Edged board exit. How much waste is obtained when sawing wood Calculation of the yield of commercial wood from round timber
Sawing wood is a cycle of actions using a variety of technologies aimed at obtaining lumber from round timber suitable for further use in industry. The duration and labor intensity of the process depend on the chosen method of processing round timber, as well as the time of year.
Tool and equipment
Barrels go into production and big size branches. All material is divided into groups according to the thickness and presence of bark. Often, wood processing enterprises have workshops near the harvesting site, in which machines are installed for the initial processing of wood.

Manual debarking of the forest
The forest that has not passed the stage of debarking can be used on the device of floors or as ridge beam in an appropriate interior, or as a supporting device during construction.

Industrial debarking
If another option for using the tree is planned, then sawing is carried out, resulting in the following segments:
- unedged and semi-edged (rough material from which the bases of the floor, walls or ceiling are mounted);
- edged (designed for finishing flooring).
The sawing can be carried out by a field organization that has all essential tool.

Tree sawing map
The rational use of the material is ensured by compliance with the sawing map. This allows you to reduce the cost due to waste, the percentage of which the card can significantly reduce. The used tools and types of forest processing equipment depend on the volume, desired quality and size of the finished lumber.

Most often use a circular saw and various machines:
- the circular saw allows you to make precise cuts of various directions. Suitable for both professional and home use, perfectly copes with the diameter of the round timber above the average;
- chainsaw;
- machines for clean removal of bark;
- sawing on a band sawmill makes it possible to process dense logs, is considered the most popular, as the output gives quality material and a small amount of waste;
- disk machine: production of two-edged timber and unedged boards;
- a frame sawmill does not need a foundation, the technology with its use allows you to install equipment in close proximity to the cutting site;
- thin gauge process universal machines, the output gives high-quality building materials even from low-grade whips;
- sawing roundwood at a large woodworking enterprise should be carried out with the largest amount of sawn timber, which differs from the rest in special quality and exact dimensions. For this purpose, special lines are installed for sawing.
At the sawmill, a beam and an edged board are obtained due to the cut of a log up to 7 m long and 15-80 cm in diameter along the longitudinal line. A circular saw has one or more discs, processes different diameters of the forest according to their number.

If at home it is necessary to process a small amount of wood, then you can use a regular chainsaw.
cutting wood
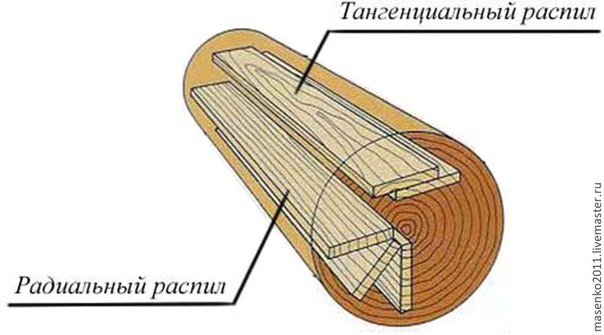
Before choosing a tool, you need to decide on the type of cut, focusing on the annual rings of the log. There are several types:
- radial (along the radius);
- tangential (the cut is parallel to one radius, touches the annual rings);
- the fibers are arranged parallel to the cut being made.
Among the cutting methods, the one that is most suitable for a particular case is selected:
- Razval. Sawing the forest in this way is carried out for deciduous trees with a small trunk thickness, it is considered the simplest processing. Exit: unedged elements and slabs.
- If there is another woodworking machine, then it is possible to cut up to 65% of the material to produce edged boards of the same width. First, a two-edged timber and boards are sawn from the sides, and then a certain amount of edged lumber is obtained from the timber.
- More specific methods are sector and segment sawing. The number of elements in the first method varies from 4 to 8, and depends on the thickness of the trunk. After separation, elements are sawn from each sector along a tangential or radial line. The second method begins with the exit of the beam from the central part, and boards are sawn from the side segments in a tangential direction.
- For individual sawing of wood, the circular method is suitable. It is based on turning the log along the longitudinal line by 90° after each sawn board. This allows you to monitor the quality of wood and timely remove the affected areas of the trunk.
Handmade: chainsaw application
For home cutting of several trunks, it is not advisable to purchase a tool whose cost is several times higher than the price of finished products. If you have the necessary skill, then it is more efficient and cheaper to do all the necessary work with a conventional chainsaw, or chain equipment powered by electricity. Of course, such work requires much more physical costs and time, but the price of the issue is significantly reduced.
