Marketing in tourism. Technology for implementing the concept of marketing in a tourism enterprise The concept of marketing concepts in tourism
Marketing in social and cultural services and tourism Yuliya Bezrutchenko
2.3. Tourist enterprise is the main link in the implementation of the marketing concept
Tourist enterprises are an important component that forms the tourist offer in the subsystem "subject of tourism". A variety of tourism enterprises operate in the tourism area. Some of them offer only tourism services, while for others, tourism is one of their areas of business. Enterprises that live only at the expense of tourism are called tourism enterprises in the field of primary services, and enterprises that earn profit not only from tourism activities are called tourism enterprises in the field of secondary services. Consequently, the services of the first group are the basis of its existence, and the services of the second satisfy only a separate part of the tourist demand, since tourism for this group is one of several ways to generate income and not only tourists can use their services.
But we must remember that individual tourism enterprises, depending on the functions they perform, may belong to these two categories at once. For example, hotels and tourist agencies invariably provide exclusively primary tourist services, and catering places in a sanatorium or hotel are primary service enterprises, but the same catering places in the city are no longer tourist organizations, as they implement a secondary tourist function.
Tourist enterprises of primary services
A tour operator is a tourism enterprise that synthesizes its own services and services of third parties into a new independent tourism product. This new product is called a lump-sum (complex) tour. The tour operator offers the consumer a comprehensive tour on its own behalf, at its own peril and risk and at its own expense.
All tour operators operating in the tourism market can be grouped according to their size, place of work, depth of the tourism program and economic goals.
There are large, medium and small tour operators. Enterprises that serve more than 100 thousand customers a year, and their turnover reaches 35 million dollars, are classified as large tour operators. Enterprises serving from 30,000 to 100,000 customers per year are classified as medium-sized tour operators. In most cases, they are highly specialized: they occupy only one of the market niches (they can specialize in a certain tour - for example, medical tours; in a specific region - for example, the Caucasus). To the group small tour operators include all kinds of enterprises whose specialization is hiking or youth tourism, they can organize cruises; it can also be bus companies, one of the activities of which is the transportation of tourist groups.
According to the geography of activity, international, interregional, regional and local tour operators are distinguished. International tour operators Little. Only a few major tour operators offer their services in a few countries. The most common option is when they open their branches in different countries or interact with local enterprises.
Category interregional tour operators include enterprises operating in a large area (several regions). Regional tour operators carry out their business activities only in a certain geographical region, but in terms of turnover and the number of tourists served, they can easily be included in the group of large tour operators. Local Tour Operators operate within a small radius.
Offers of tour operators also have their differences. Wide offer includes many different types of travel - for example, relaxing on the lake, sightseeing and medical trips, getting to know the sights of cities. The offer of the tour operator can be considered more deep, if for any type of trip a sufficiently large selection of all kinds of products is offered.
Tour operators differ from each other in terms of economic goals. Not every company, when organizing a trip, seeks to get the highest income in the first place. In this sense, one should distinguish commercial tour operators, generally useful (non-commercial) tour operators and enterprises of "black tourism". The primary task of commercial tour operators is the acquisition of a permanent and large income. Non-profit tour operators also seek to make a profit, but the interests in terms of increasing income are not the main ones. They pay much more attention to organizational and educational goals. The category of tour operators of "black tourism" includes enterprises that are engaged in tourism activities not all the time, but for certain reasons. For example, the director of a manufacturing holding decided to organize a trip to some city for his colleagues. To do this, he orders hotel rooms and buys tickets for travel to this city and back, orders a city tour and books tickets to the theater.
Travel agents are, one might say, a collective image. It includes all enterprises and organizations that in their main and secondary activities are intermediaries.
The concept of a travel agency refers exclusively to those enterprises whose main activity is mediation. In no other field of activity is mediation as important as in tourism. Sometimes this can be explained by a rather large geographical distance between producers and consumers of services (for example, between a tourist base and a vacationer), sometimes ignorance of the market (a vacationer is rarely familiar with the offers of a country he has never been to), the need for advance booking with limited capabilities of the manufacturer services. A trip abroad, to unfamiliar places, is booked in most cases with the help of several intermediate organizations. The operator involved in inbound tourism also supervises the organization of travel on the spot (booking, collection, sale, etc.), i.e. the intermediary performs significant management tasks for producers and consumers. In most cases, travel agents are contacted if they want to implement a comprehensive trip, as they are the link between the consumer and the producer of tourist services. Travel agents can be characterized by such parameters as assortment, legal and economic status, size of the enterprise.
Range of travel agent services. The assortment is the main criterion that makes it possible to recognize travel agents. It is determined by the quality and quantity of tour operators and service providers with which the intermediary enterprise interacts. There are eight types of enterprises.
1. Travel agency offering a full range of tourist services on the market. This type of travel agency operates under a license. The company must be licensed by the International Air Transport Association to sell air tickets and, quite often, a license to sell rail tickets. Participates in representing the interests of not only large, but also numerous medium and small tour operators.
2. Bureau of travel and excursions. These bureaus specialize in the implementation of lump-sum (complex) tours, sometimes they sell air and railway tickets.
3. Specialized travel agencies. They are engaged in the marketing of a certain type of tour, while they have high professional competence in their field (for example, medical tours, pilgrimage tours, etc.).
4. Travel agency for the sale of last-minute trips, cheap plane tickets (they do not have a license to sell air tickets).
5. Travel agency branch. The branch has a narrow specialization of activity, it can be located outside the country.
6. Department of reservations. It implements tours of one tour operator, can function as one of the structures of the tour operator, and can be one of any types of enterprises.
7. The travel agency for the reception of guests (inbound tourism) implements tourism services that a certain region can offer tour operators from other regions or visiting tourists.
8. Tourism department, which cannot be called a tourism organization. This is a department of an organization whose main activities lie outside the tourism sector.
Legal and economic status of travel agents. Booking departments, as well as travel agencies related to tour operators, do not have a legal and economic status. Licensed travel agencies operate on the basis of contractual obligations with numerous tour operators and have the right to open their own representative offices and branches; associations of tourist agencies that coordinate their activities with common aspirations; travel agencies formed on the basis of a concluded franchise agreement.
The scale of the work of travel agents. Depending on the size of the enterprise, there are large, medium and small intermediaries. In the tourist area, mainly small and medium-sized enterprises operate.
Transport enterprises of special purpose. There are also transport companies that specialize in transporting tourists on the tourist services market. Since the central direction of their activity is related to tourism, they are classified as tourism enterprises of primary services. At the same time, the distance of transportation of tourists and the duration of the move are completely unimportant. This category includes both a charter airline that transports tourists from America to Australia, and an organization that operates elevators and ski lifts. This category also includes railways, ferries, sightseeing and cruise liners, cable cars.
