General information about elevators. Main parameters of loaders and stackers
To perform work on the movement and warehousing of goods in conditions warehouse or platforms the most common self-propelled mechanisms are forklifts. These devices allow you to move goods over long distances and to store goods due to the ability to lift goods to a certain height.
Loader designs a large number of. The market for this special equipment is quite extensive, so there is always an opportunity that will best meet the required working conditions. The main criterion when choosing is the load capacity of forklifts. According to this parameter, forklifts are divided into 4 classes: small, medium, above average and heavy.
In the conditions of a warehouse, the most common is a forklift, the carrying capacity of which is 1-4 tons, that is, small class loaders.
Center of gravity position and rated load
When selecting forklifts, you need to take into account several criteria for carrying capacity. The first criterion by which the choice is made is the position of the center of gravity of the transported goods. This criterion is the distance from the front of the fork horizontally to the center of gravity of the load itself. Without calculating the position of the center of gravity, it will be difficult to choose the right loader. The nominal position of the center of gravity for small loaders is a distance of 500-600 mm. For example, let's take loaders of the most common brands Toyota model 8FD20 and Linde model H20D. Both of these loaders belong to the small class with a load capacity of 2.0 tons. So, for these loaders, the distance from the center of gravity of the load to the fork wall is 500 mm.
The next selection criterion is the rated capacity of the forklift trucks. Rated load capacity is the weight of the load set by the manufacturer with a given position of the center of gravity and the height to which the loader is able to lift this load.
Rated lifting capacity for the mentioned trucks with standard lifting mechanism is 2.0 tons. But the height of the load they lift is somewhat different. The Toyota standard lift loader is capable of lifting 3.0 m. The Linde loader has a rated lift of 3.1 m.
Maximum load capacity
In addition to the concept of “nominal load capacity of forklifts”, there is also the concept of “maximum load capacity”. The maximum load capacity is the weight of the load, with the center of gravity set, that the forklift can lift as high as possible. This criterion should also be taken into account, since instead of a standard hoist, masts can be installed on the loader with a reach that is much larger than that of a standard hoist. For example, the Toyota 8FD20 loader can be equipped with a mast with a maximum reach of 7.0 m. The Linde H20D has the same maximum reach. But it should be borne in mind that the lifting height affects the load capacity. The higher you need to lift the load, the less it can lift the weight of the load. The Linde model H20D can lift a load up to 7.0 m and weighing around 600 kg. The loader from Toyota has the same load-bearing indicator for this height. This criterion is specified in the manufacturer's recommendations, the weight of the load is limited, and attempts to lift heavier loads may cause the truck to tip over.

The maximum load capacity is directly affected by the lift height, the lower it is, the more weight the loader can lift. These forklifts can lift a nominal weight of 2.0 tons to a maximum height of 5 m. In order to be able to lift the load to a greater height, it will be necessary to reduce the weight of the load.
| Engineering Communication | 34 | |
| Equipment, tools, machines | 172 | |
| Other | 106 | |
| Construction, reconstruction, repair | 212 | |
| Technical security equipment | 8 | |
| Construction management | 11 | |
| Energy efficient and environmental technologies | 8 |
 One of the main characteristics when choosing a loader is its rated load capacity. On what it depends, and will be discussed further.
One of the main characteristics when choosing a loader is its rated load capacity. On what it depends, and will be discussed further. The rated load capacity is understood as the maximum weight of the load, which forklift capable of lifting according to the ratio of the center of gravity to the load. The center of gravity is the only point of the load, relative to which the machine will be balanced in all directions, and the height of the lift. When choosing the load capacity of a forklift, it is important to consider the following characteristics:
Cargo weight,
cargo dimensions;
DH location;
lift height.
This relationship is indicated in a special catalog, which is attached to each individual model.
