Active rest and travel in Russia
Send your good work in the knowledge base is simple. Use the form below
Students, graduate students, young scientists who use the knowledge base in their studies and work will be very grateful to you.
Hosted at http://www.allbest.ru/
9. The boundaries of time zones are the meridians. However, on land, these boundaries do not always coincide with the directions of the meridian. How does this explain
55. What types of forests have suffered the most from human activities? What does it have to do with
61. What pattern exists in the distribution of natural zones on the Earth? Which of them do not form continuous bands
97. What is the peculiarity of the sectoral composition of mechanical engineering? On what grounds and into what groups can the industries included in it be divided?
156. What are the main branches of the economy are formed in the economic regions that form Central Russia? Why
Literature
engineering forest natural area
9. The boundaries of time zones are the meridians. However, on land, these boundaries do not always coincide with the directions of the meridian. How does this explain
reduced volumetric model The globe is a globe. Parallels and meridians are marked on it. Meridians are the boundaries of the hour poles, but on land these boundaries do not always coincide with the directions of the meridians because the globe is smooth, and the Earth is covered with mountains and depressions that violate the regular spherical shape. However, these irregularities are so small compared to the size of the Earth that it is almost impossible to depict them on a globe. So, the highest peak on Earth, Chomolungma, has a height of 8848 m, which on a medium-sized globe (scale: 1 cm 500 km, or 1 mm 50 km) gives less than 0.2 mm. Thus, on the globe, this peak would have a height equal to the thickness of the paper with which the globe is pasted over, and it would be impossible to notice it. In addition, the earth is not perfectly round. It has the shape of an ellipse. A geography manual for applicants to universities / Ed. V.G. Zavriev. - Mn.: Higher. school, 1978. - P.56.
Therefore, the meridians, ideally drawn on the globe, on the earth's surface change their shape in accordance with changes in the shape of the Earth's surface.
55. What types of forests have suffered the most from human activities? What is it connected with?
Natural resources used by man can be divided into exhaustible and inexhaustible. Exhaustible resources include minerals, renewable resources include plants, animals and soils. Inexhaustible riches are solar heat, air and water.
It is necessary to use all the riches of nature wisely and economically.
However, there are many examples of the negative impact of man on nature. Over the past 10 thousand years, 2/3 of the world's forests have been destroyed on Earth, and the area of deserts has expanded by 500 million hectares. In the mountains, for example, in the Alps, the destruction of forests on the southern slopes caused the shallowing of rivers, destructive floods during high waters, and the destruction of the top fertile soil layer.
In almost all countries of the world, the pursuit of maximum profits leads to a predatory attitude towards nature.
Thus, the colonialists in the previously enslaved countries of Africa and South Asia destroyed vast areas of tropical forests that provided valuable timber, exterminated elephants, ostriches and other valuable animals. Diamonds, gold, non-ferrous metal ores were exported from these regions to the capitalist countries. Zheltikov V.P. Economical geography. Ed. 3rd.- Rostov n / a, 2004.- P.156.
Thus, the richest forests and fauna of Africa suffered the most. This is due to the fact that crocodile skin, for example, was used to make haberdashery items, and valuable breeds trees for the construction of ships and expensive furniture.
61. What pattern exists in the distribution of natural zones on the Earth? Which of them does not form continuous bands?
The natural conditions of each continent are determined geographic location, history of its formation, relief, climate. On the surface of the Earth, zonal patterns are observed in the distribution of these components of nature and large natural complexes. Change from equator to poles climatic zones and natural areas.
The largest natural complexes geographical envelope, many of which encircle the globe almost in rings, are geographical zones.
The ring form of geographical belts is disturbed by the configuration and topography of the continents. In all geographical zones, where there are mountains, areas of altitudinal zonation are distinguished.
There are 13 geographical zones on Earth: one equatorial, two subequatorial, two tropical, two subtropical, two temperate, two subpolar (subarctic and subantarctic), two polar (arctic and antarctic). Geographical zones are subdivided into natural zones.
A natural, or geographical, zone is a territory, all natural components (soils, relief, waters, climate, soils, flora and fauna, human economic activity) of which are closely interconnected. The geographical zones of the land do not form continuous bands, they are interrupted in the seas and oceans, but are especially pronounced on the plains. Zoning depends on the amount of heat, precipitation, their ratio, remoteness from the oceans, mountain ranges that stand in the way of air currents, and all this, ultimately, depends on the shape of the Earth.
Natural zones are distributed in a strictly defined order, which is determined by the climate, mainly by the ratio of heat and moisture. First of all, the distribution of vegetation on Earth depends on the climate. It is with the climate that the duration of the growing season and all the features of the development of green plants are associated. Therefore, the main types of climate identified on the globe correspond to various natural zones with their characteristic plant types of communities.
The equatorial geographical belt occupies part of the territory on all continents on both sides of the equator, without forming a continuous ring. In this belt there is one natural zone - the zone of humid equatorial forests, dominated by humid equatorial air masses. Heat is supplied in large quantities and relatively evenly throughout the year. The annual amount of precipitation is 2500-4000 mm. Atmospheric moisture is excessive. The soils are red-yellow.
The zone of equatorial forests is well expressed in South America (Amazon basin), Africa (Congo basin), and on the islands of Indonesia. Huge areas of virgin forests (giley) are formed by evergreen large-leaved trees, which are located in 4-5 tiers. Lianas are plentiful, grass cover is poor. Excess moisture determines the development of swamps.
