage is a one and a half ton container dug into the sand.
Why should I pay for compulsory insurance of hazardous production facilities (OSOPO), if in my case regular insurance is enough? The question sparked a lively discussion, highlighting the importance of the problem of compulsory health insurance among a certain segment of the population. In our article we will understand what OSOPO is, why it is needed and what its features are.
| Content: |
What are “Hazardous Production Facilities”?
HPFs are facilities where there is a possibility of an emergency situation causing harm to the health and life of third parties. The list of hazardous facilities is regulated by Federal Law of the Russian Federation No. 255 “On compulsory insurance of civil liability of the owner of a hazardous facility for causing harm as a result of an accident at a hazardous facility.” The text of the law can be found
We present this list in a slightly optimized form for ease of reading:
- Warehouses, special closed and open storage facilities in which hazardous substances (HS) are stored.
- Enterprises that use, process and transport hazardous substances (gas stations, fuel depots, oil storage facilities).
- Enterprises where chemical agents are manufactured from non-hazardous components.
- The premises of a production facility will be recognized as a hazardous production facility if it:
- Equipment operating at high pressure (more than 0.07 megapascal) is used.
- The production cycle uses highly heated liquids, gases, metals - more than 115 °C.
- Dangerous mechanisms and transport routes are used in production (an ordinary elevator in an apartment building is considered a dangerous mechanism).
- The work cycle of the facility involves underground work, as well as work at high altitudes.
- Hydraulic engineering structures (dams, dikes, locks, berths, ship lifts).
Attention! 1) A hazardous substance is a material that can easily ignite, explode, has poisonous properties, is toxic when burned, and is hazardous to the environment. 2) An important indicator of the “danger” of a production mechanism will be the assessment of its suitability given by a specialist expert.
What determines the need for compulsory HIF insurance?
To understand the need for compulsory insurance of hazardous production facilities, you should familiarize yourself with the historical reasons for the emergence of this type of insurance.
On December 3, back in 1984, a large-scale accident occurred at the American plant of the Union Carbide company in the Indian city of Bhopal. A series of explosions occurred, after which fires started. In the first hours of the tragedy alone, thousands of people died - the total number of deaths was 18-22 thousand according to sources from American news agencies and 27 thousand according to Indian newsmakers.
These figures include workers who died from injuries, burns, and poisoning in the days following the disaster. The total number of people affected by the accident - dead and survivors, workers and city residents - amounted to more than 600 thousand. Such a significant number of victims made the Indian accident the largest man-made disaster of the twentieth century.
The pressure of the Indian government on representatives of American industrial companies led to the emergence of a new type of insurance, which quickly spread throughout the world. From 1997 to 2010, the Russian Federation created all the necessary legal grounds for the full operation of this type of insurance in our country. The legislative framework is constantly updated and improved, creating conditions for interaction that are convenient for the Insurer and the Policyholder.
Features of HPO insurance
In this part of our article, we will look at the rules for concluding and terminating the “OSOPA Agreement”, what the “Insured Sum” is and how “Insurance Payments” are formed.
OSOPO Agreement
The main feature of the OSOPO agreement is its non-binding nature as a document. The contract plays a secondary role. Of primary importance is the insurance policy, which is issued to the Insured on the basis of an application written by him.
Regarding what type of dangerous object is insured, the Policyholder must provide the Insurer with a certain set of documents. For convenience, we display the list of required documents using a table:
Important! 1) The application and the insurance policy are integral parts of each other, they cannot be considered separately, they are a common part of a single document. 2) The OSOPO agreement can be concluded before the registration of the OPO by the Rostechnadzor authorities. 3) The list of required documents may vary depending on the regulations adopted by a particular Insurance Company (IC).
Features related to the conclusion, amendment and termination of a FOSO agreement
When concluding a FOSO agreement, it is important to take into account the following possible actions of the insurance company:
- Compulsory insurance of dangerous objects involves the actions of the insurance company aimed at assessing the insurance risk. Risk analysis can be carried out by the insurance company on its own or with the help of specialists specially engaged for this purpose. External experts must be employed by a special state or private company. The opinion of an “independent” expert working independently will not have legal significance.