Work on garden plot needs pruning fruit trees, and it also becomes possible to additionally produce material for outbuildings without resorting to the services of specialists, so that any zealous owner would prefer to buy a chainsaw. Most often, conifers are harvested for the home, and this tool does an excellent job of sawing them. Thanks to even trunks, it is easier to outline the cut lines, which increases the speed of work. Professionals, by the way, most often use a chainsaw, since it is more powerful than an electric one and you can use it anywhere, regardless of whether there is a cutting or sawing of power supplies at the site.

To work with a chainsaw on cutting logs, you will need such a device as a nozzle on the saw, as well as saw cut guides and base-trunk fixers. The nozzle in the form of a frame is attached to the tool so that it remains possible to adjust the distance between the chain and the frame itself. This is done to enable the output of finished lumber, different in thickness. You can take on the role of a guide either desired length profile, or flat wooden plank with sufficient rigidity. A special chain is selected for the tool, designed to cut the trunk along. Its difference from the rest is in the teeth, sharpened at a certain angle.

Before starting work, it is necessary not only to prepare all the necessary tools. Regardless of whether a woodworking machine or a manual device is intended for processing the trunk, the first step is to familiarize yourself with the cut map. This is done in order to minimize the percentage of waste, and increase the yield of useful products.
The first thing you need to worry about when ripping is the uniform density of the finished boards. To do this, a competent sawmill guides the tool with east side logs to the west, or in the opposite direction. This is due to the greater density of round timber in its northern part than in the southern.
Next, the slab is removed from both sides with a chainsaw in such a way as to obtain a two-edged beam. It, in turn, is sawn in accordance with the sawing scheme chosen at the beginning of the work. The output gives an unedged board. If there is a certain percentage of defects in the trunk, then a circular cut is possible with the trunk turning at a right angle or 180 °.
Quantity of finished material, cut price
Output useful material with coniferous and hardwood differs in percentage terms. For lumber obtained from coniferous trees, are characterized by the following indicators:
- provided that the operation is carried out by a professional and a sawmill is used, the percentage of finished wood will be the highest (80-85%);
- edged material, which is given by machines, averages 55-70%;
- unedged board when working with a chainsaw leaves up to 30% of waste.
The figures are given without taking into account the finished rejected wood, the amount of which can reach 30%. However, such material is used for products that allow a certain marriage.

Deciduous round timber gives 60% of the finished unedged wood and about 40% of the trimmed wood. This is due to the initial curvature of the round timber. You can increase the amount of products received: this will require woodworking machines of various kinds. A certain kind of fixture can increase the amount of lumber by 10-20%. For one cube of lumber, you will need about 10 cubes of hardwood round timber. Installation price additional equipment will pay off the cost of the finished wood. Special lines give more volume, but their use is advisable only on a large area. The average price of sawing wood at a conventional sawmill will be approximately 150-180 rubles per cubic meter of boards.
sawing map
The sawing map is a calculation of the optimal amount of finished lumber from one log. It can be calculated independently for each specific log diameter, or you can use computer program, which greatly facilitates the calculation, and the price of which is quite affordable.

Or the source can be a regular guide to sawmilling. The result is a table that is taken as a basis. The sawmill must always be oriented to its data, in order to obtain more lumber of any kind of wood.
The economic efficiency of sawmill production largely depends on the degree of use of raw materials. The equipment used in production, rational cutting of logs according to optimal deliveries, competent cutting planning determine the efficient use of resources and, accordingly, high product quality.
The main schemes for cutting sawn raw materials
Methods and schemes for cutting logs directly depend on the requirements for the quality and size of products, the characteristics of raw materials and the type of equipment used.
The main methods of sawing logs
a - waddle; b - with a bar; b '- with the receipt of two bars; b "- waddle bars; in - sector; in '- sawing the sector into radial boards; in "- on tangential boards; g - segment; g '- breakup-segment; g "- beam-segment; d - circular; 1 - unedged boards; 2 - edged boards; 3 - rail; 4- bars; 5 - parts of logs in the form of sectors; 6 - parts of logs in the form of segments; 7 - one-sided edged boards
cutting logs waddle consists in its division along parallel planes by one or more cutting tools. This scheme allows you to get unedged boards with different location layers relative to the annual layers. The method is rational when cutting logs up to 18 cm in diameter and for sawlogs with trunk curvature (most often used in cases of cutting birch raw materials, which have simple or complex curvature in 70% of cases).