Hotel enterprises. The next group, which belongs to the tourist enterprises of primary services, is hotels. Hotel complexes make a profit only from the accommodation of guests. Hospitality enterprises include large hotel complexes (hotels, boarding houses, holiday homes) and small hotel-type enterprises (camping sites, youth hostels, apartments).
Other tourist enterprises of primary services. In addition to transport companies, tour operators, hotels and travel agents, there are a number of organizations that can also be attributed to tourism. The main ones are sports equipment and boat rental stations, insurance companies, credit institutions, manufacturers of goods for tourism and recreation, sports schools, advertising agencies, etc.
Organizations that issue and track the movement of money are related to organizations of primary tourist services. Tourists are usually happy to use credit cards during their travels abroad. A credit card can be used to pay for services and purchases of goods. With this method of payment, there is no need to carry cash with you.
Insurance companies, if they specialize in tourist insurance, can also be classified as tourist enterprises. One of the main special products of insurance companies is insurance in case of withdrawal from contractual obligations, insurance of belongings of tourists and insurance in case of illness during a trip outside the country.
Primary service tourism enterprises are related to rental organizations sports equipment, boats, and specific sports schools. It does not matter what is offered for rent - surfboards, boats or sailing yachts, skis, bicycles, diving equipment, sleds. The largest part of the rental users are tourists.
sports schools can be considered tourism enterprises in the event that their services are used not by the local population, but by visiting tourists. Very often this happens when a person can engage in any kind of sport exclusively during the holidays.
When listing the tourist enterprises of the first group, you need to remember about manufacturers of goods for tourism and advertising. Itinerant tourists are always in need of goods such as guidebooks and maps, suitcases, travel bags. Of no small economic importance is the sale of souvenirs that tourists buy in order to preserve the memory of the places they visit.
Advertising, of course, is a significant tool that promotes the marketing of tourism services. If an organization specializes in the production of advertising for tourism, this is the basis for classifying it as a tourist type enterprise.
Tourist enterprises of secondary services
If a tourism organization offers a product that is used by both tourists and non-tourists, then in this case it can be considered as a tourist enterprise of secondary services. Among these are public catering organizations, some transport organizations, as well as industrial, trade organizations and organizations in the sphere of personal services.
The group of public catering organizations includes restaurants, cafes and bars, the services of which can be used by both tourists and the local population. Transport organizations of secondary services differ from tourist transport organizations in that their consumers are dominated not by tourists, but by the local population (on the usual routes of ski resorts in winter there are additional bus routes for transporting skiers). Additional income from tourism is received by individual industrial and commercial enterprises (a confectionery shop supplying confectionery to a hotel restaurant, etc.), as well as organizations in the service sector (insurance companies with various activities, consumer services enterprises, etc.) .
A common feature of all tourism enterprises of secondary services is the impossibility of determining the true volume of goods and services used by tourists. The division of demand between tourists and the local population can vary greatly depending on the season. In addition, the location of the enterprise plays a significant role in determining the degree to which an enterprise belongs to the tourism sector (for example, in a cafe or bar located near the railway station, the bulk of visitors are travelers).
From the book Marketing. And now the questions! author Mann Igor Borisovich From the book Marketing author Loginova Elena Yurievna52. The concept of international marketing. Concepts of international marketing International marketing is carried out as an expression of the business activity of companies operating in markets with the aim of generating income in more than one country. The main goal of marketing is to obtain
From the book Marketing: lecture notes author Loginova Elena Yurievna3. Concepts of international marketing Differences in the international focus and approaches to international markets in which international business organizations operate can fall under one of three concepts of international marketing: 1) concept
From the book Marketing. Lecture course author Basovsky Leonid EfimovichMarketing concepts Over time, all those involved in the exchange process learn, marketing improves, concepts are formed on the basis of which management in this area is carried out. Marketing management is analysis, planning, implementation and
From the book Marketing in Socio-Cultural Service and Tourism author Yulia BezrutchenkoMarketing Concepts The products of a certain firm cannot please all buyers. Buyers differ from each other in their needs and habits. Some firms are best served by focusing on serving certain parts, or segments, of the market. expedient
From the book Enterprise Planning: Cheat Sheet author author unknownChapter 2 Tourism Marketing Concepts
From the book Organization of Time. From personal effectiveness to company development author Arkhangelsky Gleb From the book Marketing author Rozova Natalya KonstantinovnaThe essence of the concept of "implementation of values" In the first half of the XX century. the focus was on production - its efficiency, the improvement of appropriate methods and technologies, etc. In the past few decades, we have seen an inexorable shift in emphasis
From the book Management: a training course author Makhovikova Galina AfanasievnaQuestion 18 Concepts of the marketing mix (marketing-mix) Answer The marketing mix is a set of practical tools for adapting a company to a market situation and measures to influence the market. A good marketing mix helps the firm to gain a strong market position.
From the book Benchmarking - a tool for developing competitive advantages author Loginova Elena Yurievna3.2. The enterprise as a key link in the market economy
From the book How to overcome the crisis. 33 effective solutions for your company author Haman Simon7.3. Concepts and directions of marketing in the enterprise As noted earlier, marketing is used both in commercial and non-commercial activities, for example, in activities related to charity, the dissemination of public ideas
From the book Target Marketing. New rules for attracting and retaining customers author Brebach GreshSolution 10: Increase Primary Sales Time One of the major sales challenges is that salespeople spend only a small fraction of their time directly on sales activities. According to some trading experts, this part is no more than
From the book Startup Guide. How to start... and not close your Internet business author Zobnina M. R. From the book The whole truth about IKEA. What lies behind the success of a megabrand the author Stenebu JohanHow to do it right? Rule #1 (Basic): Be Prepared! Do not rely solely on your charm and charisma (although, perhaps, they will give you money for them), but think over the arguments in order to provide the investor with exactly the amount of information that he wants from
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Similar Documents
- ? formation of contacts with consumers of tourist services;
- ? development of contacts through innovation;
- ? control over the results of the service.
- 1 http://www.aex.ru
- 2 Adopted at the international WTO conference in Budapest in February 1993.
- ? material environment ( physical evidence),
- ? maintenance process ( process) and staff (People).
- ? the demand for tourism services is elastic in relation to the level of income of the consumer and prices, subject to seasonal fluctuations;
- ? the dependence of the tourism product on such variables as space and time;
- ? the offered tourist services are divided geographically: booking a tour in a travel agency, booking a hotel or air tickets via the Internet, tourists receive in the place of their permanent residence, transport services can be obtained during a tourist trip, hotel accommodation, participation in festivals, excursion services, meals - in the place temporary stay;
- ? tourism product offering is characterized by inflexible production. Hotels, airports, museums, theme parks cannot be moved at the end of the tourist season to another region to accommodate changing demand and seasonality;
- ? assessment of the quality of the tourist product is highly subjective. Local residents, members of the tourist group can influence the perception of the quality of tourist service;
- 1 Innovators E. Features of behavior of consumers of services. Zh-l "Sales Management", 2003.
- 2 Ibid.