Many representatives of the animal world spend almost their entire lives on the crowns of trees (monkeys, semi-monkeys, sloths, birds).
Subequatorial geographic zones (northern and southern hemispheres) are located on both sides of the equator. These belts occupy a large area in Africa and South America. The climate is subequatorial, with humid summers dominated by moist equatorial air masses and dry hot winters dominated by dry tropical air masses. In these geographical zones, two natural zones are distinguished: variable-humid deciduous forests and savannahs. Soils are red, and in drier places red-brown.
Tropical geographic zones are located in the northern and southern hemispheres, on the continents they correspond to deserts. Dry tropical air masses prevail here, trade winds blow, in summer - the most high temperatures on the ground. In these belts there are natural zones of deserts and semi-deserts, and only in places where the trade winds bring moisture from the oceans do tropical rainforests grow on red-yellow soils.
Subtropical geographic zones are transitional from tropical to temperate. The climate is subtropical, the air masses change seasonally. Due to the significant extent of subtropical geographical zones, especially in the northern hemisphere, natural conditions different in different parts. Different humidification determines the presence of five natural zones in these belts. On the western coasts of the continents, the climate is Mediterranean, summers are dry, hot - tropical air masses dominate, winters are warm, humid - air masses of temperate latitudes prevail. Here is a zone of hard-leaved evergreen forests and shrubs. In the central parts of the continents, the climate is subtropical continental with cold winters and hot dry summers. Here are deserts and semi-deserts with gray soils. On the eastern coasts of the continents, the climate is subtropical monsoon, zones of humid forests, forest-steppes and steppes are common.
Temperate geographical zones are located in temperate latitudes. In the northern hemisphere temperate zone occupies large spaces and its northernmost border is located almost at 70 o N. In the southern hemisphere, the temperate zone occupies a small land area in the south of South America and in the southern part of about. Tasmania. In these zones, the seasons of the year are clearly expressed, air masses of temperate latitudes prevail, westerly winds prevail, and monsoons prevail on the eastern coasts of the continents. On the territory of the temperate geographical zone there are zones: taiga, mixed forests on podzolic soils, deciduous forests on brown forest soils. Then, inside the continents, forests give way to forest-steppe and steppe on chernozem soils, and steppes to semi-deserts and deserts on chestnut and gray-brown soils.
Subpolar belts occupy tundra and forest-tundra zones. In the northern hemisphere, the subpolar belt covers the northern parts of Eurasia and North America. The climate is subarctic, moderate air masses prevail in summer and arctic in winter. Permafrost interferes with the infiltration of moisture, evaporation is low, this causes waterlogging.
Polar geographic belts - in the northern hemisphere, the polar arctic belt is located on the islands of the Arctic Ocean, in the southern hemisphere, the polar Antarctic belt occupies the mainland Antarctica. Cold air masses with negative temperatures prevail. There are long polar days and nights. Large areas are covered with continental ice and are ice deserts. Only in some places, freed from snow and ice, mosses and lichens grow in summer. In the Arctic zone there is a zone of Arctic deserts, which occupies the islands of the Arctic Ocean; in the Antarctic - the zone of the Antarctic deserts. Karlovich I.A. Geecology: Textbook for high school. - M.: Academ. Project: Alma - Mater, 2005. - P.25.
Thus, zonal patterns are observed on the Earth's surface in the distribution of these components of nature and large natural complexes. From the equator to the poles, climatic zones and natural zones change depending on the proximity to the Earth's poles.
97. What is the peculiarity of the sectoral composition of mechanical engineering? On what grounds and for what groups can be subdivided into its constituent industries
Mechanical engineering is the leading branch of industry. He holds the first place in terms of the cost of products and the number of employed workers. Structurally, this is the most complex and branched industry. industrial production. As part of mechanical engineering, about 80 specialized branches and industries are distinguished, united by a common technology and raw materials used.
For the manufacture of various machines required unequal quantity metal. Most of all it is necessary for heavy engineering. This is the production of mining, metallurgical, oil equipment, diesel locomotives, powerful steam boilers and turbines. It is advantageous to place heavy engineering enterprises near metallurgical plants.
Depending on the purpose of the manufactured products, there are energy, transport, road construction, agricultural engineering and many other industries. Instrument-making, machine-tool building, the electrical engineering industry, etc., also stand out.
The production of products in mechanical engineering is associated with various labor costs. In the machine tool industry, instrument making, radio and electronic industries, labor costs are high, highly skilled workers are required. These are labor intensive industries. Their placement depends on the availability of highly qualified personnel. The centers of these industries are, as a rule, large cities in which there are research and design institutions.
Many branches of engineering are oriented in their location to the areas where their products are consumed. This applies primarily to the production of machinery and equipment for a number of industries. Coal harvesters and cutters are produced in areas where coal is mined, machines for harvesting peat in areas of the peat industry, etc. Grain, beet and cotton harvesters, and tea pickers are produced in areas where the corresponding branches of agriculture have developed. The territorial coincidence of the places of consumption of products with the areas of sources of raw materials is the most advantageous option for locating machine-building enterprises.
Machine-building plants are either specialized enterprises that produce individual parts, blanks, or assembly plants that complete the production process of machines and mechanisms. In any case, they cooperate with many other enterprises. The implementation of these production links is possible only if there is a developed transport network. Therefore, one of the main factors in the location of all branches of engineering is the transport location of the point, which ensures uninterrupted communications with allied enterprises. It is advantageous to place enterprises cooperating with each other close to each other. They then form machine-building complexes in which factories interconnected in terms of production jointly participate in the production of finished products.
