Classification of solutions.
Final project for the course: "Technological systems and products"
Chapter:
"Technological development and environmental problems of mankind"
Topic: "Fighting forest fires"
Artist: Mogilevskaya Irina
Lecturer: Bronstein Boris Zelikovich
Moscow 2005
annotation
Forest fires are a global problem all over the world. There are many methods to deal with them. I considered the method of controlled burning and the use of aviation. Each of the ways I have considered is characterized by positive and negative influences, and the problems associated with them.
Terms and Definitions
by fire
called uncontrolled burning outside a special hearth, accompanied by the destruction of valuables and representing a danger to human life.
fire zone- the space in which the fire occurs.
Combustion- physico-chemical process with the release of heat, light, smoke. For the occurrence of combustion, the presence of three factors is necessary: a combustible material, an oxidizing agent, and an ignition source.
Burning zone- the space in which the combustion process takes place.
smoke zone- the space adjacent to the combustion zone, filled with smoke.
Flame- the space in which vapors, gases, suspensions burn ..
Aviation Forest Protection - aviation service for the protection of forests.
Propaganda
(lat. propaganda - to be distributed, from propago - I distribute), the dissemination of political, philosophical, scientific, artistic and other views and ideas in order to introduce them into the public consciousness and intensify mass practical activities.
Sanitation- application in practice of measures developed by hygiene and aimed at improving public health, improving the environment and prolonging human life. In the Russian Federation, sanitary control is carried out by sanitary and epidemiological stations.
lat. Sanitas - health.
Alive ground cover- herbaceous plants, mosses, lichens and shrubs growing under the forest canopy.
Wood,
xylem (from the Greek xýlon - tree), a complex tissue of woody and herbaceous plants that conducts water and mineral salts dissolved in it; part of the conducting bundle, formed from the procambium (primary D.) or cambium (secondary D.). It makes up the bulk of the trunk, roots and branches of woody plants.
Under raw materials refers to the material used in production as a material basis, which, as a result of sequential technological processing (processing), turns into finished products.
Fauna(new lat. fauna, from lat. Fauna = goddess of forests and fields, patroness of herds of animals), a set of animal species living in a certain territory or water area. The fauna of a particular region is formed in the process of historical development from various groups of animals (faunistic complexes).
Clearings- non-forested land; places where the forest has been reduced as a result of logging, and its young generation has not yet closed its crowns.
|
1. Introduction |
|
|
2. Analytical stage |
|
|
2.1. System selection |
|
|
2.2. Choice of Negative Influence |
|
|
2.3. Formulation of the problem |
|
|
3. Solution |
|
|
3.1. List of solutions and their classification |
|
|
3.2. Consequences of implementation of adopted decisions |
14-19 |
|
4. Conclusions |
|
|
5. List of used literature |
Introduction
Fighting forest fires.
Throughout the world, forest fires are among the natural disasters of moderate severity. Forest fires destroy trees and shrubs, wood harvested in the forest. As a result of fires, the protective, water-protective and other useful properties of the forest are reduced, fauna, structures, and, in some cases, settlements are destroyed. In addition, forest fire poses a serious danger to people and farm animals.
The causes of forest fires are different, but 90% of them are caused by people. Sometimes forest fires are caused by spontaneous combustion of peat bogs or other natural phenomena.
Ground fires occur most often - the lower tier of the forest burns. When the fire passes to the crowns of trees, crown fires occur. They quickly spread and destroy the forest over large areas.
There are many ways to fight forest fires. A fire can stop if it meets raw non-combustible material, a stream, a wide road, or a clearing on its way. For the timely detection of fires, observation towers 25-30 meters high are being built. In summer, forest rangers keep a round-the-clock watch. Aviation is widely used to detect and extinguish forest fires in a number of sparsely populated areas. In higher educational institutions, fire prevention propaganda is carried out among the population. Early spring and late autumn controlled burning of deadwood, twigs, leaves, dry grass accumulated in forests is carried out. When conventional means are powerless in fighting a forest fire, the oncoming fire method turns out to be the most effective. Even satellite images are used as information about the presence of fires. Various techniques are used to fight fires.