- 3 Ibid.
- ? the assessment of the quality of a tourist product can be influenced by such factors as weather and natural conditions, political events.
- 1) from the position of a tour operator company (intermediation area);
- 2) from the position of territorial authorities (the scope of supply);
- 3) from the position of the client (the sphere of demand).
- ? marketing at the level of tour operators and travel agents;
- ? marketing at the level of territories and regions - tourist destinations.
- ? the image of a tourism enterprise, the level of its corporate culture;
- ? technology for organizing the process of quality customer service, a system of service quality indicators;
- ? the customer base of the tourism company and the information system of data on the opinions and preferences of customers;
- ? a system of service quality indicators, a system for tracking customer complaints;
- ? human resource management system, including the principles of training the personnel of a tourism company, empowering personnel, studying the degree of satisfaction of personnel with their work, i.e. Availability of qualified and motivated staff.
- ? stand out from competitors;
- ? enhance the attractiveness of your image in the eyes of customers;
- ? minimize sensitivity to price changes;
- ? increase the profitability of the work;
- ? improve customer satisfaction and retention;
- ? to gain the maximum number of supporters of the tourism company who promote its services;
- ? raise your reputation;
- ? increase the degree of staff loyalty.
- ? marketing at the level of public tourism organizations - national tourism administrations (NTAs); tourist information centers, public associations in the field of tourism;
- ? marketing at the level of territories and regions - tourist destinations;
- ? marketing at the level of producers of tourist services - accommodation facilities, catering enterprises, transport enterprises, excursion service enterprises, etc.;
- ? marketing of tour operators and travel agents.
- ? zoning of the territory of tourism in the state;
- ? creation of a regulatory and legal framework for the development of tourism, consistent with international practice;
- ? formation of economic mechanisms to stimulate the development of foreign and domestic tourism;
- ? attracting investments in this area, etc.
- ? the creation of large transport systems for the transport of tourists to and from the country, as well as through its territory;
- ? protection of attractions, such as state reserves and national parks;
- ? creation of an information and advertising system dedicated to the promotion of destinations and countries as tourist centers.
- 1 Pike S. Destination branding. An integrated marketing communication approach. - Oxford: Elsevier, 2008.
- 2 Page S.J., Connell J. Tourism: a Modern Synthesis. - London: Cengage Learning EMEL, 2009.
- ? destination attractions - what directly attracts tourists (natural, cultural, historical attractions);
- ? tourist infrastructure (accommodation facilities, catering establishments, tour agencies, museums, souvenir shops, etc.);
- ? accessibility (transport, visa, etc.);
- ? event calendar;
- ? support services (banks, telecommunications, security system, healthcare system);
- ? the presence of marketing intermediaries - tour operators, travel agents, etc.
- 1. Give the characteristic of the market of tourist services.
- 2. Describe the concept of "tourist product".
- 3. Types of tourism products.
- 4. What are the features of the formation of the concept of marketing in tourism?
- 5. Describe the levels of formation of the tourist product.
- 6. Why is the tourist destination the basis of the tourism system?
- http://www.gks.ru Kiryanova L.G. Destination marketing as a modern approach to tourism region management. - Bulletin of the Tomsk Polytechnic University, 2010.
- formation of contacts with consumers of tourist services, which aims to convince them that the proposed place of rest and the services existing there, attractions and expected benefits are fully consistent with what the clients themselves want to receive;
- development of contacts through innovations that can provide new sales opportunities. Such innovations should meet the needs and preferences of potential customers;
- control over the results of the service, which involves the analysis of the results of activities to promote goods and services on the market and check how the results reflect the full and successful use of the opportunities available in the tourism sector, a comparative analysis of the costs of promotional marketing activities and the income received.
- the demand for tourism services is elastic in relation to the level of income of the consumer and prices, subject to seasonal fluctuations;
- tourism product depends on such variables as space and time;
- the offered tourist services are divided geographically: booking a tour in a travel agency, booking a hotel or air tickets via the Internet, tourists receive in their place of permanent residence, transport services can be obtained during a tour, hotel accommodation, participation in festivals, excursion services, meals - in a place of temporary stay;
- tourism product offering is characterized by inflexible production. Hotels, airports, museums, theme parks cannot be moved at the end of the tourist season to another region to accommodate changing demand and seasonality;
- assessment of the quality of the tourist product is highly subjective. Local residents, members of the tourist group can influence the perception of the quality of tourist service;
- the assessment of the quality of a tourist product can be influenced by such factors as weather and natural conditions, political events.
- 1) from the position of a tour operator company (intermediation area);
- 2) from the position of territorial authorities (the scope of supply);
- 3) from the position of the client (the sphere of demand).
- marketing at the level of tour operators and travel agents;
- marketing at the level of producers of tourist services - accommodation facilities, catering enterprises, transport enterprises, excursion service enterprises, etc.;
- marketing at the level of public tourism organizations - national tourism administrations (NTAs); tourist information centers, public associations in the field of tourism;
- marketing at the level of territories and regions - tourist destinations.
- URL: http://www.aex.ru
- Adopted at the international WTO conference in Budapest in February 1993.
- Lankar R., Ollie R. Tourist marketing. M.: Economics, 1998.
- Durovich A.P. Marketing in tourism. M.: Business book, 2001. S. 496.
- Novatorov E. Features of sales management in the service sector // Sales Management. 2003. No. 1. S. 26-34.
- There.
- There.
- URL: http://www.consultant.ru/document/cons_doc_LAW_129632.
Basic concepts of marketing in tourism and its principles. Marketing of tourist enterprises. Tourism marketing at the national level. Market segmentation. Organizational and economic characteristics and marketing analysis of the activities of the company LLC "Ladya".
term paper, added 11/09/2014
Essence, principles, functions and goals of marketing. Features of modern marketing concepts: improvement of goods and production, intensification of commercial efforts, pure marketing, social and ethical marketing, international marketing.
term paper, added 10/15/2011
Modern concepts of marketing: essence, main goals and objectives. Terms of choice marketing concept. Ways to determine the budget for marketing activities. Development of activities within the framework of selected marketing concepts on the example of Flamingo LLC.
term paper, added 05/04/2014
Essence of marketing in tourism. The main components of the marketing information analysis system in tourism enterprises. The concept of a marketing information system. Specific features of marketing in tourism. Marketing information analysis system.
term paper, added 11/27/2011
The function of marketing as an activity of all types of entrepreneurship to ensure the sale of products. The evolution of the concept of marketing. The essence of the concept of socially oriented marketing. Serving the economy as a modern concept of marketing.
abstract, added 03/31/2010
Prerequisites for the emergence of marketing. Stages of marketing focused on production, sales, society. Socio-economic essence of marketing. The main functions of tourism marketing: establishing contacts with customers; development; control.
abstract, added 04/05/2010
On the evolution of the concept of "marketing". Theories, principles, concepts of marketing. The essence of marketing in the era of mass production, in the era of saturation of demand, at the present stage of economic development. "Three pillars" of marketing. Trends in the development of modern markets.