When choosing the construction sites for the new largest automobile plants - Volzhsky in Togliatti and Kamsky in Naberezhnye Chelny - the proximity of the metallurgical bases of the Urals and the South, a powerful construction industry in the Volga region were taken into account. Not the last role was played by the availability of convenient communication routes connecting the Volga region with the western and eastern regions, with the CMEA countries.
Moscow, Gorky, Minsk, Zhdanov, Ulyanovsk, Zaporozhye, Lvov, Kremenchug are also major centers of the automotive industry. Railway engineering is developed in Novocherkassk and Tbilisi (electric locomotives), Voroshilovgrad, Kharkov, Kolomna (diesel locomotives), Kalinin, Riga, Bryansk, Mytishchi (cars), etc. The country's largest car building plant was built in Abakan (Eastern Siberia). different types sea and river vessels are produced by enterprises in Leningrad, Gorky, Kherson, Nikolaev, Astrakhan, and Tyumen.
Tractor plants are located in Kharkov, Volgograd, Chelyabinsk, Minsk, Vladimir, Lipetsk, Pavlodar. Combine harvesters are supplied by factories in Rostov-on-Don, Taganrog and Krasnoyarsk. The leading centers of heavy engineering are Sverdlovsk, Kramatorsk, Zhdanov, Karaganda, Novosibirsk. Kozlovsky E.I. Mineral and raw material problems of Russia on the eve of the 21st century. - M.: Nedra, 1999. - S. 98.
Mechanical engineering was most developed in the European part of the USSR. There are qualified labor resources, a wide network of design, design, research institutions, well-developed communication routes, and there is a great need for engineering products.
129. Using a map and statistical material, characterize one of the metallurgical bases according to the plan
-geographical position;
- share in metal production;
- sources of raw materials;
- sources of fuel.
Metal ores include ores of iron, manganese, chromium, aluminum, lead and zinc, copper, tin, gold, platinum, nickel, tungsten, molybdenum, etc. The size of their extraction and composition significantly affect the economy of individual countries, the development and location of industry.
Iron ores are the main raw material for the production of ferrous metals. The predicted world reserves of iron ore are estimated at 600-800 billion tons, and explored - at 260 billion tons. The average iron content in ore is 40%. Depending on the percentage of iron, ores are divided into rich and poor. Rich ores with an iron content above 45% are used without enrichment, while poor ones undergo preliminary enrichment. Iron ore resources are located in many developed and developing countries. Russia, Brazil, Australia, USA, Canada, China, India, France, Sweden stand out in terms of their reserves. Large deposits are also located in a number of other countries: Great Britain, Norway, Luxembourg, Venezuela, South Africa, Algeria, Liberia, Gabon, Angola, Mauritania, Ukraine, Kazakhstan, Azerbaijan. In Russia, the explored (balance) reserves of iron ore amount to 55.6 billion tons, with an average iron content in the ore of 35.9% - There are also rich ores containing from 50 to 69% iron. Iron ore reserves are sufficient to fully meet the country's domestic needs. More than half of the balance reserves of iron ores (31.9 billion tons) are concentrated in the basin of the Kursk Magnetic Anomaly (KMA), located in the center of European Russia (Belgorod, Kursk, Voronezh and Oryol regions). The Kursk magnetic anomaly, the largest iron ore basin in the world, is characterized not only by huge reserves, but also by high quality indicators of raw materials, favorable mining and geological conditions for its occurrence. The average iron content in KMA ores exceeds the average for Russia as a whole and is 41.5%, rich ores (hematites) contain 55-65% iron.
The ferruginous quartzites prevailing here (35% of iron in the ore) are easily enriched and occur close to the surface, which makes it possible to develop them. open way. Yakovlevskoye, Lebedinskoye, Stoilenskoye (in the Belgorod region) and Mikhailovskoye (in the Kursk region) stand out among the developed fields. Zheltikov V.P. Economical geography. Decree. ed. P.256.
Thus, KMA is one of the richest iron ore deposits in the world.
156. What are the main branches of the economy are formed in the economic regions that form Central Russia? Why?
In the center of the European part of the country, metallurgical enterprises have been created and are operating on the basis of KMA iron ore and Donetsk coal. They are located in Tula and Lipetsk. On the basis of KMA ores, the powerful Oskol Electrometallurgical Plant and the plant for hot metal briquetting in Gubkin operate.
The production of synthetic rubber originally arose on the basis of alcohol from food raw materials (grain and potatoes). The first factories were created in the Center. Now the main raw material is synthetic alcohol from petroleum products. Enterprises for the production of synthetic rubber operate in the Volga region, the Urals, Western Siberia, Transcaucasia.
The industry of chemical fibers is developing mainly in the European part of Russia. It focuses on areas provided with labor resources, with a developed textile industry. At the same time, the availability of sources of raw materials and energy, water is taken into account. Companies in this industry, like most chemical industries consume a lot of clean water,
The regions with the most developed chemical industry are the Center, the Volga region, the Urals, the Donbass, Belarus, and Transcaucasia. In each of them, based on the availability of types of raw materials, fuel, electricity, and the availability of labor resources, a complex of chemical industries has developed that differ in the structure of products produced on local or imported raw materials. Light industry includes industries that provide the population with fabrics, footwear, clothing, knitwear, fur products and other consumer goods. In accordance with this, the textile, leather and footwear and clothing industries are distinguished.