Unedged boards obtained after cutting at random are processed into edged boards or transferred for cutting into blanks in an unedged form.
In the event that the predominant quantity of finished products must have fixed dimensions cross section, the cutting method is applied with bar. This scheme is also used for cutting logs of large diameters in the production of general purpose lumber.
Sawing with a bar is carried out on multi-saw equipment in two passes. At the same time, at the first stage, bars are obtained from roundwood with a thickness equal to the width necessary board. Then these bars are divided into boards of the required dimensions in thickness.
For cutting large-sized ridges, they are used segment and sector methods. It should be noted that these schemes are specific and are used in special types production facilities for the production of tangential and radial lumber.
Individual cutting of large logs and logs with internal rot is carried out in a circular way.
Processing of round wood by milling
The formation of the section of sawn raw materials by milling is carried out by combining this method with sawing. In this case, three main cutting schemes are used:
- obtaining a double-edged beam at the first node;
- obtaining unedged boards and two-edged timber on the head machine;
- obtaining a profiled beam with dimensions corresponding to the cross-sectional dimensions of edged lumber with the development of boards on one equipment.
Double-edged timber is a semi-finished product for the further production of edged lumber by dividing the timber into boards.

The main methods of cutting logs by milling
a - obtaining a two-edged beam on the head machine; b - obtaining a two-edged beam and unedged boards; c - obtaining a profile bar; g - obtaining long edged lumber; e - obtaining edged lumber of various lengths; e - obtaining edged lumber of various lengths and widths; 1 - lumber zone; 2 - edged lumber; 3 - curly timber; 4 - two-edged timber; 5- unedged lumber
The concept of setting for sawing round wood
A set is a set of saws, clamping and inter-saw spacers installed in a saw frame to obtain sawn materials with specified thickness parameters.
In other words, a delivery is a plan-scheme for sawing sawmill raw materials (logs) of uniform quality and size into products of specified parameters and quality.
When sawing in a waddle, the setting is implemented by a digital series showing the thickness of the sawn boards in millimeters:
19-19-32-32-19-19.
This row of numbers means that two boards 32 mm thick are cut from the central part of the log, and four boards 19 mm thick are cut from the side parts.
When breaking up with a bar, for example, the setting is written in two rows of numbers, for sawing a log (first pass) and a beam (second pass):
19-19-150-19-19 (first pass);
19-32-40-40-32-19 (second pass).
As in the previous example, these numbers mean that on the head machine of the first row, on which the log is sawn, one beam with a thickness of 150 mm is obtained and, accordingly, four unedged boards of 19 mm each (two on each side), and on the machine of the second rows, the resulting timber is sawn into boards with a thickness of 40, 32 and 19 mm.
When sawing logs on single-saw machines, the setting determines the order of cutting.
Drawing up deliveries
The preparation of the set essentially means determining the optimal dimensions and proportions of the boards in terms of thickness, ensuring the rational use of the cross-sectional diameter of the log.
Basic rules for compiling a delivery:
- postavy should be symmetrical;
- in one set there should not be boards that differ in thickness by less than 5 mm;
- start drawing up the set with the largest lumber in terms of cross-section;
- the dimensions of the thicknesses of the boards should decrease from the axis of the log to the periphery;
- do not provide for sawing out more than two thin (16, 19 mm) boards at the edge of the set when cutting raw materials on sawmill frames;
- choose the height of the timber on the first pass according to the width of the leading boards in the specification according to the dimensions of the thicknesses of the boards;
- the face of the timber, sawn in the second pass, sawn into boards of equal thickness;
- when compiling deliveries for lumber without specifying specifications, use tabular or graphical methods;
- when sawing using the method with a bar, determine the thickness of the bar from the ratio (0.06-0.08) of the top diameter of the log - d;
- the setting should not exceed the value of the maximum coverage of the diameter of the log;
- determine the smallest thicknesses of the central boards according to this table:

Graphical method of drawing up assignments
It is possible to draw up a rational delivery in accordance with GOSTs without specifying specific cross-sectional dimensions (without tasks in the form of specifications) - using special graphs.

An example of using the graph of the limiting thicknesses of lumber according to P.P. Aksenov
In order to determine the limiting thicknesses on the abscissa axis, the distance from the axis of the set to the inner part of the face of the set of the required board is plotted. Then a vertical line is drawn until it intersects with an inclined line that corresponds to a given diameter, and the resulting intersection point is taken down to the coordinate axis.