- The insurance company has the right to demand from the Insured, Rostechnadzor or other supervisory authority information about the operation of the production facility.
When amending the OSOPO agreement, you need to know the following nuances:
- In the event of a serious change in conditions affecting the significance of the insurance risk, the Policyholder is obliged to notify the Insurer about this. This clause is mandatory for all insurance policies of this kind. This nuance should be understood both ways - the degree of insurance risk has increased, the degree of insurance risk has decreased. So, for example, if there is a threat of collapse at the mine, this will be considered an increased risk; if major repairs have been carried out at the mine, this will be considered a risk reduction.
- Actions related to the conditions of changes in insurance risks affect the amount of the insurance premium.
In most cases, termination of the FOSO agreement is carried out by the insurance company if the following conditions are met:
- At the initiative of the Policyholder. Termination of the contract in such cases is possible in the absence of claims by the Insurer against the Policyholder.
- At the initiative of the Insurer. The most common reason for such actions is late insurance payments. The criticality of the overdue period depends on the specific insurance system.
- By agreement of the parties.
- Termination of the existence of the Policyholder (liquidation - for a legal entity, death - for an individual). This provision will not necessarily lead to the termination of the contract. In cases where the new owner manages to notify the insurance company of his existence within a critical period, the contract can be continued. Naturally, the contract itself will be changed.
- A radical change in the status of the insured object. Insurance of hazardous production facilities loses its necessity if the insured facility is recognized as “non-hazardous”. This legal status is typical for closed or mothballed enterprises.
Sum insured
The insured amount is calculated in relation to the rules established on December 28, 2016 by Bank of Russia Regulation No. 574-P -
The amount of the insured amount depends on the number of injured people. The minimum is 10 million rubles, the maximum is 6.5 billion rubles. The law specifically stipulates the insurance amount intended for injured coal industry workers. In more detail -
Important! Payment of the insurance premium is considered by many insurance companies from the moment it is received into the company’s account, and not from the moment the banking transaction begins.
Insured event
The actions of the Policyholder during the occurrence of an insured event may vary depending on the terms of the contract, but mainly they should be as follows:
- Every effort must be made to prevent an accident. It is impossible for an insured event to ripen like an egg in an incubator - the conditions that contribute to the occurrence of an emergency situation must be eliminated in a timely manner.
- If third parties (not employees of the enterprise) were injured as a result of the accident, then the owner of the hazardous production facility is obliged to provide them with information about the Insurer (contact details).
- The policyholder is obliged to provide the Insurer with all information about the nature of the insured event: the time of the accident, the causes of the accident, the number of victims, possible damage to property.
Pool of Insurers
There are a certain number of Insurers who are entitled to HIF insurance. All of them are members of the NUSO (National Union of Liability Insurers) and have significant capitalization. The ten largest insurance companies as of 2014 are below in the table:

The law provides for mandatory insurance by the owner of objects that pose a potential danger.
The insurance policy will allow the owner to fully compensate for the damage caused to victims as a result of a man-made disaster.
Man-made disasters at the end of the twentieth century led to massive loss of life. Today, the state obliges owners of hazardous industries to insure the risk of death and harm to the health of fellow citizens as a result of industrial accidents.
What are the basic principles of HIF insurance?
The list of industries recognized as dangerous and the rules of compulsory insurance are clearly established at the federal level by the 2012 law “On compulsory insurance of civil liability of the owner of a hazardous facility for damage caused by an accident at a hazardous facility.”
Insurance for the owner of a hazardous production facility (HIF) is mandatory.
The object of insurance is the liability of owners of hazardous production to persons who suffered harm as a result of a man-made disaster. Damage includes physical, property and environmental damage.
What structures are recognized as hazardous production facilities?
The list of public safety organizations in the 2012 federal law is exhaustive. Those productions are considered which, in the event of a failure, could cause significant property, physical or environmental damage.

Enterprises classified as hazardous industries have the right to carry out production activities only if they have an insurance policy. The absence of a policy is an obstacle to obtaining a license to operate and a basis for the application of financial sanctions.