Since light industry is designed to provide the population with the necessary consumer goods, the material standard of living of the people largely depends on its development.
The Soviet Union had a highly developed light industry. In the production of cotton, woolen and linen fabrics, leather shoes, our country ranked first in the world.
Light industry developed in close contact with agriculture, which supplied raw materials for processing: cotton, linen, raw silk, wool, and leather. The close connection of light industry with agriculture was reflected in the influence on its geographical location. Recently, in the manufacture of fabrics, knitwear, shoes and other products, materials supplied by chemistry have been increasingly used: chemical fibers, artificial leather. This expanded and strengthened the raw material base of the industry, contributed to an increase in output. a wide range, reducing its cost. In terms of output in value terms, light industry was second only to mechanical engineering in terms of the number of employed workers.
The leading branch of light industry is textile. All types of fabrics are produced in Russia: cotton, woolen, linen and silk. In our country, as well as throughout the world, cotton fabrics are produced most of all. They differ good quality, low cost, are in great demand.
The process of manufacturing fabrics is divided into several stages: primary processing of raw materials, spinning, weaving, finishing (dyeing). All types of raw materials undergo primary processing. It is produced at flax mills, wool-washing and silk-winding factories, cotton gins. The product yield is approximately 1/5 - 1/3 of the weight of the feedstock. Therefore, the primary processing of raw materials is carried out in the places of its receipt. Cotton-cleaning plants are located in Central Asia, in the south of Kazakhstan and in Azerbaijan, wool-washing factories are in the North Caucasus, in Kazakhstan. The resulting products are pressed cotton fiber, washed wool can be transported over long distances. In the subsequent stages of processing, the waste is small. Therefore, enterprises for the production of fabrics, with the exception of linen, are more profitable to locate in areas of consumption.
The predominant part of the fabrics is produced by large textile mills, i.e. enterprises that combine the main stages technological process: spinning, weaving and finishing.
Despite the great changes that have taken place in the geography of the textile industry, the Center remains the leading area for the production of fabrics. It accounts for 66% of the output of cotton, about 50% of wool, silk and 60% of linen fabrics. Main centers: Moscow, Ivanovo, Kostroma, Kalinin, Orekhovo-Zuevo.
The food industry, processing agricultural raw materials, produces a variety of food products. This is the most widespread branch of industrial production. Its enterprises are available not only in urban, but also in many rural settlements. However, the level of development of the food industry is determined by large plants and factories, created in most cases in cities.
In terms of the number of employed industrial workers, the food industry follows machine building and light industry.
The complex structure of the food industry is determined by the diversity of raw materials. Agriculture supplies grain, potatoes, sugar beets, sunflowers, fruits, vegetables, tea leaves, meat, milk, etc. for industrial processing. The group of industries is based on the use of raw materials of plant origin. These are flour and cereals, starch, sugar, oil and fat, fruit and vegetable canning, tea, winemaking, and tobacco industries. Raw materials of animal origin are processed by enterprises of the meat, dairy, butter and cheese industries. Industries such as baking, pasta, confectionery, and the production of food concentrates use raw materials that have already undergone primary processing. And, finally, the salt and fish industries also stand out in the food industry.
Branches of the food industry, depending on the material intensity, gravitate mainly either to the areas of production of raw materials, or to areas of consumption. Where the cost of raw materials per unit of finished product is high and its transportation is associated with large losses and deterioration in quality, enterprises are located in areas where the corresponding branches of agriculture are developed. This applies, first of all, to the sugar, oil and fat, fruit and vegetable canning, wine-making industries. The sugar industry is best represented in Ukraine and the North Caucasus. The same regions, as well as the Volga region and the Chernozem Center, are distinguished by the production vegetable oil from sunflower seeds. There are large flour mills both in areas of developed grain farming and in the cities of the Center and West of the European part of the country. In areas of consumption, i.e. First of all, in large cities, densely populated industrial areas, enterprises are located for the production of the most important food products - bakery, dairy, meat products.
The food industry is a necessary link in the economy of any economic region. However, the set of industries in each region is mainly determined by the specialization of agriculture. Zheltikov V.P. Economical geography. Decree. ed. P.78.
Thus, such sectors of the economy as metallurgical, chemical, textile, food predominate in central Russia.
Literature
1. Zheltikov V.P. Economical geography. Ed. 3rd. - Rostov n / a, 2004. - 384 p.
2. Karlovich I.A. Geoecology: Textbook for higher education. - M.: Academ. Project: Alma - Mater, 2005. - 512 p.
3. Kozlovsky E.I. Mineral and raw material problems of Russia on the eve of the 21st century. - M.: Nedra, 1999. - 467 p.
4. Handbook of geography for applicants to universities / Ed. V.G. Zavriev. Mn.: Higher. school, 1978. - 304 p.
Hosted on Allbest.ru
Similar Documents
The process of formation of economic and social geography. Socio-economic geography, representing the social direction, as a subsystem of geographical sciences. A place Russian Federation on the world market and the geography of its foreign trade.
test, added 06/28/2012
Features of mechanical engineering as a branch of heavy industry. The specifics of engineering industries, product overview, geography of production locations. Factors of placement of mechanical engineering, share in total production, its environmental safety.
report, added 09/30/2009
Geography as a science about the laws of development of space-time systems (geosystems) on the earth's surface in the process of interaction between nature and society. Levels of organization of geographic material systems. Place geography with the system of modern culture.
test, added 03/25/2009
Characteristics of engineering industries by groups. Products manufactured by the heavy engineering industry. Sub-sectors that are part of the medium engineering industry. Leading branches of precision engineering. Directions of development of the sphere at the present stage.