Loader Attachment Changes CG
Very often, attachments are used on loaders to expand its functionality. It can be a variety of grabs, load stabilizers, pushers, buckets and much more. In this case, the calculation of the residual capacity must be carried out taking into account the weight, overall dimensions and center of gravity of the optional accessories.Another factor that should not be overlooked when determining the load capacity is the specification of the racking equipment that is used in the warehouse where the loading equipment is supposed to be operated.
Very often, buyers make mistakes if euro pallets are actively used in warehouses. The width of such racks - without flooring is 1200 mm. Pallet sizes - 800x1200 and 1000x1200. In this case, one load will have two different centers of gravity, depending on whether it is on the long or short side on the forks of the loader. Therefore, the residual load capacity will be different.
| |
|
||||||||||||||||||||
General information about elevators
TO Category:
Elevator operation
General information about elevators
1. What is called an elevator?
An elevator is a discontinuous hoist, the cabin or platform of which moves along fixed vertical rigid guides installed in a shaft equipped with lockable doors on landing (loading) platforms (GOST 23748-79).
2. How are elevators divided by purpose?
By appointment, elevators are divided into:
a) passenger;
b) cargo and passenger;
c) sick leave;
d) trucks with a conductor;
e) trucks without a conductor;
e) cargo small.
Passenger elevators are used to transport people, move household goods. Passenger-and-freight elevators are designed to transport goods and people. These elevators differ from passenger elevators in the increased size of the cabins. Hospital elevators are used to transport patients to hospitals. vehicles with accompanying staff. Freight elevators with a conductor are designed to transport cargo and persons accompanying it. On freight elevators without a conductor, only goods are transported. Small freight elevators are freight elevators without a conductor, with a carrying capacity of up to 160 kg inclusive, with a cabin floor area of up to 0.9 m2 and with a cabin height of not more than 1 m.
3. On what basis are elevators classified?
Elevators are classified according to the following main features:
a) the type of transported objects;
b) type of load-carrying device;
c) type of traction body;
d) elevator drive;
c) door drive;
f) type of mine;
g) the design of the doors of the mine or cabin;
h) the location of the engine room;
i) type of control system.
For various transported objects, elevators can serve to lift and lower people and goods.
According to the load-carrying device, elevators are divided into elevators with a cabin and elevators with a platform; by type of traction body - for cable, chain, rack, screw and plunger; by type of drive - electric and electro-hydraulic; according to the door drive - elevators can be equipped with doors:
a) manually opened;
b) semi-automatic; c) automatic.
Elevator shafts are divided into:
a) deaf, fenced on all sides and to the full height by solid walls;
b) metal frame, fenced on all sides and to the full height metal mesh or shields;
c) combined, some of which are deaf, and some are metal-framed.
According to the design of the doors of the mine and the cabin, elevators are divided into:
a) elevators with swing doors;
b) elevators with horizontal sliding doors;
c) elevators with vertical sliding doors. According to the location of the machine room, elevators are:
a) elevators with a machine room located above the shaft;
b) elevators with a machine room located directly under the shaft;
c) elevators with a machine room located on the side of the shaft.
According to the type of control system, elevators can be:
a) with push-button internal control;
b) with push-button external control;
c) with mixed management;
d) with normal (simple) control;
e) with collective control when moving down;
f) with pair control; g) with group management;
h) with group control when moving down;
i) with software control.
4. What lift is called release?
An elevator in which the cabin is driven by a force acting from below.
5. What kind of elevator is called sidewalk?
A release lift in which the car exits the shaft at the top stop.
6. What is a construction hoist?
construction hoist this is a transport device of intermittent action, installed during the construction of any structure and designed for lifting and lowering building materials and people (cargo and cargo-passenger lifts) from one level to another in a cabin (platform) moving along vertical guides.
7. What is the rated capacity of the elevator?
The rated capacity is the weight of the largest load that the elevator is designed to carry.
The value of the nominal load capacity does not include the mass of the cabin and the mass of all devices permanently located in it (railways, monorails, hoists, etc.).