It should be noted that not all fires pose a threat to forests. Low-intensity fires can even be beneficial, burning out the undergrowth, "breaking open" the seeds, and returning nutrients to the ground. Mature trees, as a rule, survive such "grassroots" fires without problems. This process goes especially well in pine forests after a fire. Even if the forest burned out on the site completely, this place will not remain empty. Other types of vegetation, new species of birds and animals will appear.dominance of dark coniferous forests. It has been noted that where there are no fires in the forest, there are many overmature trees. They gradually fall out and die, but there is no generational change. During extreme fire seasons, such forests burn out over large areas due to the accumulated excess reserves of combustible material.
Forest fires, most often arising from careless handling of fire, are very expensive for the state, and therefore for every person. Any person should know about this and not leave unextinguished bonfires behind. It is impossible to burn dry grass, especially at the edges of forests, since fire can cause the forest to catch fire and quickly spread to the area.
Analytical stage
System selection
Methods of fighting forest fires.
As a result of the search for ways to improve fire fighting in the first half of the 20th century, the main conclusion was made - in order to reduce the cost of extinguishing a fire, it is necessary to detect it at the earliest possible stage and immediately begin to eliminate it. When the fire area is only a few acres, only 2-3 people and an hour of work are needed to extinguish it. Therefore, minimum costs and minimum damage. But how can this be achieved? It is possible to regularly patrol the protected area by foot, horse or vehicle fire brigades. You can put a network of observation towers. This works great if the area of the leshoz is relatively small and has a well-developed network of roads where fire brigades can get to the fire site in the shortest possible time. But how to protect the forests of large areas where there is no developed road network?
Much has been said about the causes of forest fires. It is difficult to find people who do not know the elementary rules of fire safety in the forest. But unfortunately, not all of them perform. Neglect often leads to sunbathing. There are many natural causes as well. The fight against forest fires is primarily dealt with by professionals. These are forest firefighters and employees of the state forest guard. Aviation, fire engines, motor pumps and various other equipment are at their disposal. But the main thing in the fight against fires is to detect in time and especially to start extinguishing in time. But it often happens that just people working in the forest and vacationers can come across a fire. What to do in this case?
As mentioned above, a small fire can be stopped in half an hour - an hour by a group of 2-5 people even without special means. For example, with a broom of green branches, a young tree, burlap, tarpaulin or clothes, knocking down the flame. The fire must be overwhelmed, swept away towards the source of the fire, small flames must be trampled under foot.
Another common technique is to throw earth at the edge of the fire. First, taking soil on a shovel, they need to bring down the flame, then make a continuous strip of soil several centimeters thick and up to half a meter wide. One person in half an hour can thus fill up about 20 meters of the edge of the fire.
If you stumble upon a small fire in the forest, you must immediately take measures to stop it and at the same time, if possible, send someone to the nearest settlement or forestry for help.
If you, having got into the zone of a forest fire, do not know how to deal with it, then you need to properly leave the place of the fire.
It is better to prevent a fire than to extinguish it later at the risk of life. Be careful in the forest.
A special interdepartmental commission has been set up to fight forest fires in Novosibirsk. Its functions include coordinating the actions of operational services in case of emergency situations.
Detection of forest fires is mainly carried out from ground observation posts, as well as during aviation and ground patrols of forests.
Works on extinguishing a large fire can be divided into the following stages: fire reconnaissance; localization of the fire, i.e. elimination of the possibility of a new spread of fire; elimination of the fire, i.e. extinguishing the fires; guarding fires. reconnaissance of a fire includes clarifying the boundaries of a fire, identifying the type and intensity of burning on the edge and its individual parts at different times of the day. According to the reconnaissance results, the possible position of the edge of the fire, its nature and the intensity of burning are predicted for the required time ahead.
The choice of methods and technical means for extinguishing fires depends on the type, strength and speed of the spread of fire, the natural environment, the availability of fire extinguishing forces and means, and the intended extinguishing methods.