presentation, added 09/21/2012
Geography and location factors of world mechanical engineering. The main branches of the modern machine-building complex on the example of general, transport engineering, electronics and electrical engineering. Machine-building complex of Latin America, Japan.
term paper, added 08/06/2010
Economic geography as a scientific direction, subject and methods of its research. Russia's position in modern world and the general direction of its development. Natural conditions and resources of the state, population and resettlement. Regional development and politics.
tutorial, added 03/11/2011
Composition of industries of the world economy, characteristics of fuel energy, mining, metallurgical industry, mechanical engineering and other industries. Geography of agriculture, fishery, transport. Labor resources and employment.
abstract, added 06/10/2010
Industry Composition, Location Factors and Industry Performance chemical industry Russian Federation. Contemporary Issues and prospects for the development of the chemical industry in the country. Production dynamics the most important types chemical products.
term paper, added 12/24/2010
Modern natural conditions on the earth's surface, their evolution and patterns of change. The main reason for the zonality of nature. Physical properties water surface. Sources of precipitation on land. Latitudinal geographic zonality.
abstract, added 06/04/2010
Subject, method and meaning of the course economic geography and nature management. System of geographical sciences of land description. Characteristics of the new independent states. Overview of the constituent entities of the Russian Federation, resource availability, population, economy.
The earth makes a full rotation around its axis 360 degrees in 24 hours (day). IN different places of the globe, located on different meridians, i.e. having different longitudes, at the same moment, the clock shows different times.
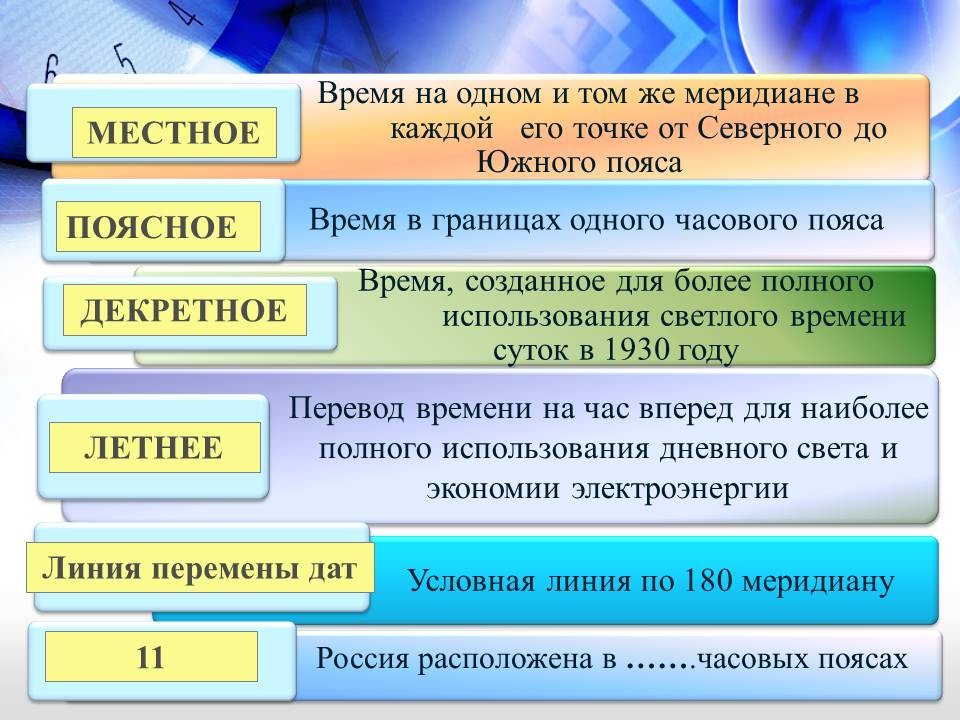
Solar time at points located on the same meridian is called local. To find out the difference in local time between two geographical objects, it is necessary to know the geographical longitude of these points. Multiply the difference between the longitudes by 4 minutes (since the time difference between neighboring ones is 4 minutes) and get the time difference. Since it is different at each specific moment of the day, even on neighboring meridians, it is inconvenient to use it. Therefore, according to the international agreement, standard time was introduced. To do this, the entire surface of the Earth is divided into 24 by 15 degrees of longitude in each.
From west to east, so at points located to the east, the time of day will be longer.
Time at points located within the same time zone is called zone time. Within each zone, the time is set according to the local time of the median meridian of this zone. For example: a zero belt is a belt whose median meridian is the zero meridian. The same belt is the 24th. From it, the belts are counted to the east. The difference in time between zones is equal to the difference between the numbers of time zones. For example: the time difference between the 2nd and 3rd zones (3 - 2 = 1) is 1 hour. The boundaries of time zones are not drawn strictly along the meridians, but take into account administrative boundaries.
It is located in 11 time zones - from the 2nd to the 12th, but the 11th and 12th zones are combined into one, so the time difference between the extreme western and eastern points our country is - 10 hours.
Examples of problem solving
Task #1
Determine the local time at , if it is 12 o'clock in Novosibirsk.
Solution:
Because the local time - solar time at points located on the same meridian, we determine the longitude of Vladivostok and .
Vladivostok - 132° E D., Novosibirsk - 83°E d.
Determine the difference between these settlements(in degrees) - 132° - 83° = 49°
Because 1° = 4 minutes, then 49 times 4 minutes = 196 minutes (3 hours, 16 minutes).