List of enterprises classified as hazardous industries:
- Production facilities:
- HIFs that in the production process use, process, store, transport or destroy hazardous substances such as:
- flammable, flammable or oxidizing;
- toxic and highly toxic;
- explosives;
- hazardous to the environment.
- HIFs using equipment operating at a pressure of 0.07 MPa and above or at an operating water temperature above 115 °C;
- HIFs that use stationary lifting mechanisms, funiculars, escalators, cable cars and elevators in apartment buildings, public catering facilities, trade, administrative buildings and other facilities that support the livelihoods of citizens;
- Industrial production facilities where, as a result of the production process, metal melts (ferrous and non-ferrous) and alloys based on them are obtained;
- HIFs carrying out underground work, mineral processing and other mining operations.
- hydroelectric power station buildings;
- dams;
- channels;
- tunnels;
- water inlet/outlet and spillway structures;
- ship lifts;
- shipping locks;
- dams, etc.
Special conditions for HPF insurance apply to state property, which is financed from the budget, as well as to elevators and escalators installed in apartment buildings.
Why was compulsory insurance for hazardous industries introduced?
Compulsory insurance for hazardous industries was introduced after a series of large-scale man-made disasters at the end of the 20th century. The consequences of accidents in industries working with hazardous substances have been serious and long-lasting.

In 1984, an accident occurred in India (Bhopal) at the American Union Carbide plant. About three thousand people died on December 3, 1984, and about 15 thousand more in subsequent years. But, according to scientists, the total number of victims of the disaster is about half a million human lives. This man-made disaster is the largest in the world.
The history of the accident at the Chernobyl nuclear power plant, which occurred in 1886, is known to all Russians.
It is not surprising that back in 1997 the state adopted a law on insuring the activities of industries that pose a potential danger to citizens and the environment.
The Federal Law “On compulsory insurance of civil liability of the owner of a hazardous facility for damage caused by an accident at a hazardous facility,” in force since January 1, 2012, obliges all owners of hazardous production facilities to insure the risk of damage to citizens and organizations as a result of an industrial accident.
What are the amounts of insurance compensation?
The limits of insurance payments are established by federal law and depend on the type of activity of potentially hazardous production.
Some enterprises are developing Declaration of industrial safety at a hazardous facility. In accordance with the declaration, the possible number of victims as a result of an industrial accident is determined.
Depending on the likely maximum number of victims, the amount of the insured amount is determined. If the number of victims is less than 10 people, the insured amount will be 10 million rubles, more than 3,000 people - 6.5 billion rubles, etc.
In the absence of an industrial safety declaration, the insurance amount is determined by the type of hazardous facility:
- oil refining, petrochemical and chemical production – 50 million rubles;
- gas supply facilities, gas consumption and gas networks – 25 million rubles;
- other hazardous production facilities – 10 million rubles.
How is HIF insurance carried out?
To obtain insurance, the owner of a hazardous production has the right to contact the insurance company of his choice.
The amount of insurance compensation is determined as a result of an examination. Experts set the maximum amount of payment, depending on which the amount of the insurance premium is assigned.
The contribution can be paid in installments - this issue is agreed upon by the owner of the PPO with the insurance company.

- Carry out an examination to assess the degree of potential danger of the object;
- Provide the following package of documents:
- documents establishing the right of ownership (ownership): purchase and sale agreement, inventory card, invoices with payment orders, etc.;
- documents characterizing the object (attachment to the accounting card);
- hazardous production facility registration card;
- certificate of registration of a dangerous object;
- UB form;
- MVKP form;
- statement;
What is the object of HIF insurance?
The object of insurance for hazardous production is the owner's financial liability arising as a result of an accident. Only the policyholder's risk in favor of third parties is subject to insurance.
Civil legislation regulates that the owner of a hazardous production bears full financial liability to persons who have suffered damage as a result of the production activities of a hazardous facility.
The presence of an insurance policy guarantees the owner of the hazardous production facility the opportunity to pay damages to the victims, and the victims the opportunity to receive compensation.
The insurance company checks compliance at the enterprise that has entered into the insurance contract, safety standards.