The main ways to combat forest ground fires are: flooding the edge of the fire, filling it with earth, pouring water (chemicals), creation of barrier and mineralized strips, launching of oncoming fire(annealing).
Extinguishing a forest crown fire is more difficult to carry out. It is extinguished by creating barrier strips using annealing and using water. Wherein the width of the barrier strip should not be less than the height of the trees, and burnt out before the crown fire front - at least 150-200 m, before flanks - not less than 50 m.In order to improve the environmental education of the population, sections on the study of fire safety rules in forests are included in the programs of general education schools, technical schools and universities, the organization of programs on forest protection topics on the Rossiya TV channel during the fire hazard period and regular informing the country's population about the fire situation in forests and fire extinguishing measures.
Information received from artificial Earth satellites is used.
During the fire hazard period, it is forbidden to make fires in young coniferous forests, old burnt forests, in damaged areas of the forest (windfall, windfall), in places with dried grass, under the crowns of trees; throw burning matches, cigarette butts; leave oiled or gasoline-soaked cleaning material; use machines with a faulty power system. Violators will be held accountable.
|
System name |
System name |
||
|
early spring and late autumn controlled burning of deadwood, twigs, leaves, dry grass accumulated in forests. |
|||
|
throwing the edge of the fire with earth. (first, taking the soil on a shovel, they need to bring down the flame, then make a continuous strip of soil several centimeters thick and up to half a meter wide) |
|||
|
creation of an interdepartmental commission to combat forest fires. |
The system of fire barriers: protective mineralized strips, gaps, barriers, edges and fire ditches. |
||
|
use of fire trucks |
construction and repair of forestry fire roads |
||
|
oncoming fire method (tongues of flame rush to each other, and when they connect, the revelry of the elements comes to an end. After all, there is simply nothing more to burn!) |
Using satellite imagery as information about the presence of fires. |
||
|
arrangement of fire reservoirs |
fire propaganda |
||
|
use of observation towers |
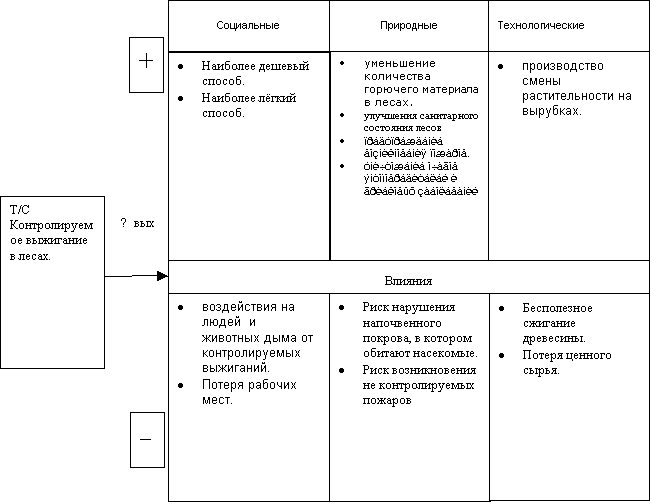
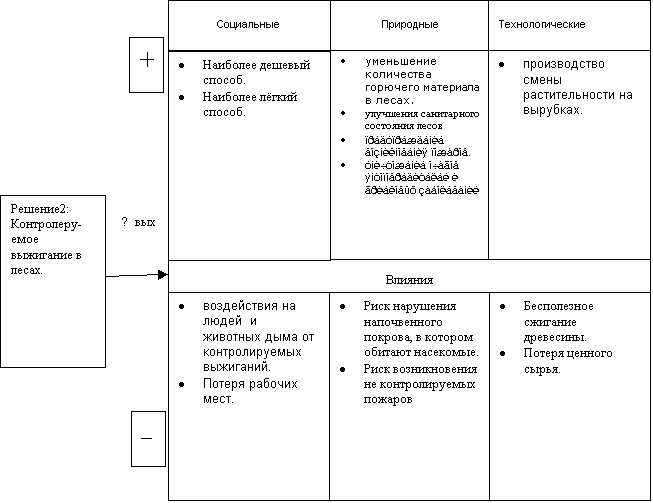
Selected system: early spring and late autumn controlled burning of deadwood, twigs, leaves, dry grass accumulated in forests.