Because in Novosibirsk 12 hours, and Vladivostok is located to the east (which means that the day starts earlier there) 12 + 3 hours 16 minutes = 15 hours 16 minutes.
Task #2
Determine standard time in Murmansk, if it is 18 hours in Yakutsk.
Solution:
Determine where these cities are located. Murmansk - 2nd time zone, Yakutsk - 8;
Determine the difference in time zones - 8 - 2 = 6 time zones (each time zone is 1 hour difference);
If it is 18 hours in Yakutsk, Murmansk is located to the west, then there is less time - 18 - 6 = 12 hours.

























 Back forward
Back forward
Attention! The slide preview is for informational purposes only and may not represent the full extent of the presentation. If you are interested this work please download the full version.
Target: To study the position of Russia on the map of time zones and types of time in the country.
Tasks:
- educational- to form knowledge about standard, maternity and local time; define the concept of time zones.
- Educational- develop skills self search information - “date line”, to form skills and abilities to determine standard and local time; solve practical problems using a geographical map; develop the ability to apply existing knowledge and skills in everyday life.
- Educational- organization of mental activity of students, creative self-realization; creation of a positive microclimate, sincerity and openness of communication. Education of firmness of character, the ability to express one's point of view.
Planned result:
Subject:
- Ability to explain: the specifics of time calculation in Russia.
- Ability to identify: differences in time on the territory of Russia;
Metasubject:
- Search and selection necessary information, listen and objectively evaluate the other, be able to conduct a dialogue, developing a common solution.
Personal:
- Formation of a responsible attitude to learning, readiness for self-development; orientation in social roles and interpersonal relationships;
- Perform self-assessment of acquired knowledge.
LESSON TYPE: lesson of new knowledge
EQUIPMENT: presentation, fragments of educational films, Internet,
Physical and political-administrative maps of Russia, globe, atlas maps, textbook, reference notes, computer, interactive map.
METHODS AND TECHNIQUES OF WORK:
- Teacher's lecture followed by practical work of schoolchildren to consolidate the studied material (on a computer)
DURING THE CLASSES
I. Organizational moment. (Slide 1)
Slide 2. Introduction to the course of the lesson. (Introduction to the stages of the lesson, consisting of a prologue, main part and epilogue).
Our Motherland is great and beautiful. Its nature is varied. Huge plains, large areas of forests, amazingly beautiful mountains, rivers, lakes, minerals - all this is our country. "To love your country means to know it."
II. Checking homework. (Slide 3-4)
Thematic geographical dictation "Borders of Russia".
1 task. GEOGRAPHY IN FIGURES; EXTREME POINTS
1. 17.1 million km - the area of Russia
2. 16 - neighboring countries
3. 14 - land neighbors
4. 2 - sea neighbors
5. 12 miles (22.2 km) - territorial waters
6. 200 miles (370 km) - exclusive economic zone
7. 60.9 thousand km - the total length of the state border
8. 38.8 thousand km - the length of the sea borders
9. 7,200 km - the longest border with Kazakhstan
10. 85 - the number of subjects of the Russian Federation
slide 4. 2 task.(The guys should go out and make a “living” map of Russia. Pupils receive cards with the name of the seas washing the territory of the country.
Slide 5. 3 task. Oral dictation of eloquence.
My Russia has boundless expanses,
You won’t take a look, you won’t drive around soon.
Go to the mountains, walk through the plain -
All that you see is all my Russia.
Russia is a Great Power .... (Develop the topic)
slide 6 (Summarize)
Slide 6. III. Learning new material.
How big is my country
How wide is its space!
Lakes, rivers and fields
Forests, and steppe, and mountains...Spread my country
From north to south:
When spring is in one side,
In the other - snow and blizzard.In Moscow they go to bed now
The moon looks out the window.
Far East at the same time
Rise to greet the sun.
What is the topic of our lesson? (Time difference in Russia)
What is the reason for the time difference at the same time in our country? (Great stretch of country from west to east)
Slide 7 - Remember why there is a change of day and night on Earth.
The Earth rotates around its axis from west to east, that is, counterclockwise, if you look at the Earth from the North Star (from the North Pole). The rotation of the Earth is associated with a natural unit of time - a day and a change of day and night. (During the teacher's story, students fill out the reference notes)
A complete revolution (360 `) the Earth makes in a day, that is, in 24 hours. This means that in 1 hour the Earth rotates by 15`, since 360`: 24 = 15`. 1 hour is 60 minutes, 60 minutes: 15` = 4 minutes. Thus, in 4 minutes the Earth rotates by 1`.
Slide 8 types of time
Slide 9 local time
On different meridians at the same moment there is a carved time of day. This means that the day begins simultaneously on the entire meridian, each meridian has its own local time. Local time depends on geographic longitude. (Cities on the 40th meridian) Arkhangelsk-Vologda-Yaroslavl-Voronezh-Rostov-on-Don)
Slide 10 (Determining local time)
slide 11 standard time
It was proposed in 1878 by the Canadian engineer Sandford (Steve) Fleming, which in 1884 was adopted at the International Astronomical Congress in the USA (Washington), where 26 countries were present.
The entire surface of the globe was divided into 24 time zones of 15` each. Standard time is the local time of the middle meridian of each zone. The zero (it is also the twenty-fourth) belt is the one in the middle of which the zero meridian (Greenwich) passes. To the east of any zone, time increases, to the west it decreases. The boundaries of time zones do not always pass strictly along the meridians (Why?). They are carried out taking into account administrative boundaries, so that one or another administrative unit is in the same time zone.