Only large companies that can provide compensation for damage on a large scale are granted a license to enter into a hazardous production insurance contract. There are less than a hundred such large firms in the insurance market.
What damage is compensated by the insurance company?
Upon the occurrence of an event provided for in the insurance policy (an accident that causes harm to human health, property or environmental damage) The insurance company makes the following payments to victims from its own funds:
- costs of eliminating the consequences of a man-made disaster;
- costs to reduce losses from an accident, if such actions were taken as a result of instructions from the insurance company;
- costs of investigating the causes of the accident and identifying those responsible;
- costs of saving the lives and property of victims of the accident;
- costs of conducting cases for compensation for damage caused by an industrial accident in court and arbitration.
As practice shows, even at those enterprises where all safety requirements are faithfully followed, accidents can occur. The list of hazardous industries was not compiled by chance - it is the result of many years of sad experience.
Mandatory insurance of hazardous industries allows not only to reduce the costs of the owner of a hazardous production facility, but also to receive full compensation for victims of the disaster.
What damage is not compensated by the insurance company?
The rules for insurance of hazardous industries provide for a number of situations when payments are not made, since they are not provided for by the legislation on insurance of hazardous production facilities.
Insured events do not include:
- removal of a dangerous object from the possession of the insured due to the fault of third parties;
- natural disasters;
- civil unrest, civil war, strike;
- terrorist attack;
- war;
- nuclear explosion and radioactive contamination;
- intentional actions of the beneficiary (victim) or owner of the hazardous production facility.
In the latter case, the insurance company pays compensation if damage is caused to the life and health of a third party due to the fault of the policyholder.
Let's sum it up
Since January 1, 2012, owners of hazardous industries are required to enter into an insurance contract in the event of an accident resulting in death, harm to the health of citizens, property or environmental damage.

HPFs include industries working with hazardous substances, at high pressures, with high-temperature water, gas stations, hydraulic structures, underground production, facilities operating elevators, cable cars, escalators, etc.
In the event of a man-made disaster, compensation to victims is paid by the insurance company.
The insurance rate for hazardous production facilities and the maximum amount of compensation depend on the nature of production and the amount of potential damage, which is determined by examination.
To conclude an insurance contract, the owner of a public health insurance company contacts the insurance company of his choice, fills out an application and provides a package of documents. After an examination is carried out to assess the amount of potential damage, a hazardous production facility insurance contract is concluded.
Video about insurance of dangerous objects
Read more:
One Comment
Fukushima immediately comes to mind. Here it becomes clear why insurance of such objects is mandatory. I am sure that insurance companies are not too fond of such clients, because in the event of some kind of environmental disaster, the payments will be colossal. On the other hand, a dangerous object is not necessarily some kind of “nuclear reactor”. The tunnel could be like that too.
Insurance of especially dangerous objects today is mandatory for owners, as well as organizations involved in their operation.
Dear readers! The article talks about typical ways to resolve legal issues, but each case is individual. If you want to know how solve exactly your problem- contact a consultant:
APPLICATIONS AND CALLS ARE ACCEPTED 24/7 and 7 days a week.
It's fast and FOR FREE!
This point is fixed at the legislative level. That is why today a very large number of insurance companies provide this service to their clients.
What is it
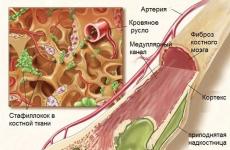
A hazardous production facility today is an object during the use of which an incident may occur that causes serious damage to the property, life and health of third parties.
Hazardous objects also include anything that can have a negative impact on the environment. In the legislation in force on the territory of the Russian Federation, all types of hazardous production facilities are enshrined at the legislative level.
You should know that a dangerous object is not considered a separate structure or equipment, but the entire site on which the property falling under the definition is located.
But it happens that the enterprise as a whole is not a dangerous object. But they recognize any separate division of it.
That is why it often happens that at an energy or other enterprise there are several dozen or even hundreds of sites that are especially dangerous.
This point is very important to take into account when concluding a contract for hazardous production insurance. Since the amount of the insurance premium directly depends on the property that is included in the insurance coverage.