Graph of optimal lumber thickness according to G.G. Titkov
Before sawing round timber, it is required to calculate how much volume will remain for further operation, and how much material will be spent on processing. This is important because it affects the final cost of production. The amount of uncut received will depend entirely on what wood species are used. At the same time, there are certain measures that allow you to increase the yield of lumber after cutting.
What is the yield percentage and its dependence on the diameter of the lumber
To understand this, it is necessary to open the concept itself. Percentage of lumber yield from roundwood is everything useful tree after cutting. The rest is waste that is sent for further processing to obtain materials such as MDF, fiberboard, chipboard. It should be understood that the volume that will be obtained as a result of cutting a tree is calculated for each individual diameter and the selected sawing option.
It is worth understanding the question of why the parameter under consideration depends on the diameter of the forest. Everything is extremely simple here: the fewer cuts on the tree, the higher the volume value will be. Of course, much will also depend on the sawing technology and on the sequence in which the cutting was carried out. The correct sequence will be shown in Fig. 2. At the same time, it should be understood that small lumber is obtained from medium-sized wood species, and a thick board and timber are made from a large forest. It is also worth considering the average diameters with approximate norms for the volumetric flow rate:
- 14 - from 45 to 50%;
- 20 - about 52%;
- 25 - on average up to 57%;
- 34 - such a diameter has lumber wood, which has the highest value of the volume fraction, equal to 66%;
- if the forest has a diameter of more than 40 cm, then there is a sharp decrease in the obtained materials.
The volume of waste after sawing
In order for the finished product to have a large percentage, everything should be correctly calculated and prepared. And the workflow itself must be carried out in full accordance with the technology. At the same time, it should be taken into account that roundwood coniferous and deciduous trees will give a different yield of sawn timber from edged board in m 3.

Note! conifers timber are considered the best option, due to the fact that they have a straight trunk and a relatively larger diameter. In addition, such a forest is not so prone to the process of decay, which leads to fewer rejects.
When working with hardwoods, 2 processing methods are used:
- Using a band sawmill at 375 or 363.
- Into collapse. This technology involves cutting a half-beam, which is subsequently passed through a multi-blade device.
In this case, the first method allows you to get about 40-50% of the output. But the collapse technique differs in a slightly larger volume - up to 70%. The disadvantage of this technology is that the cost of it is relatively high. When sawing round lumber 3 m long, you can notice a fairly high level of marriage. In this case, the remaining wood will not be immediately useful due to the fact that it requires an additional processing process.
The ratio of the volume of produced lumber V n to the volume of sawn raw materials Vc as a percentage is called volume output R, %:
This is the main indicator of the rationality of the use of raw materials, because. in the cost of sawn products, the cost of raw materials is 80% of all costs for its production. The volume output is proportional to the diameter (for example, when sawing logs with a diameter of 16 cm and a length of 6.5 m into collapse, it is about 55%, with a diameter of 32 cm - 61.5%, with a diameter of 40 cm - over 63%) and is inversely proportional to its length (for example, for every 0.5 m reduction in the length of logs from 6.5 m, it increases by an average of 0.65%). The curvature of logs in 1% reduces the yield by 8...12%. When sawing with a bar, the output is 2.5 % higher than collapse. An increase in saw blade thickness by 0.2 mm in a 7-saw set leads to an increase in wood loss and a decrease in product yield by 0.3 ... 0.5%. The volumetric output of sawn products is influenced by the organization of labor, the qualifications of workers and engineers, technical supervision of equipment, and technological discipline at all production sites.
The output of lumber by grade as a percentage of the volume of sawn raw materials is called sorted output:
The total yield of all varieties gives volume output lumber
Yield distribution by varieties and assortments in % total volume of lumber C, = 100 V ni – V n% - there is a variety composition of products. The qualitative composition of sawn products is evaluated grade factor Ks, depending on the type of wood, purpose and grade. As basic assortment (K with= 1) edged softwood lumber 2 ... 6.5 m long grade 3 (GOST 8486-86 *), (for selected grade K c = 2). The percentage ratio of the volume of specification lumber to their total volume is called specification output:
In order to stimulate sawmills for the integrated rational use of raw materials, the so-called coefficient of integrated use of raw materials- the ratio of the total volume of lumber ( V n), other sawn products (obapol, tare plank - V DP), technological chips (V SH), technological sawdust (Von) sold to the waste side (VP) and waste used for the production of steam and energy ( Vn/e) to the volume of sawn raw materials:
In this regard, equipment for the aggregate processing of raw materials appeared. Indicators of the degree and rationality of the use of sawn raw materials R, Rs, Rep, Kisp, divided into planned and reporting.