Tourism is one of the leading and most dynamic industries in the global service sector. Due to its rapid growth, tourism has been recognized as an economic phenomenon of the 20th century. The Russian tourism market is also developing.
The volume of the Russian tourism market has been progressively increasing throughout the last decade. In 2012, its volume (compared to 2011) increased by 14% (or by 149 billion rubles), exceeding 1 trillion rubles (about 1.7% of Russia's GDP). If the current growth rate is maintained, in 2013 the tourist services market will reach 1.35 trillion rubles.
Rice.
The prerequisites for the positive dynamics of the tourism market in the Russian Federation are the growth of the solvency of the population and the consistent development of tourism infrastructure, the growth in the level of penetration of remote banking services, the Internet and Internet services in our country.
The tourism industry is one of the brightest examples of the introduction, development and active use of information and communication technologies in the world. Booking tickets, choosing and paying for a hotel room in any city around the world, anytime, anywhere, using a mobile device, using electronic payment methods, is becoming commonplace for tourists of all ages with a wide range of income levels.
The tourism services market is moving towards greater transparency and accessibility for the end consumer. According to Aviation EXplorer 1, the growth in the share of travel services issued on the Internet was recognized as the most noticeable trend in the Russian market in 2012. The structure of demand is changing, shifting towards self-registration of tourist services on the Internet by the population.
The development of the tourism market in the Russian Federation will inevitably lead to an increase in the level of competition in this sector of the economy, which, in turn, will require companies operating in the tourism industry to reconsider their attitude to the role of marketing in the company. In order to remain competitive in the new environment, travel industry companies need to move from a consumer-oriented culture to a market-oriented one.
At present, a unified approach to the definition of marketing in tourism has not yet been developed. Therefore, we will consider different views on the problem.
Establishing contacts with clients aims to convince them that the proposed holiday destination and the services, attractions and expected benefits that exist there are fully consistent with what the clients themselves want to receive.
The development of contacts involves the design of innovations that can provide new sales opportunities. Such innovations should meet the needs and preferences of potential customers.
Control involves the analysis of the results of activities to promote goods and services to the market and check how the results reflect the full and successful use of the opportunities available in the tourism sector, a comparative analysis of the costs of promotional marketing activities and the income received.
French scientists R. Lankar and R. Ollier give the following definition of tourism marketing: “Tourist marketing is a series of basic methods and techniques developed for research, analysis and solving the tasks. The main thing to which these methods and techniques should be directed is to identify the possibilities for the most complete satisfaction of people's needs in terms of psychological and social factors, as well as to determine the ways of the most rational business management from a financial point of view by tourist organizations (enterprises, bureaus or associations), allowing to take into account the identified or hidden needs for tourism services. These kinds of needs can be determined either by recreational motives (entertainment, holidays, health, education, religion and sports) or by other motives that are often found in business groups, families, various missions and unions.
The Swiss specialist E. Krieendorf puts a more complete content into the concept of tourism marketing: “Tourist marketing is a systematic change and coordination of the activities of tourism enterprises, as well as private and public policies in the field of tourism, carried out according to regional, national or international plans. The purpose of such changes is to best meet the needs of certain consumer groups, while taking into account the possibility of obtaining appropriate profits.
The concept of marketing in the field of tourism is developing in accordance with modern trends in the development of marketing theory and service marketing theory.
The tourism product has the distinctive characteristics inherent in the service described in the previous paragraph, namely, intangibility, inseparability from the source, perishability and variability of quality (4 "NOTs"). The four "NOTs" of the tourism service as a product seriously affect the specifics of tourism activities. .
To the traditional elements of the marketing mix: product - price - place - promotion, used in traditional marketing as a set of company-controlled strategies for influencing the consumer, in tourism it is recommended to use additional strategies for the marketing mix of services. These include:
Material environment ( physical evidence)(the atmosphere of a hotel, restaurant, office of a travel agency) involves working on the impact on the sensory channels of perception of customers: visual (organization of space, lighting, color), auditory (volume and tempo of music accompaniment), olfactory (ventilation of the room), tactile (room temperature) one .
Maintenance Process (Process) guests, customers can be developed using diagrammatic design methods, common ground, customer scenario and reengineering 2 .
Staff (People) contact staff is the staff of the company, which simultaneously produces and sells a tourist service. Therefore, contact personnel in service marketing are sometimes called "part-time marketers" (part time marketers) 3 .
Together with the rest of the marketing mix strategies (product, price, distribution channels, promotion), these additional three elements form the tourism marketing mix.
The result of activity in tourism is a tourist product, which has its own distinctive features:
The problem of defining a tourist product remains debatable. Consider the most common definitions of a tourist product presented in Table 1.
Tourism product definitions
Table 1
|
Tourism product definition |
|
|
The policy of a tourist product can be considered and conducted from two positions: a certain territory and a certain enterprise. |
|
|
Medlik S „ 1995 |
Tourist product in the narrow sense ( sensustricto) and in a broad sense ( sensulargo). Tourist product in the narrow sense - everything that tourists buy separately (for example, transport services, hotel reservations) or in the form of a package of services. The tourism product in a broad sense covers the totality of the impressions received from the moment of departure from home until the moment of return. |
|
Middleton V.T.C., 1996 |
A tourism product is a combination of three main components: attractiveness, tourism infrastructure, and their accessibility. |
|
Middleton V.T.C., 1996 |
From the perspective of a potential customer considering any form of travel, a product can be defined as a package of tangible and intangible |
|
Holloway J. Ch., Robinson Ch., 1997 |
A tourism product is a complex product that encompasses a place, services, and some tangible products. |
|
Golembski G., 1998 |
A tourism product combines all goods and services created and acquired in connection with leaving one's place of permanent residence and before the start of the trip, and during the trip, and while staying outside one's home area. |
|
Mazurkiewicz L., 2002 |
Tourism product - an arbitrary combination of place services and tourism services |
|
Nowakowska A., 2002 |
A tourist product can be called a package of tangible and intangible components available on the market that allows realizing the purpose of a tourist trip. |
As can be seen from Table 1, most often in approaches to the definition of a tourist product, a structural or component approach can be traced, where, along with material objects, various services, images, places, ideas, ideas are considered.
Less common are definitions of a tourism product that focus on meeting the needs and expectations of tourists (Middleton V.T.C.).
S. Medlik for the first time made an attempt to combine two points of view on the tourism product, considering it in a narrow and broad sense.
Thus, the tourism product can be considered from three positions:
According to Federal Law No. 132-FZ “On the Basics of Tourism in the Russian Federation”, “a tourist product is a set of transportation and accommodation services provided for a total price (regardless of the inclusion in the total price of the cost of excursion services and (or) other services) under an agreement on the implementation of the tourism product.