Insurance rules for hazardous production facilities
As well as for other services of this type, insurance of hazardous production facilities must be carried out on the basis of insurance rules.
This document contains the following sections:
- "Terms and Definitions";
- "Insurance Subjects";
- “Object of insurance”;
- “Insurance risks and insured events”;
- “Procedure for determining the insured amount”;
- “Term of insurance”;
- “The procedure for determining the insurance tariff, insurance premium, insurance premium”;
- “Conclusion of an insurance contract”;
- “Rights and obligations of the parties”;
- “The procedure for determining the amount of damage and making insurance payments”;
- “Grounds for refusal to make insurance payments”;
- "Procedure for resolving disputes."
The paragraph entitled “Terms and Definitions” contains interpretations of the terms used in the insurance rules. This point is very important for understanding the document.
Since if the policyholder does not familiarize himself with it, then there is a high probability of misunderstanding of the terms of the agreement being concluded. In the section “Insurance Subjects” all participants of the insurance contract are indicated.
Most often there are only three of these subjects:
There is a special item called “Object of Insurance”. It highlights issues relating to the property interests of the policyholder. Since they are the ones who are protected by a special insurance program designed for public health organizations.
“Insurance risks and insured events” - highlights events upon the occurrence of which the insurance company is obliged to fulfill its obligations.
The list of insurance risks may include a variety of events. All of them are agreed upon in advance and included in the insurance agreement. Subsequently, it must be signed by the policyholder and the insurer's representative.
The paragraph entitled “Insurance Period” indicates the duration of the concluded contract. During the entire period, the insurance company is responsible for all risks.
Most often, the client, according to these rules, has the right to choose the duration of the insurance contract.
“The procedure for determining the insurance rate, premium, contribution” announces prices for the provision of insurance services of the type in question.
This section also identifies all the factors that are taken into account when calculating the amount of the insurance premium required to be paid.
The concluded contract comes into force only after the required amount of funds has been received into the account of the insurance company.
The paragraph entitled “Rights and obligations of the parties” contains all the information regarding the obligations that arise between the policyholder and the insurer immediately after signing the agreement.
This section is one of the most important in the document under consideration. Since it contains information regarding the rights of the client and the insurance company itself.
A contract of this type may include a fairly large number of different risks. At the same time, there is a list of exception cases, in the event of which the obligation to pay monetary compensation does not arise.
All information regarding this issue is indicated in the section entitled “Grounds for refusal to make insurance payments.”
The very last paragraph of the rules under consideration is the “Dispute Resolution Procedure”. Various situations often arise in which the insurance company and the insurer cannot find a common language. Most of these cases can be resolved through peaceful negotiations.
The procedure for resolving the situations under consideration is covered in this section. If a compromise solution has not been found, then the policyholder or the insurer have every right to go to court to resolve disputed cases.
The need for a policy
Insurance of dangerous objects is strictly mandatory, this point is enshrined in law.
The main reason for this is the very high probability of the risk of damage to property, health, and the lives of third parties.
Moreover, in most cases the damage is extremely great. Many objects (for example, nuclear) during an accident can hit an area with radiation many times larger than the area of the enterprise itself.
Organizations that own or operate hazardous facilities, carrying out any work on them, very often do not have sufficient funds to pay for the damage caused by the accident. At the same time, they bear civil liability. That is why it is imperative to insure hazardous industrial facilities.
Since a special program from a strong insurer will not only protect the property interests of the owner of the property, but also compensate for all damage caused to third parties.
Most insurance companies use reinsurance services. This allows the insurance company to compensate for the damage at the expense of the pool even if it exceeds its financial capabilities. Therefore, the policyholder should not fear bankruptcy.
What applies to objects
The following can be classified as HPO:
- facilities where various types of work are carried out with the following substances:
- highly flammable;
- rapidly oxidizing - this process causes a rapid increase in temperature, which leads to a fire;
- spontaneously combustible;
- easily explosive;
- toxic.
- facilities where all kinds of equipment are used, the operation of which is carried out at an excess pressure of more than 0.07 megapascals with:
- gas, steam (any type);
- water (the temperature of which is more than 115 0 C);
- various other liquids that begin to boil at a pressure of 0.07 megapascals.