Postav
The scheme for cutting a log or a group of logs into sawn products of the required dimensions, which establishes the order and place of cuts, the thickness, and sometimes the width of the materials obtained, is called set up, (in contrast to the so-called "saw set" - a set of installed in gang saw machines saws at a certain distance from one another to obtain boards and beams of certain sizes from logs). Postavy are symmetrical And asymmetrical. (rarely used, for example, when sawing sleepers), even And odd. In even symmetrical settings, the core falls into the central cut and ends up in two central boards, in odd settings - into the core board. Breakup and beam postavay given parameters are called settlement: a set that provides the highest volumetric yield of lumber is called maximum, and the setting that provides the highest yield of sawn timber of a given specification - optimal. Sets are recorded according to the nominal dimensions of lumber (without shrinkage allowances taken into account when calculating the sets). An even symmetrical breakup is written in different ways, for example,
19-25-50-50-25-19 or 50/2-25/2-19/2 or:
2 boards 50 mm
2 boards 25 mm
2 boards 19 mm.
The beam setting is recorded in two passes, for example:
a) 1st pass - 16-16-175-16-16, 2nd pass - 16-16-50-50-50-16-16;
b) 1st pass - 175/2 - 16/2 - 16/2, 2nd pass - 50/1 - 50/2 - 16/2 - 16/2;
c) 1st pass - 1 beam 175 mm, 2nd pass - 1 board 50 mm
2 boards 16mm 2 boards 50mm
2 boards 16 mm, 2 boards 16 mm
2 boards 16 mm.
There are other types of recording settings.
The thickness of the inter-saw spacer is equal to the sum of the values of the nominal thickness of the board, the allowance for shrinkage along its thickness and the bilateral broadening of the saw teeth by flattening or setting.
When drawing up and calculating the sets, it is necessary to know the consumption of the width of the set BUT, mm - the distance between the symmetrical outer surfaces of the outermost side boards in the set, consisting of the sum of the nominal thickness of the boards, shrinkage allowances and the width of the cuts e(at P boards in the setting):
Drawing up sets for a given specification of lumber with a known diameter of logs consists in determining the number of boards and in sequential selection (fitting) of their thicknesses in a given diameter of logs. First, the most favorable log diameter is selected to obtain a beam of a certain size, and then the board thicknesses are selected for the first and second passes. Rules for compiling deliveries the following:
a) in case of mass sawing of raw materials, the deliveries must be symmetrical;
b) the preparation of postavs should start from the axis of the log;
c) the number of sections cut from a log should be minimal - no more than 1-2 thicknesses of thick lumber and two thicknesses of thin lumber should be obtained from a log;
d) should not be included in the supply of boards of adjacent thicknesses with a difference of less than 5 mm, because they are difficult to sort;
e) do not cut the central boards from logs with a thickness of 36 ... 62 cm and more, and the core ones are not thinner than 40 ... 100 mm, and from logs with a diameter of 14 ... .50 mm;
f) avoid multi-saw "heavy" sets: with log diameters from 14 ... 16 to 30 ... 32, the number of boards in the set should be from 4 ... 7 to 8 ... 12;
g) take the height of the beam within 0.6 ... 0.8 of the top diameter of the log (Fig. 3.17);
h) receive side boards on the 1st in the 2nd pass of the same thickness;
i) the width of the set must be equal to or close to the maximum coverage of the diameter of the log by the set, depending on the minimum width bmin board length lmin(assumed 1.5 m), from the diameters and length of the log D And L:
j) when sawing logs into collapse, the limit and optimal thicknesses boards are installed according to graphs (Fig. 3.18) or according to formulas;
l) the thickness of the edge boards, in order to avoid gaps, is recommended to be taken depending on the diameters of the logs: 16 and 19 mm with a diameter of 14-18 cm; 19 and 22 mm at 20-24 cm; 19, 22 and 25 with a diameter of 26-36 cm; 22 and 25 with a diameter of 38-42 cm; 25 and 32 with a diameter of 34-56 cm; 32 mm at 
diameter 58 cm or more.