According to this definition, a tourist product is identified with the concept of a tour. They should be distinguished. The tour is an integral part of the tourism product. It is a set of primary services that a tour operator provides on a specific route and in a specific period of time. As a rule, the tour includes transportation, accommodation and meals according to the type chosen by the tourist. Tourist product is a much broader definition.
Let's consider a simplified classification of tourist products according to the characteristic elements that determine the essence of the tourist product (Table 2).
As you can see, the tourism product is diverse and is created by the efforts of many enterprises and organizations, each of which has its own methods of work, technologies, specific goals and objectives for the creation, promotion and implementation of a tourism product, using various marketing policy tools. This objectively creates great organizational difficulties in coordinating actions in the production, supply and sale of a tourist product and ensuring a high level of tourist service. At the same time, it should also be taken into account that the ultimate goals and content of the marketing process for enterprises involved in the creation, promotion and sale of a tourist product are also different. There are several levels of marketing organization in tourism:
Classification of tourism products
table 2
|
tourist product |
An example of a tourism product |
|
|
Tourist |
Material object - a guidebook, a tourist map, tourist equipment, souvenirs, multimedia products: multimedia city plans, guides to museums and historical sites, presentations of regions on Internet sites, mobile applications |
Virtual travels of the Kizhi Museum Reserve (http://kizhi.karelia.ru/); Virtual walks around the Russian Museum (http://www:virtualrm.spb.ru/) Virtual tours through the streets of London (http://virtualizacija.ru/) |
|
Tourist product - service |
Single service - hotel, gastronomic, transport, excursion, etc. |
Booking a hotel room, lunch in a restaurant, air ticket, etc. |
|
Tourist product - event |
Thematic focus of the event, specific localization in time and space |
Tourist exhibitions - WorldTravelMarket (London), ITB (Berlin), MITT (Moscow), INTURMARKET (Moscow); Oktoberfest (Wiesn, Munich); Olympic Games Sochi-2014; Cartoon Festival (http://www.multfest.ru/); music festival "White Nights" in St. Petersburg, etc. |
|
Tourist |
A tour that includes a certain set of services (transportation, accommodation, meals, excursions |
"All Spain" (http://www.natalie-tours.ru/); Music Festival |
Ending
|
tourist product |
Characteristics of the tourism product |
An example of a tourism product |
|
etc.), the total sale value of which is equal to the value of its elements |
in Sanremo (http://www.tez-tour.com); "Petersburg every day", etc. |
|
|
Tourist product - display object |
The presence of one main attraction (service) and several additional services located in one place - a museum, a historical monument, a natural monument, etc. |
St. Isaac's Cathedral in St. Petersburg, the Kremlin in Moscow, Madame Tussauds in London |
|
Tourist product - route |
Several places or objects united by a certain idea and interconnected by a specially marked route (pedestrian, water, automobile), with a developed infrastructure, the elements of which are located along the route |
"Golden Ring" (Russia), Wine and gastronomic tour (Nice - Avignon - Marseille), Die Goldene Strasse (Nuremberg - Pilsen - Prague) |
|
Tourist product - place |
Region, locality, national park, etc., identified on the basis of a specific spatial localization and having the character of a tourist attraction |
Paris, Disneyland, Carinthia - the land of lakes |
At the same time, marketing at the level of tour operators and travel agents and marketing at the level of tourism service providers belong to the field of commercial marketing, and marketing at the level of the national tourism administration and marketing at the level of territories belong to the field of non-commercial marketing.
The comprehensive nature of the concept of marketing in tourism involves consideration of the marketing process at various levels of management of the creation, formation, promotion and implementation of a tourist product. The subjects of the marketing process are not only commercial enterprises, but also public authorities in the field of tourism, as well as territories.
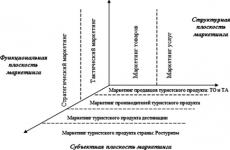
On fig. Figure 9 presents an approach to the concept of marketing in tourism as a system based on a three-dimensional coordinate system.

Rice. 9.
On a functional basis at all levels of formation of a tourist product, it is necessary to use the tools of strategic and tactical (operational) marketing.
Strategic and operational marketing complement each other and find their concrete expression within the marketing policy.
Operational marketing focuses on such variables as price, distribution system, sales, advertising and promotion of the product, strategic marketing focuses on the selection of product markets in which the company has a competitive advantage, and on the forecast of total demand in each of the target markets. Based on this forecast, operational marketing sets goals for the development of market share, as well as the marketing budget necessary for this.
No matter how powerful an operational marketing plan is, it cannot create demand where there is no need and cannot sustain a line of business that is doomed to disappear. Therefore, to be profitable, operational marketing must be based on strategic marketing, which, in turn, is based on the needs of the market and its expected evolution.
Market orientation is the main condition that determines the sustainable economic growth of a company operating in the tourism industry.
On a structural basis in the field of tourism, marketing of goods and marketing of services can be distinguished. The combination of trade in services and trade in goods in tourism, according to experts, is 75% and 25%, respectively.
When developing marketing strategies for companies operating in the field of tourism - travel agencies, hotels, catering establishments, tourist display facilities, it is necessary to take into account the specifics of the "intangible" product. The development of a marketing program should not only build on the traditional elements of the marketing mix, but also need to involve additional elements - the service delivery process, contact personnel (personnel working in direct contact with guests and customers) and the physical environment.
Experience of international hotel chains such as Hyatt, FourSeasons, Marriott, Intercontinental and others, large tour operators - TUI, Carlson tourism indicates that the key competence in the field of tourism is the strategy of "precautionary and perfect service".
Creating a system of perfect service that meets the values of the clients of tourism enterprises is a long-term competitive advantage that cannot be copied.
In this regard, the main task is to establish a connection between the needs and expectations of customers and the internal processes of creating a value model for customers in the tourism industry, aimed at meeting these needs.
The customer value model includes five main elements that determine the customer's perception of value and level of satisfaction. These are the quality of the product itself, the quality of service through the technology of its provision, the image of the enterprise, the price and the relationship between the service provider, the client and the contact staff of the tourism company.
The implementation of the customer value model is facilitated by the internal marketing assets of the tourism company, which include:
Each of these elements is a direct result of the work of various processes within a tourism company.
Providing quality customer service will:
Achieving a sustainable competitive advantage by a tourism company is possible through the introduction of the concept of internal marketing.
The concept of internal marketing is to combine the motivation of employees and the formation of their professional knowledge for the identity of the brand of the tourism company. The motivation and high level of knowledge of employees is the source of high quality services.
The implementation of the concept of internal marketing will allow building the relationship "loyal staff - loyal customer - company profitability". The output of this process will be the developed technology of quality customer service and its control, a system of performance evaluation of staff depending on customer satisfaction, a marketing information system of a tourism company that gives staff the opportunity to provide quality customer service, as well as the education of loyal employees who provide excellent service.