By burning combustible materials under the forest canopy near settlements, we prevent the development of a crown fire, preserve the vital activity of people. Annealing is more often used in case of large fires and a lack of forces and means for
firefighting. It starts from a reference strip (river, stream, road, clearing), on the edge of which, facing the fire, create a shaft of combustible materials (twigs, dry grass). When the urge starts to feel air towards the fire, the shaft is first set on fire opposite the center of the front fire in the area of 20-30 m, and then after the advance of the fire by 2-3 m and neighboring areas. The width of the burnt strip should be at least 10-20 m, and with a strong ground fire - 100 m.With the help of this method, it is possible, under certain weather conditions, to change the vegetation in clearings. In clear cuts, this method is applied to the accumulation of combustible materials and will speed up reforestation. And by burning combustible materials under the canopy of the forest near settlements, we prevent the development of a crown fire, and preserve the vital activity of people. In silkworms, controlled burning eliminates pockets of accumulation of pests and diseases, creates the prerequisites for rapid reforestation. With the help of this method, it is possible, under certain weather conditions, to change the vegetation in clearings. In the current economic situation in the forestry industry, it is impossible to carry out controlled burning for one enterprise. It is proposed to create inter-forestry mechanized forest fire brigades, one for 5-6 forestry enterprises. It includes equipment, a trailer for transportation, 6-8 extinguishers. They would be able to burn the clearings, receiving money from the leshozes for their maintenance. Also engage in planting forests on renovated clearings, and quickly extinguish fires. It is necessary to burn the reserves of combustible timber in forests, especially near settlements. Then the forest will be clean and there will be no soil for the crown fire.

Choice of Negative Influence
Technological system:
Formulation of the problem
List of problems:
|
Problem |
|
|
How to prevent the death of animals? |
|
|
How to prevent a possible fire in nearby villages |
|
|
How to prevent possible loss of life |
|
|
How to prevent plant death |
|
|
How to prevent a possible fire on a power line |
|
|
How to prevent people from feeling bad |
|
|
there is no opportunity to hunt - there are no food sources for people |
|
|
How to prevent economic problems in the country |
Selected issue: How to prevent people from feeling bad.
Prolonged and large-scale forest fires are usually
accompanied by the transport of pollutants and especially
suspended particles over very long distances and posing a threat
for the health of the population of other cities or even neighboring countries.
Remote (after the cessation of fires) manifestations
adverse effects on the health status of the population are:
in the period up to three months - increased mortality of patients
cardiovascular diseases from myocardial infarction;
significant increase in mortality
newborns due to low body weight; increase in frequency
congenital malformations of the cardiovascular system in
newborns and respiratory diseases of children of the first year
life; syndrome of sudden death of newborns; promotion
incidence of lung cancer (in a longer period).
The leading components that determine damage to health in the data
situations are: suspended solids and especially their
fine fractions, ozone and other photooxidants, dioxide
sulfur, nitrogen dioxide, carbon monoxide, benzene, formaldehyde,
polychlorinated dioxins and benzofurans, etc.
Solutions
It is proposed to use the systems described earlier.
General list of solutions to the problem:
|
aviation forest protection (specialized aviation forest protection service) |
backfire method |
||
|
ground forest protection (forest fire divisions, personnel, and technical means of forestries) |
arrangement of fire reservoirs |
||
|
call an ambulance |
|||
|
use of fire trucks |
Mandatory presence of first-aid kits. |
||
|
wearing gas masks |
fire barrier system |
||
|
strengthen the duty of all types of fire safety. |
|||
|
do not use controlled burn |
Classification of solutions.
