Natural ventilation in the apartment. When is forced ventilation necessary in an apartment?
Apartments in high-rise buildings are connected to a common ventilation system, which ensures the removal of exhaust air masses into environment through the exhaust duct.
Such a structure of the ventilation system is very effective, but only when we are talking about new buildings. At the same time, over time, its functionality decreases and leads to disruption of the microclimate in the building. Forced ventilation in an apartment is a way out of this situation and allows not only to create the most comfortable conditions for people’s lives, but also to save them from many problems.
Air flows and types of forced ventilation systems
Most residential apartment buildings equipped with ventilation systems natural type. It consists of several exhaust air ducts connected to a single outlet channel, which runs along the riser. Windows, doors, vents and balconies serve as supply channels, i.e. all objects through which air can freely flow into the apartment.
Such an air exchange system is quite effective and ensures the creation of optimal conditions for people’s lives. However, over time, its functionality gradually decreases, which can lead to disruption of the microclimate in the apartment. The main reason The effectiveness of the system is reduced by insufficient maintenance of communications, which leads to their filling with debris and a decrease in diameter.

Typical scheme for organizing natural exhaust in apartments
The consequences of disturbances in the distribution of air masses in an apartment are varied, ranging from the development of mold to the appearance of various insects. A good ventilation system in the apartment, designed to eliminate excess humidity and normalize air exchange.
The principle of operation of forced ventilation is based on the use of various mechanisms that enhance the air flow and ensure its cleaning. Today, there are several types of similar systems that allow you to normalize the ratio of humidity and thermal parameters inside the apartment. They look like this:
- exhaust;
- supply;
The above models are able to fully satisfy the needs of the room for fresh air and ensure complete removal of waste materials.
Calculation of parameters and their influence on the selection of system components
The choice of one type of system or another is made based on the degree of functionality of the existing ventilation system. In most cases, it is this criterion that plays a fundamental role. However, when calculating the parameters of forced ventilation, it is necessary to take into account other factors that influence the aeration of the apartment:
- room area;
- level of tightness of windows, doors and balconies;
- existing air flows;
- location of supply and exhaust openings.
All these criteria must be taken into account when choosing a ventilation system model. However, the air exchange parameters specified in the technical documentation have different values for residential and utility premises, which should not be forgotten.
The bedroom and living room should be provided with 3 cubic meters. fresh air per 1 sq.m. area. Wherein forced ventilation in the bathroom and toilet is calculated based on the requirements of 25 cubic meters / hour. regardless of the square footage of the premises.
Compliance with SNiP requirements makes it possible to create optimal conditions in the apartment and completely normalize the microclimate. In addition, based on the speed of movement of air masses and their volume, the main parameters of the system are selected, such as the cross-section of air ducts, the power and number of fans, as well as the feasibility of installing additional equipment.
Forced exhaust ventilation and its features
Installing a forced exhaust ventilation system is advisable in the case when the supply air enters normally, but the exhaust mass is not removed in full. As a rule, the reason for this is clogged ventilation ducts that are unable to fully perform their functions. As a result of circulation disruption, air masses stagnate, warm air accumulates under the ceiling and contributes to the appearance of dampness. Moreover, due to excess pressure inside the apartment Fresh air is forced back out into the street through the supply channels or does not enter at all.
To stabilize circulation and normalize the microclimate, the principle of forced exhaust ventilation is used. It is based on the use of several fans, which are installed at the entrance inside the exhaust ducts, providing the necessary draft. As a rule, they are installed on existing ventilation holes located in the kitchen or bathroom and connected to a common duct.