8. How is the nominal load capacity of elevators calculated?
The nominal load capacity of elevators is calculated according to the principle of free filling based on usable area cabin floor, according to the schedule (Fig. 1) recommended by the "Rules for the Arrangement and safe operation elevators" (PUBEL) Gosgortekhnadzor of the USSR. At
determining the usable floor area of the cabin, the area occupied by one of the wings hinged doors when opened, are not taken into account. The mass of a person should be taken equal to 80 kg.
9. What is called the rated speed of the elevator?
The rated speed of an elevator is the speed
movement of the car for which the elevator is designed.
10. What is the working speed of the elevator?
The operating speed of the elevator is the actual speed of the elevator car under operating conditions. The operating speed of the cab differs from the nominal speed by no more than ±15%. By speed, elevators are divided into: ordinary - up to 1.6 m / s and high-speed - up to 4.0 m / s.
11. What are the main parameters of passenger and freight elevators?
The main parameters of conventional passenger elevators must comply with GOST 5746-67. The standard applies to electric conventional passenger elevators with a load capacity of 320, 500 and 1000 kg with a cabin speed of 0.71, 1.0 and 1.4 m/s, designed, manufactured and installed in newly built residential and public buildings and designed for lifting and lowering passengers.
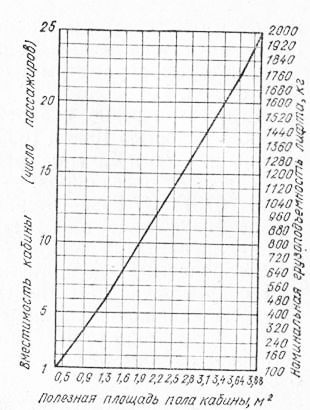
Rice. 1. Graph for determining the lifting capacity of the elevator
For electric high-speed passenger elevators with a carrying capacity of 1000 and 1600 kg with a cabin speed of 2.0; 2.8 and 4.0 m / s, intended for lifting and lowering passengers, GOST 13023-67 applies. GOST 8822-67 applies to electric hospital elevators with a load capacity of 500 kg installed in buildings medical institutions and intended for the ascent and descent of patients in bed with accompanying personnel or passengers. Cabin speed (nominal) - 0.5 m/s; cab lift height (maximum) -45 m; number of cab stops, no more than 14; cabin capacity - 6 people.
For cargo electric elevators general purpose with a load capacity of 500, 1000, 2000, 3200 and 5000 kg, installed in industrial, warehouse, commercial and other buildings and intended for lifting and lowering loads, GOST 8823-67 applies. In table. 2 gives the main parameters of general-purpose freight elevators (the weight of the cabin is not included in the rated load capacity of the elevator). generally suit with direct cab suspension and counterweight. General purpose freight elevators equipped with a pushbutton internal system controls with an attendant, can be used to lift and lower people accompanied by an attendant and in the absence of cargo in the cabin.
GOST 13415-67 applies to electric cargo squeeze elevators with a carrying capacity of 500, 1000, 2000 and 3200 kg, installed in industrial, warehouse, commercial and other buildings and intended for lifting and lowering goods. Their main parameters are: the speed of the cab - 0.5 m/s; cabin lifting height - 25 m; the number of cab stops is not more than 8. GOST 9322-67 applies to electric freight elevators with a monorail built into the cab with a carrying capacity of 1000, 2000 and 3200 kg, installed in industrial and warehouse buildings and intended for lifting and lowering loads both in a state suspended from the monorail, and and located on the cabin floor. Their main parameters are: the speed of the cab - 0.5 m/s; cabin lifting height - 45 m; number of cabin stops - no more than 12; cabin - impassable or walk-through with built-in monorail; cabin door - lattice sliding manual; mine - deaf; mine doors - swing double-leaf manual; location of the counterweight - on the side of the cab; the location of the engine room - above the mine; control system with a conductor - push-button internal with a signal call of the cabin from any floor; control system without a conductor - push-button external from the main floor platform with a signal call to the cabin from any floor.