In the middle of the twelfth belt, approximately along the 180` meridian, there is a date change line. This is a conditional line on the surface of the globe, on both sides of which hours and minutes coincide, and calendar dates are wrong by one day. For example, in New Year, at 0000 hours, west of this line on January 1st and eastward on December 31st of the old year. The meridian lies between the islands of Ratmanov (Russia) and Kruzenshtern (USA), but this is the invisible border separating “today” from “yesterday” and “tomorrow” from “today”.
Slide 12 - In our country, on February 8, 1919, standard time was introduced and 11 time zones were established throughout the territory (from II to XII inclusive). The boundaries of the state of emergency have changed several times.
The position of Russia in many time zones has certain advantages and disadvantages.
1. It is positive that night hours in different regions do not coincide in time. This time difference is used in the electric power industry to transfer excess electricity from one region to another, which results in great energy and cost savings.
2. The main inconvenience is that during the flights of residents from the European part to the Far East, the biological rhythm is disturbed.
slide 13 Daylight saving time
In fact, the time difference between Moscow and, for example, Berlin or Paris is not one, but two hours. This is due to the fact that throughout Russia there is maternity time, which differs by one hour from the zone. In 1930, by a decree (decree) of the government, the hands of the clock were moved one hour ahead of standard time. This was done in order to make fuller use of daylight hours, and therefore in order to save electricity. Decree time of the II time zone, where Moscow is located, is called Moscow time. (What time, taking into account the maternity leave, will it be in London when it is 9 hours in Kazan. Answer: 6 hours)
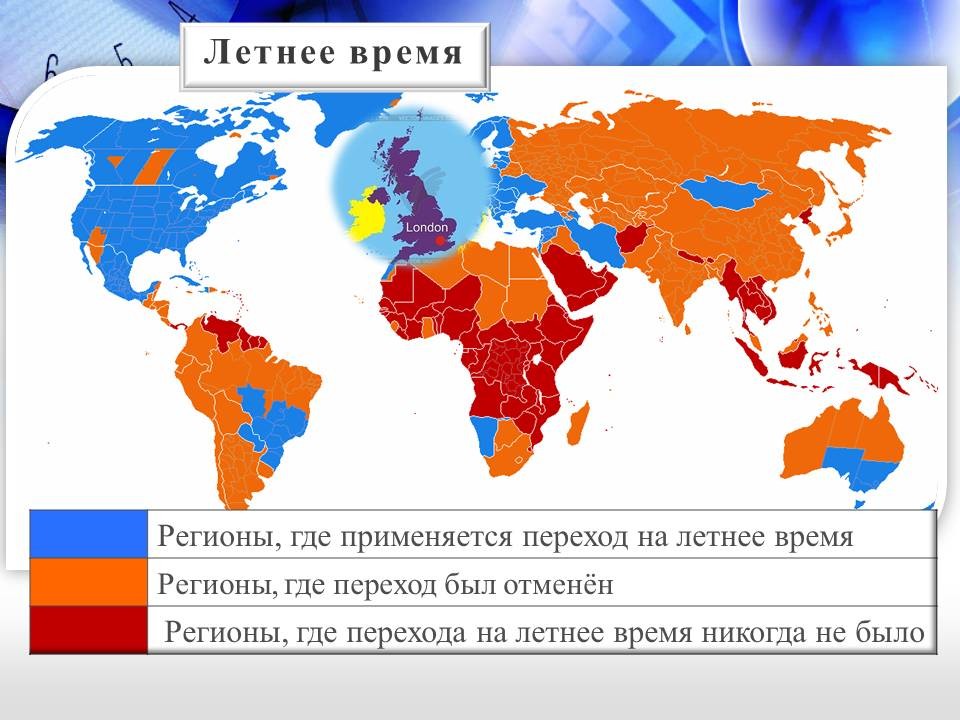
Slide 14 - Summer time in the countries of the world
Daylight saving time was “invented” in the UK in order to save energy and introduced in 1908. The clock for the summer period was moved forward 1 hour. Since then, many countries began to use a similar order of time calculation. In Europe, this time is called summer time, and in America it is called advanced time.
Slide 15 - Summer time in Russia.
Since 1981, summer time has been in effect in Russia from March to September. On the last Sunday in March, the clocks were set one more hour ahead of standard time. Since 2008, the return to daylight savings time has usually taken place on the last Saturday in October by turning the clock back one hour. Since October 2011, translation into winter time was not carried out.
However, studies soon showed that the Russians would like to return the clock to winter time. Russian President Vladimir Putin signed a law on the transition of Russia from October 26, 2014 to winter time and in the future the seasonal switchover will not be carried out.
Slide 16-21 IV. Solution of practical problems.
1. Using the map “Time zones of Russia”, determine what time it will be in Kazan (II time zone) when it is noon in Yakutsk (VIII time zone).
1. Determine the difference in time zones. 8 - 2 = 6
2. If it is 12 hours in Yakutsk, then Kazan is located to the west.
(If the city is located to the west, then we subtract the difference)
12 – 6 = 8 am
2. Using the map “Time zones of Russia”, determine what time it will be in Krasnoyarsk (VI time zone) when it is 14 hours in Kazan (II time zone).