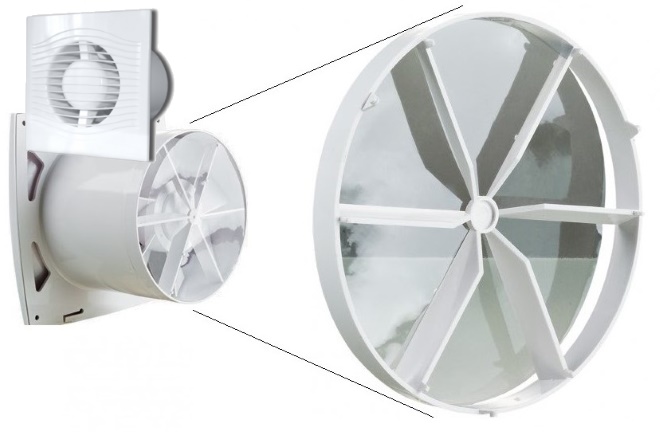

Exhaust fan with check valve
In the case when the main exhaust air duct is completely clogged and does not function, holes are created directly in the walls and are led both into the entrance and to the street. This arrangement of additional channels allows for normal distribution of air flows and an optimal microclimate inside the apartment. The power of fans and their number are selected based on the existing conditions inside the room and the design parameters obtained initially.
Supply and supply and exhaust ventilation models
Installation supply ventilation It is advisable in diametrically opposite conditions, when oxygen access is limited, but the hood is fully functioning. This situation is also not uncommon and occurs quite often. The reason for this is new metal-plastic windows and doors that provide 100% sealing of the room. As a result, cold air cannot fully enter the apartment, which is extremely important from the point of view of energy efficiency, but is absolutely not advisable in relation to ventilation.
To increase the circulation of air masses, supply fans are used, the installation of which requires the creation of special through holes that go directly to the street. They are equipped with a special supply valve or fan, which increases the speed and volume of incoming air, and on the other side, special blinds are installed that allow these parameters to be adjusted.

The supply and exhaust forced ventilation system in the apartment is installed when general violation air flow distribution. Sometimes it is used to improve functionality existing system who fails to fulfill her responsibilities. However, in most cases, this model involves the creation of new channels intended for the installation of mechanical equipment, and the complete blocking of old inactive holes.
Additional components and their purpose
The apartment's forced ventilation system may include some additional components, in addition to the necessary fans and ductwork. Their inclusion in general scheme makes it possible to improve air quality and provide the most comfortable living conditions. Their list is as follows:
- Ventilation grilles that protect the ducts from the penetration of rodents or the accumulation of dust. Typically they are installed with outside air ducts and also perform a decorative function.
- Valves or louvers provide regulation of speed and volume supply air, and if necessary, they can block them altogether.
- Air heaters organize heating of supply air in winter.
- Sound absorbers eliminate all extraneous noise that comes from the street or appears due to the operation of fans and other mechanisms.
- Aerofilters prevent any small debris, dust and plant pollen from entering the apartment.
- A control unit that controls the functioning of the entire system, turning on or off certain parts of it. It works completely in automatic mode based on specified parameters and requires the constant presence of electric current.
The installation of all these devices does not at all affect the functionality of the ventilation system in the apartment, providing additional comfort for its residents. Their installation is carried out solely as a modernization and only helps to improve air quality, but does not in any way affect its mobility.
Conclusion
Using a forced ventilation model is advisable when natural system does not cope with the functions assigned to it. Poor air exchange in the apartment may be caused by blockage of the exhaust duct or high tightness of windows and doors. The type of forced ventilation is selected based on the available parameters and according to the requirements technical documents. At the same time, the installation of such systems makes it possible to optimize the distribution of flows and completely eliminate all negative factors associated with air stagnation.
Proper ventilation in an apartment (house) allows you to create an optimal microclimate and ensure the safety of structures. The basic rules for organizing air exchange and common mistakes are discussed in detail in this review.
A little theory
Ventilation is an organized exchange of air created to remove excess heat, moisture and other substances that accumulate in rooms. This process is necessary to protect and preserve structures, create an optimal microclimate and air quality.
Air characteristics that provide physiological comfort during prolonged and systematic exposure are considered optimal for humans. Typically this is:
- Air temperature - from 21 to 25 °C.
- Relative humidity - from 40 to 60%.
- Air movement speed is no more than 0.2 - 0.3 m/s.
- The gas composition of the air is close to natural (75.5% nitrogen, 23.1% oxygen, 1.4% inert gases).