Freight elevators with a monorail, equipped with a push-button internal control system with a conductor, can be used for lifting and lowering people accompanied by a conductor and in the absence of cargo in the cabin. The load on each meter of the monorail built into the cabin is assumed to be concentrated and equal to 500 kg. The weight of the car and the weight of the monorail are not included in the rated load capacity of the elevator.
The parameters of cargo sidewalk elevators must comply with GOST 13416-67. Load capacity - 500 kg, platform speed - 0.18 m/s, lift height - 6.5 m. but not more than 1.0 m. The weight of the platform is not included in the rated load capacity of the elevator. The elevator control system is push-button external, from the platform of the upper stop. Mine hatch doors are designed for a load of at least 500 kgf/m2.
The main parameters and dimensions of general-purpose electric freight small elevators are defined by GOST 8824-67. Load capacity-100 and 160 kg; cabin speed (nominal) - 0.5 m/s; cab lift height (maximum) -45 m; cabin type - through or not through; without door; control system - push-button external from one floor with an alarm call from any floor. The metal frame shaft can only be used for two-stop elevators.
Cargo small shop electric elevators with a carrying capacity of 100 kg must comply with GOST 8825-67. They are installed in the buildings of shops for lifting goods (goods) to the counters and lowering them or containers. Main parameters: load capacity - :100 kg; cabin speed - 0.25 m/s, cabin height - 5.2 m, number of stops - no more than 2; elevator control system - push-button external from two floors.
12. What is the performance of an elevator?
The productivity of an elevator is the number of passengers or goods transported per unit of time. The performance of a freight elevator depends on the rated capacity, the size of the transported cargo, the height and rated speed elevator, as well as the time spent at stops for loading and unloading. On performance passenger elevator the following factors influence: cabin capacity, installation location, time of use, working conditions (residential building, institution, educational institution etc.), height and speed of ascent; the time of filling and emptying the cabin, the time spent on operations related to starting, accelerating, decelerating and stopping the cabin.
13. How are elevators divided by drive design?
According to the design of the drive, elevator winches can be with a traction sheave and drum type. The elevator drive can be geared or gearless. Drums and traction sheaves, along with ropes or chains, are the traction elements of winches. The reducer serves to transfer rotation from the electric motor to the traction body and reduces the angular velocity of the latter. For gearless winches, the drums and traction sheaves are located on the shaft of a low-speed electric motor.
14. What is the disadvantage of elevators with a drum winch?
The main disadvantage of this type of elevators is big sizes drums, increasing as the height of the lift and the number of carrying ropes increase.
15. What are the advantages of traction sheave elevators?
A winch with a traction sheave can significantly reduce the power of the drive motor and save energy when operating an elevator compared to a drum winch. Traction sheave elevators are simple in design. They have small dimensions and winch weight. Currently, traction sheave elevators have almost completely replaced elevators with drum winches.
16. How is pulling force generated in traction sheave winches?
Traction force of winches with a traction sheave is created by friction between the ropes and the walls of the traction sheaves. The friction force depends on the angle of the rope around the traction sheave, the shape of the profile of the stream and the value of the coefficient of friction between the rope and the surface of the stream.
17. On which elevators are winches with a gear drive used, and on which ones with a gearless drive?
Winches with a gear drive are used on elevators with speeds of not more than 1.6 m / s. Gearless winches are used on elevators with high cabin speeds. Gearless winches are characterized by a large mass and complex control systems, which increases the cost of their manufacture and maintenance. The most common gear winches with a worm gear, in which the traction sheave is mounted on the console, but on the end of the low-speed shaft of the gearbox.
18. How are the elevator winches located relative to the shaft?
According to the location of the winch relative to the shaft, elevators come with a lower and upper drive arrangement.