|
Need. |
|||
|
Temporary resettlement of people |
aviation forest protection |
controlled burning |
strengthen the duty of all types of fire safety |
|
Blocking the windows of people's houses |
ground forest guard |
||
|
wearing gas masks |
Fire barrier system |
||
|
backfire method |
|||
|
arrangement of fire reservoirs |
|||
|
use of observation towers |
|||
|
construction and repair of forestry fire roads |
|||
|
uncontrolled fire |
|||
|
Fire barrier system |
Consequences of implementation of adopted decisions
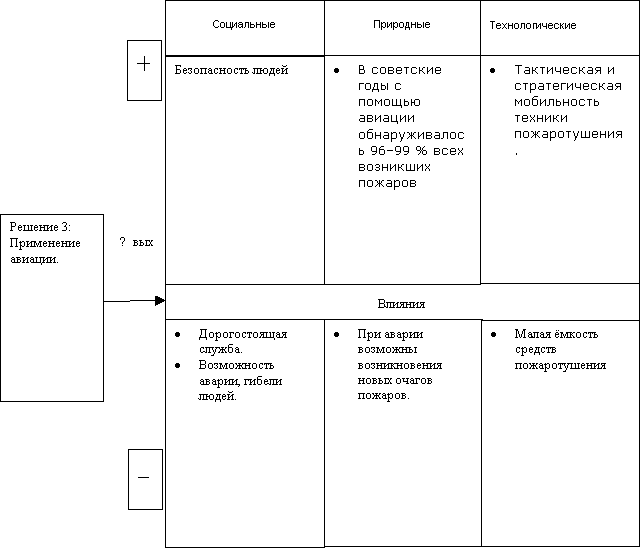
Aviation.
The use of aviation allows us to solve two fundamental problems at once: early detection of fires and prompt delivery of forces and extinguishing equipment to them. It controls 60% of the territory of the forest fund of Russia. E that territory is covered by a network of 245 air bases, air detachments and operational points, where there are 400 pilot-observers and 4 thousand paratroopers and firefighters. Every year, Avialesookhrana engages up to 400 aircraft and helicopters to detect and extinguish forest fires - mainly An-2, Mi-2, Mi-8, An-26, of which more than 100 units are its own fire aviation, including An -2P and Be-12P amphibious aircraft.
The main principle underlying the organization of the aviation fire service "Avialesookhrana”is the prevention of the development of emerging small fires into large ones, by means of their prompt detection and suppression (liquidation). This is achieved by patrolling the forests by aircraft (AF) with the presence of fire fighting forces on board. The mode of patrol flights, which ensures high efficiency in detecting fires on a minimum area, is regulated by the "Instruction for Aviation Protection of Forests". Timely aviation patrolling of the forests is the key to the effectiveness of the work of the Aviaforestry. This is the key to the effectiveness of forest fire protection in Russia.
When carrying out air patrolling on board the aircraft, the pilot-observer has an air fire service group (APS). If a fire is detected, he immediately reports information about the fire to the control center of the aviation department (forestry) and a decision is made to send ground fire brigades or to extinguish it with the help of the APS. In this case, a group of paratroopers-firefighters (paratroopers-firefighters) disembarks. Thus, from the moment of detection to the start of extinguishing, taking into account the time required for aerial reconnaissance and landing of firefighters, no more than 1 hour passes. The consequence of the use of such a "technological process" is a small amount of forces and means involved, the minimum area covered by fire and the cost of extinguishing, scanty economic and environmental damage! There are cases when one standard air fire group of five people managed to eliminate up to five fires within one day! The cost of extinguishing one fire, subject to the "technological process", taking into account the cost of an aircraft flight hour, the cost of wages for firefighters, consumables, etc., does not exceed 60-80 thousand rubles, and in areas with a very high flammability, this figure can be reduced to 25 thousand rubles.
Aviation and the network structure of the organization of aviation departments throughout Russia provide another advantage -tactical and strategic mobility of personnel. If in some area the current fire situation immediately requires the involvement of additional APS forces, they can be sent from neighboring air departments within 2-3 hours.
Functioning, structural organization, number and methods of personnel training, work technology and all actions of Avialesokhrana are aimed at one thing - to prevent (prevent) the occurrence of a critical fire situation.