Types of ventilation:
- Natural - the most common type of air exchange due to the difference in density warm air indoors and colder outside. This type of ventilation is simple to design and operate.
- Forced (mechanical) - provided using fans. It can be supply, exhaust or supply and exhaust.
- Mixed - a combination of forced and natural air exchange.
The recommended air exchange rate is determined based on the number of people living, the area of the premises and the type of ventilation. For natural ventilation in rooms where there is at least 20 m² of living space per person, an air flow rate of at least 30 m³ per hour is recommended. General rule- at least 3 m³ of air per hour for each square meter living space.
Ventilation device in a house or apartment
More often, mixed ventilation is used in houses and apartments with periodic use of forced exhaust ventilation in places of high humidity.
Natural air flow is ensured by ventilation through open windows and doors and infiltration through cracks and leaks in enclosing structures.
Modern construction technologies reduce the formation of cracks and other natural places air penetration inside. In particular, this applies. Such buildings require special attention:
- Applications of slot valves in the upper part of window frames.
- Applications of conventional air infiltration valves in external walls.
- Installation of mechanical filters providing both passive and forced air flow. At the same time, it also allows for cleaning and changing the temperature of the incoming flow.
To remove air when there is no duct ventilation use windows, vents and transoms. Air removal occurs either due to the difference in air density inside and outside the building, or due to the difference in pressure on the windward and leeward sides. This type of air exchange is the most imperfect.
A more successful scheme is the use of vertical exhaust ventilation ducts located inside the walls or in attached blocks. To prevent freezing, ventilation ducts passing through cold attic spaces, it is necessary to insulate. And to enhance traction, equip the exits with deflectors.
Options for organizing ventilation in premises:
 |
|
| A) Basic system mixed ventilation with periodically turned on exhaust fans in air pollution areas. | b) Passive channel exhaust ventilation. |
| c) Forced duct exhaust ventilation. | d) Forced channel supply and exhaust ventilation with recovery. |
| 1 - 2 cm gap under the door. | |
| 2 - exhaust fans with air duct outlet through the wall. | |
| 3 - channels with a diameter of at least 125 mm. | |
| 4 - slope no more than 30°. | |
| 5-channel exhaust fan. | |
| 6 - supply and exhaust ventilation system with heat recovery. | |
Reception openings for removing natural exhaust ventilation air from the upper zones of the room are placed under the ceiling no lower than 0.4 m from the ceiling and at the same time no lower than 2 m from the floor to the bottom of the openings. This allows you to remove only warm, polluted air from an area located above human height.
In houses with stoves and fireplaces, separate channels are laid to heating devices, which allows you to avoid a lack of air in the combustion zone, the occurrence of reverse thrust, reducing oxygen concentration.
Features of ventilation in houses with stoves and fireplaces:
| The use of passive or forced exhaust in the absence of balanced supply ventilation can lead to backdraft and combustion products being thrown into the room. |
 |
| 1 - air infiltration valve or window in the room adjacent to the steam room. |
| 2 - forced exhaust to remove hot air. |
| 3 - valve in the steam room to ensure 5 - 8 air changes per hour. |
| 4 - separate supply channel for sauna stove. |
| 5 - sauna stove. |
| 6 - adjustable air intake for passive exhaust under the upper shelves in the corner opposite from the stove. |
| 7 - additional air flow through a 3-centimeter gap under the door to the steam room. |
| 8 - stove or fireplace. |
| 9 - separate supply channel for the furnace. |
| 10 - forced supply ventilation. |
A mechanical exhaust system must be installed in places where contaminated air accumulates (above kitchen stove), in places with excessive humidity (bathrooms, saunas, swimming pools). Also, forced ventilation is indispensable when low temperatures and in cases where the air circulation in the house is less than five volumes of the space in question per hour.