19. In what cases is the drive located at the bottom?
The drive is located at the bottom only in the case when the machine room cannot be located above the shaft.
20. What are the advantages and disadvantages of bottom and top drive?
The top location of the drive simplifies the design of the elevator, reduces the number of kinks in the rope, increasing its service life. The length of the rope is reduced by 2-3 times in comparison with the lower location of the drive. Increases the efficiency of the elevator installation. The lower location of the drive causes an increase in the loads on the shaft, increases the length of the ropes, makes it necessary to install additional deflecting blocks, etc.
21. In which mines are elevators installed?
Elevators are installed in deaf (brick, reinforced concrete) or metal frame shafts.
22. Where are the control devices located near the elevators?
Control devices can be located: for internal control - in the cockpit; with external control - on landing (loading) platforms, served by elevators; with mixed control - in the cockpit and on the landing (loading) sites.
TO Category: - Operation of elevators
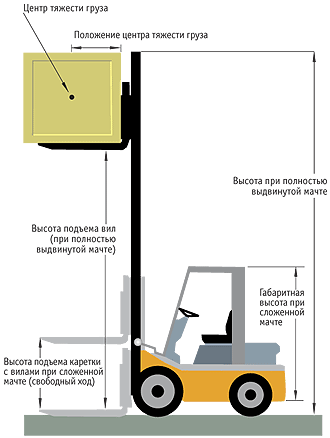
1) LOAD CAPACITY loader (stacker) is the main characteristic of any lifting equipment. In the technical documentation for the equipment, as a rule, 2 types of payload are indicated:
- Rated load capacity - this is the maximum load weight for which all loader or stacker systems (hydraulics, frame, etc.) are designed.
- Residual load capacity - this is the mass of cargo that this loader, stacker is able to safely lift to the height of the maximum mast reach while maintaining its stability. With an increase in the lifting height, the residual g / p gradually decreases. This information is indicated by the manufacturer in the form of tables or diagrams on the side of the frame and in the instruction manual.
Important!. The residual load capacity decreases, depending on how high the forks are lifted and whether the center of gravity of the load coincides with the center of loading.
Download center position (C) - is the distance from the forks to the center of gravity of the load. For most manufacturers of warehouse equipment, the loading center is approximately the same and is located at a distance of 500 or 600 mm from the backs of the forks.
For example, a stacker with a capacity of 1000 kg (load center C = 500 mm) lifts a box weighing 1000 kg, sized 1000 * 1000 * 1000 mm, with a center of gravity exactly in the middle, correspondingly coinciding with the load center of the stacker 500 mm. Under such conditions, the nominal load capacity of 1000 kg is maintained up to 3 meters, and then it decreases and at a height of 5 meters the residual load capacity will be already 800 kg.
If the dimensions of the load are non-standard or it is located unevenly, then the center of gravity will shift and the load capacity will be lost. And this can lead to an imbalance and tipping over of the loader or stacker.
Loader attachments also affect the center of gravity of the entire system, and accordingly shift the load center, and this reduces the residual capacity of the equipment.
- Sustainability loader or stacker depends on design features machines (dual wheels, additional retractable stabilizers for stackers, heavier battery, solid tires). The better the stability, the higher the residual g/n. It also depends on the slope and type of flooring.
2) Geometric parameters. They depend on the mast and base dimensions.