1. Determine the difference in time zones. 6 - 2 = 4
2. If it is 14 hours in Kazan, then Krasnoyarsk is located to the east.
(If the city is located to the east, then we add the difference)
3. 14 +4 = 18 hours
4. The plane took off from Anadyr (11 hour zone) to Moscow (2 hour zone) at 15.00 Moscow time. Estimated flight time 9 hours. Determine the time of arrival of the aircraft in Moscow.
15 - 9 = 6 hours was in Moscow when the plane took off.
6 + 9 = 15 hours
In Moscow - 15.00 hours.
5. The plane took off from Voronezh (II time zone) to Orenburg (IV time zone) at 9:00 Moscow time. Estimated flight time is 2 hours. Use the Time Zones of Russia map to determine what time it will be in Orenburg when the plane lands.
9 + 2 = 11 hours was in Orenburg when the plane took off.
11 + 2 = 13 hours
In Orenburg - 13.00 hours.
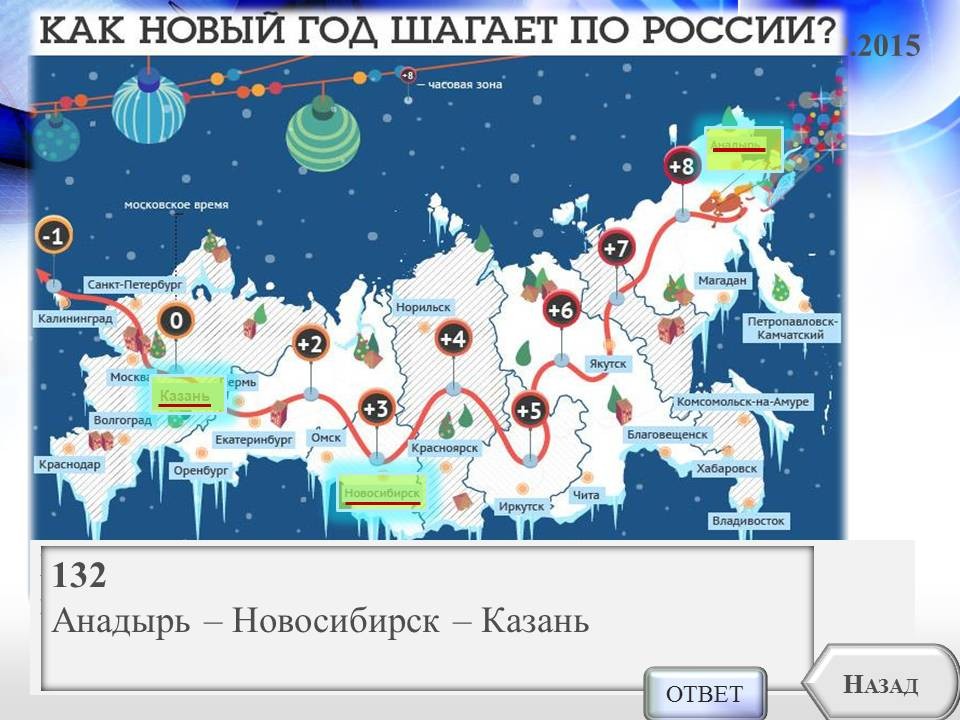
6. (OGE - grade 9) Arrange the cities of Russia in the order in which their inhabitants celebrate the New Year.
1) Anadyr 2) Kazan 3) Novosibirsk
132 Anadyr - Novosibirsk - Kazan
7. How much time, taking into account maternity leave, will it be in London when it is 9 o'clock in Kazan.
Slide 25 V. Summing up the lesson
1. Do you believe that at each moment of the day the same time happens only at points located on the same meridian.
2. Do you believe that the boundaries of time zones are strictly along the meridians?
3. Do you believe that it is convenient to use local time?
4. Do you believe that standard time is time within the same time zone?
5. Do you believe that when drawing the boundaries of time zones, the administrative division of the country is taken into account?
6. Do you believe that within the belt we agreed to count time along the meridian that lies in the middle.
7. Do you believe that confusion can arise when using standard time?
Homework: paragraph 9, questions and tasks on page 42. In the basic summary of the task.
A task. If the New Year has come in Moscow (00 hours 00 minutes), is it already possible to celebrate it at the North Pole?
slide 26 VI. Reflection “Ladder of Success in the Lesson”
“The clock measures our work and sleep,
Define meetings and partings.
For us, hours are calm, measured ringing -
Either peaceful or combat sounds.
A silent night reigns over the world.
Little by little the pavement is empty.
And only time speaks to us
Beating his clock on the tower ”
Time zones, standard and local time
Solar time at points located on the same meridian is called local. Due to the fact that at each moment of the day it is different on all meridians, it is inconvenient to use it. Therefore, according to the international agreement, standard time was introduced. To do this, the entire surface of the Earth was divided along the meridians into 24 zones of 15 ° longitude. Standard time (the same within each zone) is the local time of the median meridian of this zone. The zero belt is a belt whose median meridian is the Greenwich (zero) meridian. The same belt is the 24th. From it, the belts are counted to the east. Russia is located in 11 time zones: from the second (in which Moscow is located and whose time is called Moscow) to the twelfth (islands in the Bering Strait). The time difference between these zones is 10 hours, i.e. when it is midnight in Moscow, in the 12th time zone it is 10 am. The difference in time between zones is equal to the difference between the numbers of time zones. For convenience, the 11th and 12th time zones have been combined into one. The boundaries of time zones do not run strictly along the meridians, but coincide with the boundaries of administrative units (regions, republics) so that one administrative unit is located in one time zone.