This approach differs from the traditional promotion of a product in the field of tourism, since it is aimed not at solving current issues of attracting and retaining customers, but at building a system of relationships with customers on a long-term basis.
The implementation of external marketing strategies implies organizational changes within the tourism company, primarily related to the distribution of resources, organizational structure and building relationships with customers. Thus, the most careful attention should be paid to working on the organizational environment through internal marketing in order to achieve the goals of the company as a whole.
In the service marketing models discussed in Section 1.2, Western marketers recognize the need to use internal marketing as an additional strategy. A characteristic feature of these models is the attitude to the personnel of the service sector enterprise as to an internal client. Motivation of personnel, satisfaction of their needs contribute to the growth of the quality of customer service of the company.
Internal marketing has the same theoretical base as traditional marketing. A feature is the object and subject of study of the concept of internal marketing.
The object of internal marketing are the employees of the tourism company and its internal environment, considered in terms of the expectations and perceptions of the client.
The task of internal marketing is to create an environment within the company that is as customer-oriented as possible.
By subjective can be distinguished:
The presence of a marketing strategy is a necessary element not only in the activities of individual companies in the tourism industry, but also in coordinating and regulatory bodies and organizations in this area.
The tourism marketing strategy within the state is to implement its tourism policy. Tourism policy of the state - a set of government measures and activities that determine the conditions for the development of the tourism industry, the rational use of tourism resources, increasing the contribution of the tourism industry to the country's GDP.
The tourism marketing strategy at the state level is reflected in the adoption of relevant legislation, state long-term programs and plans. The state, entering the international tourism market, enters into a system of competitive relations with other states and regions of the world. The role and place of the state in the global tourism market depends on how correctly and effectively the strategy of tourism marketing is built and implemented. The state tourism marketing strategy is aimed at creating, promoting and selling a national tourism product in the global tourism market and within the country, i.e. is aimed at the development of international and domestic tourism. A state entering the international tourism market enters into a system of competitive relations with other states, entire world regions. The tourism marketing strategy is reflected in the adoption of relevant legislation, state long-term programs and plans. The role and place of a particular state in the global tourism market depends on how correctly and effectively the tourism marketing strategy is built and implemented.
1 Karpova G.A.,Khoreva L.V. Economics and management of tourism activities: a textbook in 2 parts. Part 1. - St. Petersburg: Publishing House of St. Petersburg State University of Economics, 2011.
The national tourism product is a set of available natural, climatic, natural, historical, architectural and cultural resources attracted and used in tourism activities, tourism and related infrastructure, as well as the activities of tourism companies, expressed in the creation, promotion and implementation of specific tourism products aimed at to attract tourists from other states and regions of the world.
In the activities of the state, the concept of marketing in tourism is based on the analysis of market opportunities, the choice of target markets, and the development of a marketing mix. The implementation of these components allows you to correctly develop the tourism policy of the state, i.e. state tourism marketing strategy. The main link in the implementation of tourism marketing of the state is the state body responsible for the state and development of tourism in general - the national tourism administration (NTA). In the Russian Federation, this role is played by the Federal Tourism Agency of the Ministry of Culture of the Russian Federation.
The tourist policy of the state is based on strategy and tactics.
Tourism strategy - the development of a general concept for the development of tourism in the international and domestic markets, targeted programs, the implementation of which requires time and large financial resources. For example, at a meeting of the Presidium of the Government of the Russian Federation on July 28, 2011, the Federal Target Program "Development of domestic and inbound tourism in the Russian Federation (2011-2018)" was adopted. The implementation of the Program will increase the competitiveness of the domestic tourism market, create conditions for the development of tourism infrastructure, and attract investment in the industry. The activities of the Program are also aimed at increasing the efficiency of promoting the national tourism product in the domestic and international markets. This program is an example of Russia's strategy in the field of tourism.
To implement this strategy, a number of measures (tourist tactics) are proposed, including:
The main objective of the state tourism marketing concept is the creation of a national tourism product and its promotion in the global and domestic tourism markets. The implementation of the tourism marketing concept begins with an analysis of market opportunities, where we understand the state as a producer, a national tourist product as a product, other states or world regions as competitors, and tourists from other countries as consumers.
At the territorial level, there is a refinement of the national strategy for promoting the tourist product, the specification of projects, territories and tourist destinations is determined. The main attention is paid to the development of a general policy and strategy for development programs, marketing, for example:
The tourist essence of each region can be revealed more deeply and its tourist product is promoted more efficiently when different types of tourist products are allocated within the region by destination.
The World Tourism Organization (UNWTO, UNWTO) singles out tourist destinations as the main elements in the tourism system that attracts a tourist to make a trip and where he spends some time 1 . Tourist destination includes tourist attractions, tourist infrastructure, related services.
In the context of global competition, when tourist destinations become products - substitutes, destination management bodies are included in the competition for the attention of tourists and investment resources for the development of the destination.
Destination marketing can be defined as a management process in which destination management bodies and businesses identify target groups of tourists, establish communications with them in order to find out the preferences of tourists, their expectations, motivation for choosing a travel destination in order to adapt the tourist product in accordance with the expectations of tourists for achieve their maximum satisfaction.
UNWTO data show that in order to additionally attract one foreign tourist, providing an average of 1,000 euros to the country's economy, the state spends from 3 to 10 euros on non-commercial advertising of a tourist product. In accordance with this, the average amount of budgetary funds allocated in European countries for the promotion of a tourism product is 31.7 million euros 2 .
Tourism destination marketing is part of a broader concept of territory management - territorial marketing. Territorial marketing is marketing in the interests of the territory, its internal subjects, as well as external subjects, in whose attention and actions the territory is interested. Territorial marketing is carried out with the aim of creating, maintaining or changing the opinions, intentions and behavior of residents and non-residents in the person of individuals and companies regarding a given territory. The founder of the concept of territorial marketing is Philip Kotler. In his work Marketingplaces, he notes that location marketing is successful when the main target audiences - residents and businesses - are satisfied with their region, and when the region meets the expectations and needs of visitors and investors. This is a philosophy of territory management that contributes to its socio-economic development by meeting the needs of individuals and economic entities in resources for the purpose of living and (or) doing business in the territory, regardless of the specific level of territorial formation - region, country, city.
Before the emergence of the concept of territory marketing and destination marketing as its integral part, "selling territories" was the dominant form of promotion of regions. However, destination marketing is part of the general concept of the development of the territory and works for an integrated sustainable socio-economic development.
The basis of the marketing approach to destination management is the consideration of a tourist destination as a complex tourist product, consisting of:
Destination marketing approach involves the development of a complex destination product. And here it is important to understand that a tourist is not going to visit a hotel, a beach, a restaurant. He travels to get new sensations, the opportunity for intercultural enrichment, for the sake of improving health, etc. Tourists are attracted not by the characteristics of the destination, but by their functional ability to satisfy certain needs.