Settlement calculation- this is the definition of the width, length of the sawn boards, their volume, volumetric and graded output for each section of the boards and for the whole log. The length and width of the boards are found graphic or analytical methods. On a sheet of paper, the circles of the top and butt ends of the log are applied on a certain scale and, starting from the center, the required sections of lumber are entered, the width is measured and the length of the boards is determined taking into account the run of the log. Sometimes they use templates made of transparent plastic. A widely used method for calculating set-ups using a quadrant chart (Fig. 3.19).
 |
To determine the length and width of unedged and edged boards and the dimensions of the beam on the abscissa axis, find the distance from the axis of the setting to the board in question. From the obtained point, a vertical is drawn until it intersects with the calculated diameter, and the intersection point is taken down to the y-axis, where the calculated width of the board is found. The allowance for shrinkage in width is subtracted from it and the result is rounded up to standard width boards. As the calculated diameter of the log, the diameter of the top section can be d or the diameter of any section d x , separated from the top end at a distance x. The diameter of a log in any section is determined by the formulas:
where b x - board width in section, cm; α - distance from the axis of the log to the layer of the board, cm;
S– log run, cm/m.
The length of the shortened board is determined by the formula
Compilation and calculation of sets is a very important and crucial stage in planning the cutting of raw materials. It determines the rationality of using wood when cutting. After compiling and calculating each set, it is necessary to immediately determine the volume of sawn raw materials, as well as the yield of sawn timber from it, and enter them in the cutting plan sheet (form 3.1).
Graded output of lumber C t, % from different sorts of raw materials is determined according to the standards for the output of sawn timber of the grade being determined R, R 2 Rz R 4,%, from logs of I, II, III, IV grades by volume (or in quantity), respectively Q 1 , Q 2 , Q 3 , Q 4 m 3 (or pcs) and calculated by the formula
The determination of the volumetric yield of sawn timber for each assortment and for the delivery as a whole is carried out in cubic meters and as a percentage of the volume of the log.
The cutting plan is drawn up for the entire volume of raw materials intended for processing within a month or for 1,000 m 3 (while maintaining the specific ratios of the size and quality of the logs specified in the specification for the month) (form 3.3). Based on it, a schedule for sawing raw materials is drawn up, taking into account the possibility of sorting it and the timing of delivery of sawn products to consumers.
All operations for planning the cutting of raw materials can be performed on a computer.
wood balance when cutting raw materials, this is the distribution of the entire volume of wood by type of product, waste and losses, reflecting the rationality of using wood and depending on the sawing methods, the size and quality of the raw materials, the purpose of the sawn products, the settings used, the thickness of the saws and other factors. The wood balance can be planned (calculated) and reporting (actual). For example, the balance of softwood sawmill raw materials in the production of edged sawn timber in accordance with GOST 24454-80 * and 8486-86 contains: sawn products 60%, technological chips 18%, sawdust 14 %, waste (screening wood chips) 2%; shrinkage 6 %. (This does not include off-balance waste - bark 10 ... 12% and allowances for the length of logs 1%).
Table 3.3
Form 3.1. Plan for cutting raw materials into lumber
for month 20
| No. No. of fittings | Log diameter, cm | Log grade | Sawing volume of raw materials, m 3 | lumber specification | |||||||||||||||
| Thickness, mm Width, mm Length, m Grade Volume, m 3 | |||||||||||||||||||
| Total, m | Lumber received by calculation, m | ||||||||||||||||||
| Total | m 3 % m 3 % | ||||||||||||||||||
| overfulfillment | |||||||||||||||||||
| underperformance | |||||||||||||||||||
woodworking today it is one of the leading domestic industries in terms of liquidity. No wonder that more and more entrepreneurs and, above all, beginners, are striving to find their niche in this business.
In the sawmill when the fight comes over ideal lumber geometry, the combination of quality, performance and price in equipment is the key to commercial success. It is very important to choose the technology of work and equipment that optimally satisfies all these indicators.
Selecting the type of sawmill
Now on Russian market represented tape, disk, as well as frame sawmills. In order to compare the effectiveness of their work, we use such a parameter as yield percentage of finished lumber. The highest score in this comparison is band saws oram, which give 82-88%. For comparison: a frame sawmill has only 61%.
The second is very important point: with which forest types one or the other sawmill works best. For band sawmills, this is a thinner and medium wood, circular sawmills they cut large wood well, but face big problems when sawing a thinner, and a frame sawmill will not be able to saw a log of more than 480 mm in diameter.