In recent years, the use of aviation to extinguish forest fires has caused such a negative assessment. As noted above, this is currently the most highly efficient "technology", its implementation minimizes the number of "expensive in extinguishing" fires.In the Soviet years, 96-99% of all fires that occurred were detected with the help of aviation. If out of 1000 fires there were 10-15 large ones, it was called an emergency! With obvious advantages, the implementation of the technology has one disadvantage - a relatively high cost. Since the mid-90s, there has been a massive reduction in funding, which continues to this day. Thus, for this reason, in 2004, the proportion of fires detected by aviation was 31%.
Of course, Avialesookhrana, like any large organization with many years of experience and traditions, is not perfect. Ways to improve the aviation fire service have been outlined and are already being implemented: reducing the cost of flight hours spent on extinguishing fires is achievable using new, more efficient aircraft, optimizing flights and changing security levels in some areas, introducing new alternative detection methods that will complement (rather than substitute!) the main technology, improving the quality of information support for ground firefighting forces through greater use of digital technologies, optimizing the structure of fire brigades, and much more.
To the rhetorical question asked - is aviation needed in forestry, it is necessary to answer categorically - yes! Avialesookhrana can recoup the costs many times over, and forestry simply cannot do without it!

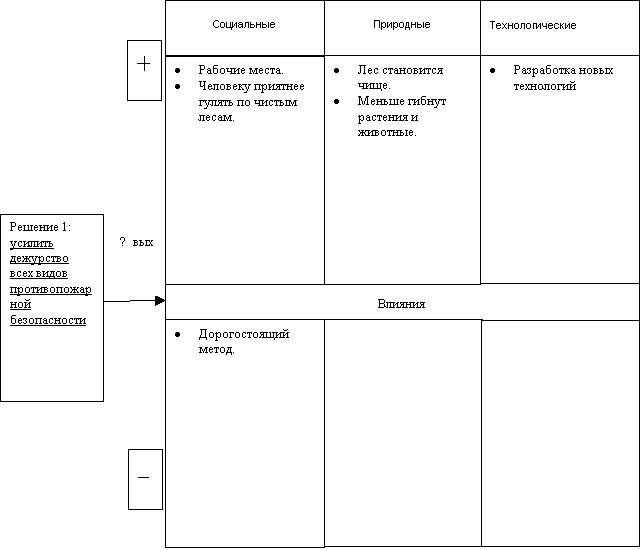
Enhanced duty of all types of fire safety.
“During the May holidays, the forests of Buryatia will be patrolled by special mobile firefighting teams. The coordination headquarters for combating forest fires decided to organize an increased watch. Patrols will take control over the observance of fire safety rules by vacationers. On May weekends, many residents of Transbaikalia like to go out into nature for the first picnics. Unextinguished fires, thrown cigarette butts are, as a rule, the cause of large fires in the taiga. So far, the fire hazard situation in the forests of the republic is relatively calm. Since the beginning of April, there have been 36 forest fires on an area of 165 hectares. Last year, by this time, 500 fires had already destroyed and damaged almost 14,000 hectares of taiga tracts.” It follows from this article that this is a very effective way to fight forest fires, but this is not the only plus of this solution: firstly, many free places will be freed up, and people will have the opportunity to work; and secondly, people will need special equipment and the development of new technologies will follow.
Temporary resettlement of people.
For foresters, evicting people from the villages adjacent to the forest during controlled burning in the forests is by far the most convenient and cheapest way to avoid people feeling unwell, but it is worth considering whether it is convenient for the residents of the villages.
![]()
conclusions
conclusions
There are many systems for extinguishing forest fires. I considered several: controlled burning, the use of aircraft to extinguish forest fires, the temporary eviction of people, the increased duty of all types of fire safety. And enhanced duty of all types of fire safety turned out to be the most reliable way in all respects.
w.forest.ru
http:// www. ecoprojects. en
http://www.temadnya.ru
http://www.pr.kg/news/041013allinformationfr.php