 |
|
| a) Ventilation in houses with basements that have free air exchange with the living space is organized as in an ordinary multi-story building. | b) Ventilation in the basement, separated from the living space, is organized as in a separate one-story building. |
| c) Ventilation in crawl spaces and basements of houses with open ground in radon hazardous areas. | d) Ventilation in crawl spaces and basements of houses with slabs on the ground in radon-hazardous areas. |
| 1 - soil insulation and building structures PVC film or waterproofing. | |
| 2 - perforated air intake pipe. | |
| 3 - permanently open vents (Smin = 0.05 m²) with a total area of 1/100 - 1/150 of the basement area. | |
| 4 - constantly running supply ventilation. It creates air pressure inside the room to prevent radon infiltration. | |
| 5 - constantly running exhaust fan. | |
| 6 - gravel (crushed stone). | |
Errors when installing ventilation in apartments and houses
- Complete lack of ventilation system. Banal savings and relying on regular ventilation through the windows will not solve all problems. Everything must be planned and justified. In rooms without windows, ventilation is required.
- No air flow. In modern houses with a continuous contour of heat and vapor barrier, there are no random sources of air circulation. Separate supply channels are also needed for normal operation stoves and fireplaces. At the same time, air must be supplied from the street, and not from underground. This is due to the possibility of the formation of radioactive soil gases in the space under the floor. If a separate channel for furnaces is not provided, then the installation of mechanical supply ventilation will be required.
- Interior doors are installed without gaps (grids) at the bottom. When organizing natural ventilation, less polluted air moves from sources of infiltration or open windows and doors through all rooms to the duct exhaust system. For free air movement, gaps under the doors (S = 80 cm²) and grilles on the doors to the bathrooms (S = 200 cm²) are required.
- Air communication with stairwells or adjacent rooms. Through unsealed channels for the passage of pipes, communications, through sockets and keyholes Polluted air enters the apartment from stairwells or neighboring apartments.
- Installation of ventilation ducts on external walls and their passage through unheated rooms without insulation. As a result of channel cooling, draft deteriorates, and internal surfaces condensation forms. If the air ducts are located at outer wall
- , then an air or insulated gap of at least 50 mm must be left between the latter and the air duct. Two or more exhaust ducts in remote areas of the house.
- This reduces the efficiency of air exchange. The presence of horizontal sections of air ducts.
- Such areas require the installation of additional fans. Connecting the hood above the stove to the exhaust duct ventilation with sealing the hole.
- As a result, air extraction from the kitchen stops. The hood must be connected while maintaining the supply grille of the exhaust duct with a non-return valve installed to prevent exhaust air from blowing back into the kitchen. Removing air from bathrooms not through a vertical duct, but through the wall to the street.
- In cold weather, air may not be removed through the through channel, but, on the contrary, may enter the bathroom. When using an exhaust fan in the same way, its blades may freeze. Common ventilation duct for two adjacent rooms.
- With this approach, the air may not be vented outside, but mixed between these rooms. Common ventilation duct for rooms on different floors.
- This contributes to the transfer of polluted air from the lower floor to the upper one. Lack of a separate channel for rooms on the top floor.
- This leads to increased humidity, temperature and air pollution. Lack of a separate channel for the rooms on the lower floor.
- Polluted air from the lower floor rises to the upper floor, preventing the flow of fresh air from outside. Lack of exhaust duct in rooms without windows.
- This leads to air stagnation. Conclusion ventilation duct to the attic.
- Leads to deterioration of air exchange and humidification of under-roof structures. Laying air ducts from technical rooms through living rooms.
- In this case, polluted air may leak into the residential part of the house. These rooms are places of high humidity and concentration of soil gases. In radon-hazardous areas (Radon is a radiogenic gas that is continuously formed in rocks during the radioactive decay of the uranium-radium series), exhaust ventilation from basements must be isolated from other ducts of the house.
- Lack or insufficient air circulation in cold underground areas. Vents should be provided in the outer walls of basements and technical underground areas that do not have exhaust hoods. with total area not 1/400 of the floor area. The area of one such hole must be at least 0.05 m². In radon-hazardous areas, the total area of vents should be at least 1/100 - 1/150 of the basement area.