Choice of sawmill technology
Gather technology (sawmill frames)
Morally outdated technology. Under the equipment, the installation of a multi-ton foundation is required. Also, sawlogs need to be sorted by at least 12 standard sizes to optimize the yield of the material's usable coefficient. Needs constant reconfiguration drank. It has poor board geometry and high surface roughness. Cutting thickness 5-6 mm. Most of the common sawmills can hardly cope with the frequently encountered thick gauge (sawlog diameter over 70 cm). The yield coefficient for edged lumber is about 50-55%.
However, it has excellent cutting stability, good performance, unpretentious in maintenance, does not require high qualification of the sawyer. It still enjoys well-deserved popularity, producing products mainly for the unpretentious domestic market, where the cheaper the better. Cannot cut radial board mainly due to poor accuracy.
Recommended apply if you have your own logging and a large number cheap raw materials of medium thickness. The undisputed leader among all production technologies unedged lumber average quality.
Band saw technology 
Relatively young technology. A steel strip welded into a ring has teeth cut on one or both sides. It is put on two rotating drums with a diameter of 0.5 to 1 m. The main thing is that the tape must be flexible enough to rotate for a long time and at the same time hard enough to cut for a long time and not dull. Sometimes the teeth are hardened, the teeth are welded from another metal. It is necessary to distinguish between machines working with narrow ribbon 20-60 mm wide and with wide ribbon 100-300 mm. The teeth on the narrow band are bred. The wide belt has flattened or stellited teeth.
Many band saws can cut logs with a diameter of more than 1 m. Do not require foundation equipment. Cutting thickness 2-3 mm. Handles hardwoods with ease. They require lubrication: in summer - water, in winter - diesel fuel. As a rule, they have an individual cut and do not require sorting of logs. Possess the highest among all technologies output ratio suitable for edged lumber - up to 75%.
Machine tools farm class on a narrow belt with a capacity of about 5 cubic meters per shift are quite cheap. Machine tools of the middle class on a tape 100-130 mm wide saw up to 10-15 cubic meters per shift and cost several times more.
Machines with narrow belts sawing badly dirty and frozen wood. They give out a wavy board, and the saw becomes dull literally after one cut through a dirty log. The cost of a decent saw is more than 25 dollars, and it can cut about 10 cubic meters of logs and becomes unusable. Technology has the most high unit cost tool per cubic meter of output and average cutting stability.
After two hours of sawing, the band saw must be removed and hung up to rest for a day to maintain fatigue strength. In reality, it turns out that to ensure two-shift operation of the machine on a narrow belt, about 100 saws in year! Required high qualification sharpener and caution of the sawyer, the slightest mistake is fraught with a break in the tape. For its repair, rather expensive imported welding machines are used. Their use allows you to weld the tape literally from meter-long pieces, which prolongs its life, significantly reducing the cost of the tool.
Band saws on a narrow belt, due to their low cost, most of the smallest sawmills and farmers have. The main disadvantage of a narrow tape is a wavy cut, which greatly limits the possibilities of production. Therefore, this technology is suitable only for small businesses, and, moreover, without the possibility of growth.
It is more preferable to use band sawmills for horizontal sawing with a tape 80-100 mm wide. Such belts have stellited teeth and are not afraid of dirty and frozen forests. These saws cost $200 and up. In their lifetime, they can cut up to 300 cubic meters of lumber. However, such saws require a whole range of equipment to maintain them in working condition, comparable in cost to the machine itself.
Horizontal sawmills with a belt width of 80-100, it is recommended to use them as first-line machines in the presence of sufficiently thick and expensive raw materials, when the efficiency of its processing comes to the fore. For these purposes, of course, you should use machines with a tape width of 100 mm and above.
Appropriate use band saw technology on narrow bands e as machines of the second row. These are four-head and five-head gang saws of the Avangard brand. This class of machines perfectly complements the currently widespread circular log saws of the Kara, Magistral, TsDS types. It is quite difficult to make and perfect a wide band saw. A high level of craftsmanship in the production and preparation for operation of wide band saws has been achieved by Pilotech.
Circular, circular saw technology
Machines working on this technology are divided into three types.
1. Vertical saws
With the beginning of market reforms, circular log saws with a large saw such as Kara, Laimet, Slidetek came to us from Finland, allowing us to produce lumber export quality with an accuracy of 1-2 mm. In Russia, they began to produce prototypes: "Magistral SPR-1100", TsDS-1100, etc.