- facilities where various types of lifting mechanisms are installed and actively used: escalators, funiculars, cable cars (with the exception of elevators, as well as lifting platforms for the disabled);
- objects where work with molten metal is carried out on equipment whose productivity is at least 500 kg/h;
- objects where mining is carried out by blasting;
- facilities where plant materials are processed, used, stored, resulting in the formation of explosive mixtures.
There is also a list of exceptions to the rules. Thus, many objects can be classified as dangerous based on their main characteristics.
But at the same time, according to current legislation, they are not such. This applies to car gas stations where you can buy liquid and gaseous fuel and other similar facilities. They cannot be insured under the type of program in question.
How it is done
The process of insuring hazardous production facilities is quite complicated. Since in most cases the insurance company carrying it out requires not only the provision of various types of documents, but also an inspection of the object by specialists.
Most often, the insurance process looks like this:
- Company specialists inspect the insured production;
- The legal department studies all submitted documents in as much detail as possible.
And only after completing the preliminary two stages do the parties sign an insurance contract. Sometimes the process of preparing to sign an agreement lasts several months - until the insurance company analyzes all the factors that influence the likelihood of an insured event occurring. The insurance premium is calculated based on these factors.
What risks might there be?
The risk when concluding an insurance contract is damage to health, property, or life caused to third parties as a result of:
- radiation exposure;
- toxic effects;
- explosion.
Moreover, payment for the risks indicated above is possible only if certain very important conditions are met:
- claims of third parties for compensation for damage caused by the insured were brought before the expiration of the limitation period;
- an accident at the facility occurred during the period of validity of the insurance contract;
- there is a connection between the accident and the conduct of permitted activities by the insured.
If at least one of the specified conditions is violated, then it will simply not be possible to receive monetary compensation from the insurance company.
Problems in the insurance of public health organizations
Insurance of dangerous objects today is carried out by a fairly large number of different companies. Despite the fact that the service in question has been provided for quite a long time, a variety of problems can arise when insuring hazardous production facilities.
They are due to the following:
- the authorized capital and insurance reserves of most companies are not large enough;
- insurance experience does not allow insurance company employees to objectively assess:
- insurance risk;
- risk management;
- damage caused as a result of an insured event.
If the problem with authorized capital and small reserves can be resolved quite simply with the help of reinsurance, then other issues continue to cause some difficulty.
This is especially true for damage assessment. In addition, many companies try to minimize their costs of paying compensation, and therefore sometimes slightly underestimate the amount of compensation.
Payment amount
The amount of insurance compensation is regulated by the legislation in force on the territory of the Russian Federation.
If damage is caused to third parties, they have the right to demand monetary compensation from the insurance company, but only within the amount specified in the insurance contract.
If the amount of damage is more than this value, then the policyholder himself is obliged to cover the difference. When calculating the amount of insurance payment, the minimum market value of compensation for the damage caused is taken into account. And regardless of its type.
If damage was caused to health, then the insurance company must pay for the treatment of the victim. If any property is destroyed, the company must pay its full value.
If there are deaths, monetary compensation is also paid to the relatives of the victim. In addition, funeral expenses are covered (usually at least 15 thousand rubles).
Insurance of hazardous production facilities is strictly mandatory today - the absence of a valid insurance contract is grounds for the imposition of a serious fine.
The need to insure hazardous production facilities (HIF) arose with the development of industry, the increase in production capacity and the increase in the danger of their operation. As a result of several major accidents, which caused the death of a huge number of people (several thousand) and significant material damage, compulsory HPF insurance was introduced.
Definition
Dangerous objects are those objects where an accident can cause harm to the life or health of third parties (not the insurer and the policyholder), as well as disrupt their livelihoods. Possible insurance risks, according to Law No. 225 F3, do not include possible damage to the environment. Therefore it refers to .
Compulsory HPF insurance is a form of redistributive financial relations, the result of which is the creation of cash reserves intended to compensate for damage in unforeseen circumstances.
The relevant laws regulate insurance rates for each hazardous facility, and also make the inclusion of the hazardous facility in the state register and obtaining a license for its operation dependent on insurance.