- Absent or insufficient ventilation of baths and saunas. For an optimal microclimate in such rooms, an air exchange of 5 - 8 volumes per hour should be organized. Air is supplied through a separate supply channel under the stove or heater. Air is removed through an air duct located in the opposite corner of the steam room.
- No or insufficient attic ventilation. In the roof with a cold attic inner space must be ventilated with outside air through special openings in the walls. Their cross-sectional area at continuous pitched roof must be at least 1/1000 of the overlap area.
Errors in ventilation devices in living quarters and bathrooms:
| WRONG | RIGHT |
| 1) Almost airtight windows. | 1) Air infiltration valve or slot valves in windows. |
| 2) Condensation. | |
| 3) No ventilation gap under interior doors. | 2) Air gap or grid S = 80 cm². |
| 4) Cold air comes in when the fan is off. | 3) Passive duct hood with a fan that turns on at high humidity. |
| 5) Condensation. | 4) Air gap or grille S = 80 cm². |
| 6) Exhaust hood through the wall to the street. | |
| 7) There is no ventilation gap or grille. | |
| WRONG | RIGHT |
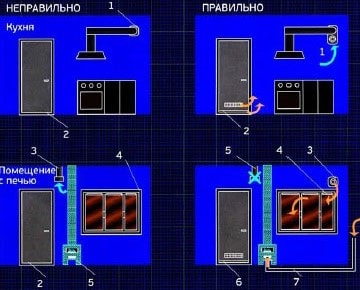 |
|
| 1) Connecting a hood instead of installing exhaust ventilation. | 1) Exhaust into a separate ventilation duct. |
| 2) Lack of ventilation gap under the doors. | 2) Air gap (grill) S = 200 cm². |
| 3) Exhaust duct ventilation. | 3) Supply ventilation during oven operation. |
| 4) Almost airtight windows. | 4) Slot valves in windows. |
| 5) There is no exhaust ventilation. | |
| 5) Lack of supply air duct for the furnace (supply ventilation of the room). | 6) Air gap (grid) S = 200 cm². |
| 7) Supply air duct stoves or forced ventilation of the room. | |
Thus, the design and installation of ventilation in an apartment or house can be done independently. The main thing is to figure it out, understand the essence of the process and not allow typical mistakes, discussed in detail in this material.
Exhaust vents in the apartment are located in rooms with high humidity and dirty air. Usually this is the bathroom and kitchen. Remember the ventilation grilles over the sink or stove? These are the exhaust holes.
Take a strip of newsprint and hold it to ventilation grille at a distance of 1-2 cm. If the newspaper sticks to the grill, it means it’s working natural ventilation. If the newspaper remains motionless or deviates slightly, then it is worth installing exhaust domestic fans to the apartment. Otherwise unpleasant odors and dampness will linger in the rooms.
As exhaust fans For bathrooms, wall fans are usually used. They are easy to install: you just need to remove the grille and replace it with a fan of a suitable diameter. It will push air through the channel and ensure uninterrupted operation of exhaust ventilation.
When choosing forced ventilation for a bathroom, you need to focus on the following parameters:
- The fan capacity should be 90-120 m3/h. You can read more about air exchange standards in an apartment.
- The fan must be waterproof. The bathroom is damp - electrical appliance with poor insulation can become a serious problem.
- Often the fan is connected to the light in the bathroom: when the light turns on, it turns on, and vice versa. This is not enough for normal air exchange. It is better to buy forced ventilation with a timer - it is more expensive, but it does the job.
- It would be a good bonus check valve. It will prevent air from the exhaust duct from getting back into the apartment. And this is possible, for example, if your neighbor also installed an exhaust fan, but it is much more powerful than yours. In this case, its fan will simply push air through the hood anywhere, including into your apartment.
You can also install a wall-mounted exhaust fan in the kitchen. But still, more often than not, a special kitchen hood-umbrella is hung above the stove.

This hood is much more complex than a conventional fan. It has so many functions and features that it would be enough for a separate article. Here we note only the most important points:
- The kitchen hood should constantly work in the background and switch to a more intense mode during cooking. If you turn it on only during cooking, then the rest of the time the hood will stick out like a plug in the ventilation duct.