The destination marketing strategy should determine what tourism resources the destination has, what tourism product can be developed based on them, who this tourism product is aimed at, how it will be promoted and what resources are needed for this.
The destination marketing strategy is an integral part of the region's marketing strategy for tourism development, which includes the development of infrastructure, optimization of local legislation regarding the tourism sector in the region, distribution of financial flows, attraction of investments, development of public-private partnerships in the field of tourism.
Tourism enterprises producing various services - hotel business, catering, excursion activities - are an integral part of the complex tourist product of the destination, as well as a sphere of joint interests of business and local authorities in implementing projects for the construction of hotels, theme parks, development of the food system, etc.
Control questions
Marketing in social and cultural services and tourism Yuliya BezrutchenkoFrom the book Marketing. And now the questions! author Mann Igor Borisovich From the book Marketing author Loginova Elena Yurievna
52. The concept of international marketing. Concepts of international marketing International marketing is carried out as an expression of the business activity of companies operating in markets with the aim of generating income in more than one country. The main goal of marketing is to obtain
From the book Marketing: lecture notes author Loginova Elena Yurievna3. Concepts of international marketing Differences in the international focus and approaches to international markets in which international business organizations operate can fall under one of three concepts of international marketing: 1) concept
From the book Marketing. Lecture course author Basovsky Leonid EfimovichMarketing concepts Over time, all those involved in the exchange process learn, marketing improves, concepts are formed on the basis of which management in this area is carried out. Marketing management is analysis, planning, implementation and
From the book Marketing in Socio-Cultural Service and Tourism author Yulia BezrutchenkoMarketing Concepts The products of a certain firm cannot please all buyers. Buyers differ from each other in their needs and habits. Some firms are best served by focusing on serving certain parts, or segments, of the market. expedient
From the book Marketing author Rozova Natalya KonstantinovnaChapter 1 Essence, content, basic concepts of marketing in tourism
From the book Profitable Travel Agency [Advice to Owners and Managers] the author Vatutin Sergey1.3. Essence and content of marketing in tourism People working in the hospitality and travel industry must understand that they are part of the product that they represent in the market. The difference is very often determined by small things, such as answering the phone, greeting,
From the book Bureaucracy. Theoretical Concepts: Study Guide author Kabashov Sergey Yurievich2.2. Levels and coordination of marketing in tourism The following levels of marketing in the field of tourism can be distinguished: 1) marketing of tourism enterprises (tour operators and travel agents) is a process of coordinating the capabilities of enterprises and consumer requirements,
From the book Benchmarking - a tool for developing competitive advantages author Loginova Elena Yurievna2.3. Tourist enterprise - the main link in the implementation of the concept of marketing Tourist enterprises are an important component that forms the tourist offer in the subsystem "subject of tourism". A variety of tourism enterprises operate in the tourism area.
From the book It won't be easy [How to build a business when there are more questions than answers] author Horowitz BenQuestion 18 Concepts of the marketing mix (marketing-mix) Answer The marketing mix is a set of practical tools for adapting a company to a market situation and measures to influence the market. A good marketing mix helps the firm to gain a strong market position.
From the book The most important thing in PR by Alt Philip G. From the author's bookChapter 2 Concepts of the origin of bureaucracy in traditional societies The concepts of "patrimonialism" and "patrimonial bureaucracy". Ancient China: Confucianism and Legalism. M. Weber on Chinese bureaucracy. The system of training and principles of staffing officials in
From the author's bookChapter 7 Concepts of bureaucratization of political parties M. Ya. Ostrogorsky: analysis of the evolution of bureaucratization of political parties in Great Britain, France and the USA. General approaches to the role of organization in society and political parties in the studies of M. Ya. Ostrogorsky and theory
From the author's book7.3. Concepts and directions of marketing in the enterprise As noted earlier, marketing is used both in commercial and non-commercial activities, for example, in activities related to charity, the dissemination of public ideas
Tourism is one of the leading and most dynamically developing sectors of the global service sector. Due to its rapid growth, tourism has been recognized as an economic phenomenon of the 20th century. The Russian tourism market is also developing.
The volume of the Russian tourism market has been progressively increasing throughout the last decade. In 2013, its volume (compared to 2011) increased by 14% (or by 149 billion rubles), exceeding 1 trillion rubles. (about 1.7% of Russia's GDP).
The tourism services market is moving towards greater transparency and accessibility for the end consumer. According to aviation explorer 1, the growth in the share of travel services issued online was recognized as the most noticeable trend in the Russian market in 2012. The structure of demand is changing, shifting towards self-registration of travel services on the Internet by the population.
At present, a unified approach to the definition of marketing in tourism has not yet been developed, so we will consider different views on the problem.
According to French scientists R. Lankar and R. Ollie, tourism marketing- this is a series of basic methods and techniques developed for research, analysis and solving problems. The main thing to which these methods and techniques should be directed is to identify the possibilities for the most complete satisfaction of people's needs in terms of psychological and social factors, as well as to determine the ways of the most rational business management from a financial point of view by tourist organizations (enterprises, bureaus or associations), allowing to take into account the identified or hidden needs for tourism services. These kinds of needs can be determined either by recreational motives (entertainment, vacation, health, education, religion and sport) or by other motives that are often found in business groups, families, various missions and alliances.
The Swiss specialist E. Krippendorf puts a more complete content into the concept of tourism marketing: "Tourist Marketing- this is a systematic change and coordination of the activities of tourism enterprises, as well as private and public policies in the field of tourism, carried out but regional, national or international plans. The purpose of such changes is to best meet the needs of certain groups of consumers, while taking into account the possibility of obtaining appropriate profits” 1 .
The concept of marketing in the field of tourism is developing in accordance with modern trends in the development of marketing theory and service marketing theory.
The tourist product has the distinctive characteristics inherent in the service, namely, intangibility, inseparability from the source, perishability and inconstancy of quality(4 "NOTs"), Four "NOTs" of tourism services as a commodity seriously affect the specifics of activities in the field of tourism.
In addition to the traditional elements of the marketing mix: Product - Price - Place - Promotion, used in traditional marketing as a set of company-controlled strategies for influencing the consumer, it is recommended to implement additional strategies for the service marketing mix in tourism. These include: physical environment (physical evidence), service process (process) and personnel (people).
material environment(the atmosphere of a hotel, restaurant, office of a travel agency) involves working on the impact on the sensory channels of perception of customers: visual (organization of space, lighting, color), auditory (volume and tempo of music accompaniment), olfactory (ventilation of the room), tactile (room temperature) .
Maintenance Process guests, customers can be developed using diagrammatic design methods, common ground, customer scenario and reengineering.
Staff(contact staff) - this is the staff of the company, which simultaneously produces and sells a tourist service. Therefore, contact personnel in service marketing are sometimes referred to as "part-time marketers" (part-time marketers).
Together with the rest of the marketing mix strategies (product, price, distribution channels, promotion), these additional three elements form the tourism marketing mix.