Also read about insurance of construction and installation risks and civil liability of builders.
an enterprise or other owner can build a hazardous production facility, but does not have the right to operate it without compulsory insurance.
Need for insurance
After concluding a contract, the insurance company constantly monitors compliance with safety standards. The frequency of inspections depends on the hazard class of the object:
- 1 time per year– for objects with hazard class 1 or 2;
- Once every 3 years– for objects with hazard class 3.
Assigning hazard class 4 to an object exempts it from compulsory hazardous production insurance. But design may be offered.
Enterprises with any type of activity and form of ownership are subject to a compulsory insurance contract. Compensation amounts are clearly differentiated according to the size and type of damage caused.
There are no consequences for compulsory HPF insurance under the following circumstances:
- The insured event occurred outside the country.
- Man-made accidents at enterprises and stations using nuclear energy.
- Causing damage to the environment (nature, water, air).
- Consequences of a terrorist attack.
- An emergency incident that occurs as a result of a strike or other illegal actions of employees.
- Consequences of an atomic explosion, radiation exposure, military action.
Responsibility for damages in the event of an insurance risk is imposed only on certain licensed companies.
List of objects for hazardous production organizations
A prerequisite for inclusion of objects in the list of hazardous production facilities is the condition of their territorial location within the country. The PPOs include:

A common practice is. This type does not fall under the definition of a hazardous production facility, but ensures the quality of work performed in the design and construction of buildings. Can be performed within large enterprises.
Insurance risks
HPF insurance implies the possibility of compensation for civil liability risks. Such risks are associated with claims by legal entities or individuals regarding harm caused to them by a source of increased danger. The owner of such a source (individual or legal entity), when concluding an insurance contract for a hazardous production facility, shifts its responsibility to the insurer, i.e., in the event of possible damage, third parties have the right to count on payment of the amounts specified in the contract for each specific case.
The same applies in the case of .

Responsibility for hazardous production
Carrying out activities at any HIF facility is permitted only after its registration in the state register and, accordingly, the conclusion of an insurance agreement in favor of third parties. Insurance is mandatory, otherwise the owners of hazardous production facilities are subject to the imposition of fines by law:
- For officials - up to 20,000 rubles. :
- For legal entities – up to 500,000 rubles.
Tariffs for insurance of hazardous production facilities are determined by law and are uniform for insurance companies. Compulsory insurance contracts are concluded in an approved form for a period of at least 1 year.
Regulation by law
The latest changes to the legislation on compulsory insurance were introduced by the Federal Law of January 1, 2012. According to this law:
- A single basic scale of tariff rates has been established, the size of which directly depends on the hazard class of the hazardous facility and its type;
- The insurance contract is drawn up separately for each HPO, payments under the contract are deducted from the cost price;
- The contract provides protection for third parties, as well as employees of the policyholder;
- There is compensation for the harm received by each victim;
- Limits for compensation for various types of damage in relation to one victim are stipulated: 2 million - damage to life and health, 200 thousand - disruption of life, 360 thousand - damage to property of individuals, 500 thousand - property damage to legal entities.

Determination of insurance rates, sum insured and insurance premium depends on:
- Object type;
- Insurance rate coefficient for various types of insurance(“fire”, mass, etc.);
- Type of insurance risk (accident, incident).
When concluding a compulsory HPF insurance contract, you must provide the following documents:
- Statement;
- A document certifying that an object is considered especially dangerous(registration certificate or identification certificate);
- Confirmation of the policyholder's ownership of the hazardous production facility;
- Documented information on the statistics of insured events that have occurred;
- Information characterizing the hazardous production facility and its accounting map;
- If available, an industrial safety declaration.
The essential terms and conditions of the insurance contract can be viewed.
Video
Key points in the insurance of hazardous production facilities according to the Deputy General Director of the Soglasie insurance company:
Conclusions
The relevance of compulsory HPF insurance is growing every year, as the number of enterprises and organizations falling under the list of HPFs is increasing, as well as their consolidation. In this regard, production risks increase, which can cause harm to persons working there as a result of unforeseen circumstances.