- Background performance kitchen hood should be 60 m3/h if in the kitchen electric stove, and 90 m3/h if gas.
- The maximum extraction capacity according to the standards should be 180 m3/h. A weaker hood may not cope with the smell of burnt cutlets.
There are no particular difficulties in installing a kitchen hood, but it is still an expensive device (the price of forced ventilation for a kitchen is about 5,000 - 15,000 rubles), so it is better not to experiment with its installation. Specialist installers will do everything better. They will also provide a guarantee.
Let us summarize the information about forced exhaust ventilation:
Problem: the hood doesn't work, the bathroom is damp and smells, the kitchen is also damp and smells.
Optimal solution: a domestic exhaust fan for the bathroom and an umbrella hood for the kitchen.
Ventilation in an apartment is included in the design during the construction of apartment buildings. It works as follows: polluted air is removed from the rooms with the most pollution: kitchens, bathrooms and toilets through exhaust vents - high-quality ventilation in the apartment is simply necessary. The main thing you should take care of before ventilating your apartment is the amount of inflow. Professional installation ventilation in the apartment always has preliminary calculations the amount of air flow. It should be large enough to be enough for the life of the inhabitants, and at the same time not exceed the volume that can be heated by the heating system.
This is the standard ventilation system in an apartment, which today is insufficient. When necessary additional installation ventilation and air conditioning systems in the apartment? Firstly, if the owners replaced the old windows with double-glazed windows. Plastic windows are sealed and do not provide additional air flow for which the system is designed. Secondly, work requires additional air volume from domestic ventilation large quantities household and computer equipment. All these units absorb oxygen during operation, heat up and, accordingly, heat the air in the room. In these cases, it is necessary to install additional supply ventilation. We should not forget that sanitary standards, according to which houses were built twenty to thirty years ago, are designed only for the average number of family members in an apartment - therefore, without household systems ventilation is difficult to imagine modern comfort in large apartments.
Today the following types of ventilation systems are used:
- Natural ventilation;
- Supply and exhaust ventilation;
- Supply and exhaust system with heat recovery.
Let's look at each type in more detail.
Natural ventilation is the most economical solution. It includes supply valves, exhaust ducts, which can be additionally equipped with temporary fans to increase air circulation or silent exhaust fans with dampers that allow you to regulate air exchange. Supply valves can be installed in external walls buildings are either already built into frames plastic windows. Thus, during ventilation, air flows by gravity into the living spaces. Equipment supply valves antioxidant, noise-insulating materials and mosquito nets help solve the problem of dust, external sounds and insects entering the house.
 Supply and exhaust ventilation implies the use of a monoblock or stacked supply unit. It provides fresh air, which is distributed throughout the rooms through a system of air ducts and diffusers installed in the walls of the rooms. Using an electric or water heater allows you to heat the incoming air to desired temperature. The exhaust air outflow is provided by the system duct air ducts. To improve efficiency, this system can be equipped with duct exhaust fans or a roof exhaust unit.
Supply and exhaust ventilation implies the use of a monoblock or stacked supply unit. It provides fresh air, which is distributed throughout the rooms through a system of air ducts and diffusers installed in the walls of the rooms. Using an electric or water heater allows you to heat the incoming air to desired temperature. The exhaust air outflow is provided by the system duct air ducts. To improve efficiency, this system can be equipped with duct exhaust fans or a roof exhaust unit.
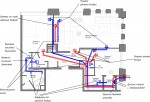
Supply and exhaust ventilation with heat recovery uses modern energy-saving technologies and is the most effective solution. It functions as follows: Supply unit blows fresh air, which passes through the heat exchanger. In the heat exchanger outside air it is heated by using the heat of exhaust air, and enters the air duct system, from which it is distributed throughout the premises. Exhaust air is removed using exhaust fans (roof or duct). The use of recovery allows you to save up to 40% of space heating costs.