The result of activity in tourism is a tourist product, which has its own distinctive features:
The problem of defining a tourist product remains debatable. Consider the most common definitions of a tourist product, presented in Table. 8.1.
As can be seen from Table. 8.1, most often in approaches to the definition of a tourist product, a structural or component approach is traced, where, along with material objects, various services, images, places, ideas, ideas are considered.
Table 8.1
Tourism product definitions
|
Tourism product definition |
|
|
Altkorn J., 1994 |
The policy of a tourist product can be considered and conducted from two positions: a certain territory and a certain enterprise. |
|
Medlik S „ 1995 |
Tourist product in the narrow sense (sensustricto) - everything that tourists buy separately (for example, a transport service, booking a hotel room) or in the form of a package of services. Tourist product in a broad sense (sensulargo) covers the totality of the impressions received from the moment of leaving home until the moment of returning |
|
Middleton V., 1996 |
A tourism product is a combination of three main components: attractiveness, tourism infrastructure, and their accessibility. |
|
Middleton V., 1996 |
From the point of view of a potential client considering any form of travel, a tourism product can be defined as a package of tangible and intangible services. |
|
Holloway J., Robinson Ch., 1997 |
A tourism product is a complex product that encompasses a place, services, and some tangible products. |
Less common are definitions of a tourism product that focus on meeting the needs and expectations of tourists (V. Middleton). Medlik S. (S. Medlik) for the first time made an attempt to combine two points of view on the tourism product, considering it in a narrow and broad sense.
Thus, the tourism product can be considered from three positions:
According to the Federal Law of November 24, 1996 No. 132-FZ “On the Fundamentals of Tourism in the Russian Federation”, “a tourist product is a set of transportation and accommodation services provided for a total price (regardless of inclusion in the total price)” of the cost of excursion services and (or) other services) under an agreement on the sale of a tourist product.
According to this definition, a tourist product is identified with the concept of a tour. They should be distinguished. The tour is an integral part of the tourism product. It is a set of primary services that a tour operator provides on a specific route and in a specific period of time. As a rule, the tour includes transportation, accommodation and meals according to the type chosen by the tourist. Tourist product is a much broader definition. Consider a simplified classification of tourist products according to characteristic elements (Table 8.2).
As can be seen from Table. 8.2, the tourism product is diverse and is created by the efforts of many enterprises and organizations, each of which has its own methods of work, technologies, specific goals and objectives for creating, promoting and implementing a tourism product, using various marketing policy tools. This objectively creates great organizational difficulties in coordinating actions in the production, supply and sale of a tourist product and ensuring a high level of tourist service.
Classification of tourism products
|
Type of tourism product |
Characteristics of the tourism product |
An example of a tourism product |
|
Tourist |
Material object - a guidebook, a tourist map, tourist equipment, souvenirs, multimedia1 products: multimedia city maps, guides to museums and historical sites, presentations of regions on Internet sites, mobile applications |
Virtual travels of the Kizhi Museum-Reserve (http://kizhi.karelia.ru/). Virtual walks around the Russian Museum (http:// www.virtualrm.spb.ru/). Virtual travels through the streets of London (http://www.virtualizacija.ru/) |
|
Tourist product-service |
Single service - hotel, gastronomic, transport, excursion |
Booking a hotel room, lunch in a restaurant, air ticket, etc. |
|
Tourist |
Thematic focus of the event, specific localization in time and space |
Tourist exhibitions - World Travel Market(London), ITB (Berlin), MITT (Moscow), INTURMARKET (Moscow); Oktoherfest (Wiesn, Munich); Sochi 2014 Olympic Games; Cartoon Festival (http://www.multfest.ru/); Music festival "White Nights" in St. Petersburg, etc. |
|
Tourist |
A tour that includes a certain set of services (transportation, accommodation, meals, excursions, etc.), the total selling price of which is equal to the cost of its elements |
"All Spain" (http://www.natalie-tours.ru/); Music Festival in Sanremo (http://www.tez-tour.com); "Petersburg every day", etc. |
|
Tourist product - display object |
The presence of one main attraction (service) and several additional services located in one place - a museum, a historical monument, a natural monument, etc. |
St. Isaac's Cathedral in St. Petersburg, the Kremlin in Moscow, Madame Tussauds in London |
|
Tourist |
Several places or objects united by a certain idea and interconnected by a specially marked route (pedestrian, water, automobile), with a developed infrastructure, the elements of which are located along the route |
"Golden Ring" (Russia), Wine and gastronomic tour (Nice - Avignon - Marseille), Die Golden Strasse(Nuremberg - Pilsen - Prague) |
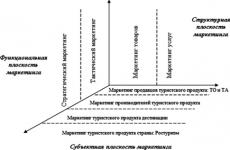
There are several levels of marketing organization in tourism:
At the same time, marketing at the level of tour operators and travel agents and marketing at the level of tourism service providers belong to the field of commercial marketing, and marketing at the level of the national tourism administration and marketing at the level of territories belong to the field of non-commercial marketing. On fig. 8.1 presents an approach to the concept of marketing in tourism as a system.
On a structural basis, in the field of tourism, marketing of goods and marketing of services can be distinguished. The combination of trade in services and trade in goods in tourism, according to experts, is 75 and 25%, respectively.
Rice. 8.1.
coordinates:
TO - tour operators; TA - guragents
When developing marketing strategies for companies operating in the field of tourism - travel agencies, hotels, catering establishments, tourist display facilities, it is necessary to take into account the specifics of the "intangible" product. The development of a marketing program should not only build on the traditional elements of the marketing mix, but also need to involve additional elements - the service delivery process, contact personnel (personnel working in direct contact with guests and customers) and the physical environment.
In this regard, the main task is to establish a connection between the needs and expectations of customers and the internal processes of creating a value model for customers in the tourism industry, aimed at meeting these needs.
The customer value model includes five main elements that determine the perception of value by the customer and the level of his satisfaction: the quality of the product itself; quality of service through technologies for its provision; company image; price; the relationship between the service provider, the client and the contact personnel of the tourism company.
The implementation of the customer value model is facilitated by the internal marketing assets of the tourism company.
The implementation of the concept of internal marketing will allow building the relationship "loyal staff - loyal customer - company profitability". The output of this process will be the developed technology of quality customer service and its control, a system of performance evaluation of staff depending on customer satisfaction, a marketing information system of a tourism company that gives staff the opportunity to provide quality customer service, as well as the education of loyal employees who provide excellent service.
This approach differs from the traditional promotion of a product in the field of tourism, since it is aimed not at solving current issues of attracting and retaining customers, but at building a system of relationships with customers on a long-term basis.
Internal marketing has the same theoretical base as traditional marketing. A feature is the object and subject of study of the concept of internal marketing. The object of internal marketing is the employees of a tourism company and its internal environment, considered from the point of view of the client's expectations and perceptions.
The task of internal marketing is to create an environment within the company that is as customer-oriented as possible.