And although there is no upward trend in this sector of insurance activity, the execution of a hazardous industrial insurance contract is still a prerequisite for its commissioning.
Read what the SRO collective agreement implies.
Owners of hazardous production sites and enterprises are obliged to protect their property interests through insurance. In the event of an emergency at production facilities, the damage caused to the victims will be compensated by the insurance company.
Necessity
It is important to understand that there are a huge number of dangerous enterprises operating in the country (more than three hundred thousand), there are warehouses with chemicals, oil pipelines and other facilities, at any of which an unforeseen situation with a negative outcome can occur. It is not known what the scale of their consequences will be.
The need for this type of insurance arose precisely after a number of major accidents occurred, as a result of which serious damage was caused to people and nature. Therefore, at the moment (since 2012), persons who own dangerous objects are required to insure against the possibility of harm to strangers, the environment and the country as a whole. All the nuances about this are prescribed by law.
Registration of such a policy allows the insured to claim monetary compensation covering the costs of treatment, burial, and compensation for property many times greater than his actual financial capabilities.
Peculiarities
Policies for hazardous production facilities are issued by enterprises of different forms of ownership and focus:
- commercial organizations;
- state enterprises;
- municipal facilities;
- companies involved in the operation of elevators in residential premises.
The liability of owners of hazardous objects is determined based on the exact amount of damage that can be caused. The dependence here is directly proportional: the more people can suffer, the more serious the cost of the policy will be.
It is important to understand that monetary compensation in the event of an accident is many times greater than the money contributed by the insured person.
There are certain rules and restrictions on public benefit organizations. The compensation amount is clearly limited:
- death of the injured person – two million rubles;
- causing harm to health - from sixty thousand to nine hundred rubles, depending on the violation of the general condition and functioning of the body;
- damage to property – from two hundred to six hundred thousand rubles.
The law on compulsory insurance of hazardous production facilities does not work in the following cases:
- The occurrence of an insured event outside the country.
- Technogenic accidents at stations and enterprises using nuclear energy.
- Harm to air, water, nature.
- Accident due to a terrorist attack.
- An emergency at an enterprise due to a strike or other illegal actions of employees.
- The outbreak of hostilities, exposure to radiation or atomic explosions.
Only certain licensed companies have the right to bear responsibility for compensation for damage in the event of an insured event.
List of hazardous production facilities
 Dangerous objects are considered to be those that are geographically located within the borders of the Russian Federation. They must be included in the register in accordance with laws on the safety of hydraulic structures and industrial facilities. The 4th hazard class HIF insurance group includes enterprises, mechanisms, structures that can lead to an accident, causing injury to people, or depriving them of their lives.
Dangerous objects are considered to be those that are geographically located within the borders of the Russian Federation. They must be included in the register in accordance with laws on the safety of hydraulic structures and industrial facilities. The 4th hazard class HIF insurance group includes enterprises, mechanisms, structures that can lead to an accident, causing injury to people, or depriving them of their lives.
HPFs include those where:
- store, operate, create, transport highly dangerous substances (combustible, flammable, explosive, toxic, hazardous to nature);
- Gas stations that fill vehicles with liquefied gas, gasoline and diesel fuel;
- mechanisms and automatic machines operate under high pressure at high temperatures (pressure of at least seven hundredths of a megapascal, temperature above one hundred and fifteen degrees Celsius);
- Fixed mechanisms for lifting loads, elevators, escalators, funiculars, cable cars are used;
- melt ferrous and non-ferrous metals, create alloys based on them;
- carry out work to extract minerals, in the mountains, underground;
- there are structures that work with water and protect from its negative effects (dams, dikes, canals, hydroelectric power stations, ship lifts, etc.).
Liability for compulsory hazardous production insurance
Individuals and companies that own hazardous production facilities are required to insure them. An uninsured object may not be operated until a policy has been issued for it.
In case of deviation from the law and failure to obtain insurance, the owners of these objects are punished, and the penalties are quite serious. The state charges an administrative fine of about twenty thousand rubles from officials, and about five hundred thousand rubles from legal entities. The insurance amount collected without reason is liquidated into the treasury.