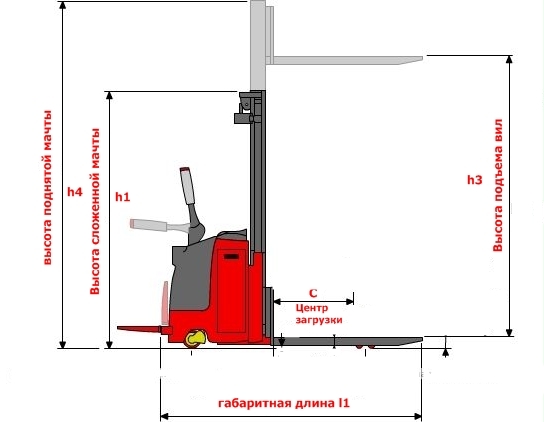
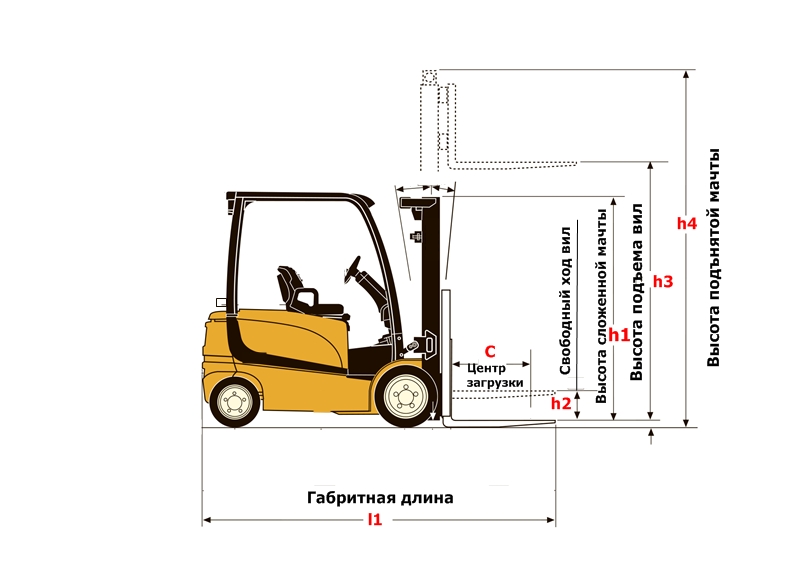
The mast of the loader (stacker) is the mechanism by which the carriage with the forks moves and lifts the load.
- Mast lifting height (respectively loader, stacker)is the maximum distance from the ground to the top of the surface of the forks or loader attachments.
Overall or building height is the height of the mast with the forks lowered. Depends on the type of mast. They are of three types:
Standard two-section without free play.
Two-section with a free wheeling. When lifting the forks from the bottom point, the mast does not immediately rise. The so-called "carriage version", designed to work in spaces with low ceilings(car body, railway wagon), hence the name.
Three-section (triplex), They have three sections for the maximum lifting height, with a minimum overall height. Always free running
Free play - the distance from the ground to the top point of the fork surface, without changing the construction (overall) height of the mast.
Tilt angle (only for loaders) is the maximum angle of inclination of the mast from itself and towards itself from the vertical (straight) position of the mast.
3) Working aisle width(designation in catalogs and technical documentation AST). Shows the possibility of turning the machine in the passage (passage) at an angle of 90 ° to handle the load (pallet). This parameter is one of the main indicators of maneuverability. It is necessary first of all to determine the distance between the racks when designing a warehouse. Given that pallets have different sizes indicated with pallets 800*1200 mm along the forks or 1000×1200 across the forks.Pay Special attention to this setting.
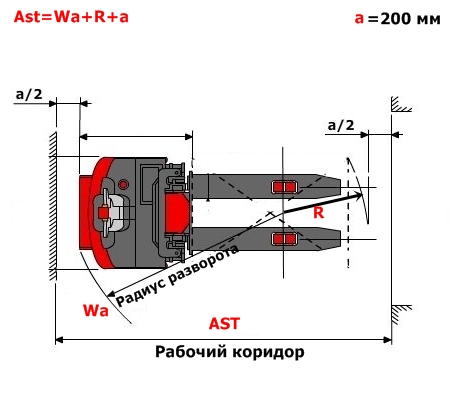
If to speak plain language, then AST is a conditional corridor where a loader with a load can turn around. Therefore, the distance between racks in your warehouse MUST NOT BE LESS THAN the AST of the forklift.