All of them, as a rule, use saws with a diameter of 900-1100 mm. Price one saw, depending on the degree of its preparation, ranges from 300 to 700 dollars. One saw is capable of sawing up to 3000 cubic meters of edged lumber, it is sharpened directly on the machine. But once a week, the saw requires balancing and shaping the teeth. This will require a sharpening machine for circular saws or a semi-automatic grinding machine, for example, TchPA-7 of the Kirov Machine Tool Plant. Steel blades dull fairly quickly. In winter, sharpening is required 2 times per shift, and in summer up to 4-5 times per shift.
Possible use carbide And stellited drank. And carbide saws it is better to apply in the summer, and stellited - in the winter. Maintaining the tool in working condition and making boards with export geometry require a qualified sawmill. Most sawmills do not have such and produce a board that can only be sold on the Russian, unpretentious market.
The cutting width of a saw with a thickness of 4 mm is 6-10 mm. The cut is individual, it does not require subsorting of diameters. The yield coefficient for edged lumber is actually 52-56%. If you cut the slab into a picket fence - 56-58%.
Circular technology has the highest cutting speed: a six-meter log is cut in 8-14 seconds, a board is cut in 4 seconds. Productivity is quite high (up to 15 cubic meters per eight-hour shift). Allows you to work at temperatures up to -30 ° C.
Accordingly, it has low tool costs: 3-4 saws can be sawed for two years. Cutting stability is high when the log is not very dirty. The machine performs the functions of a product conveyor in the workshop, which is not unimportant. The Russian machine has not very reliable, but easily accessible and inexpensive hydraulic elements: hydraulic motors, pumps, distributors. And most importantly, it is 3-4 times cheaper than its imported counterparts, while, of course, inferior to them in reliability.
Recommended for creating production of small and medium capacity as the base element of the first row. It is suitable both for the manufacture of finished edged lumber, and for breaking logs into large pieces for further processing on highly economical band saws.
2. Charcoal circular saws
There is a whole class of circular log saws called "corners". It can be two or three saws at once installed at an angle of 90 degrees to each other. For example, machines "Grizzly", "Bobr-2000", DP-1200, "Vyatka 600", "Alpha". As well as machines with a single rotary saw blade, such as the Slovak UH500 and UP700. The Bars machine has two independent saws installed at an angle of 90 degrees, and unlike imported prototypes, it performs the functions of transporting lumber around the workshop.
Machines of this class have a number of undeniable advantages: they can cut logs with a diameter of more than a meter, having a K yield of up to 70%; use saws with hard-alloy tips D=500-800 mm of rather low cost; cope well with dirty logs, because they have carbide tips; require sharpening once a day or less; have an unsurpassed sawing accuracy of 1 mm.
It is recommended to apply for the processing of thick gauge and, first of all, for the production of radial sawn timber. In particular, Slovak machines and Russian "Bars" are very good for radial sawing of larch into a blank for lamella.
The Russian market also has inexpensive machines angle saw blade, quite a substitute for small business band sawmill, but not having problems with the geometry of the lumber - "North 550", PDU1.
 3. Horizontal circular saws
3. Horizontal circular saws
There is another variety of circular saws, confirming that the possibilities of circular technology are far from being exhausted. These are machines with horizontal arrangement of two saws in one plane. Representatives here are the Slovak machine KP58 and the Russian Bars DG, Toyma 600.
Advantages: the machines are powerful enough and can process logs with a diameter of up to 500 mm; there is no need to frequently change the saws, they work for at least 24 hours without sharpening; productivity when using a loader and a log turner can reach 6-12 or more cubic meters per 8-hour shift; provide good surface quality and geometry of lumber.
As you may have guessed, there is no universal woodworking technology. The sawmill should be selected for the raw materials that you are going to saw and the products that you are going to produce.
Vladislav Permin, especially for the site
EXPERTS' OPINIONS
Dmitry Bychkov, director of Kamsky Bereg LLC (www.kbstanok.ru):
The main selection criterion is the operating costs per 1 cubic meter of lumber. Accordingly (ceteris paribus), the higher the productivity, the lower the cost.
Find professionals, study the experience of other industries, study the situation on the lumber market - demand is subject to seasonal fluctuations, profitability is, on average, low, it is very difficult to work on purchased raw materials. Profitability also depends on the depth of wood processing. And remember: the sharpener is the most important worker, since the profit of the woodworker is on the edge of the saw tooth.
I would also mention such a class of equipment as first-row cant saws and second-row multi-blade saws of the through-type. In the Russian Federation, heavy beams (log diameter up to 500 mm) are now made only by two companies - Ecodrev-Machinery (Arctant) and we, Kamsky Bereg-Stankostroy (Vityaz 640M). If you need to process from 100 cubic meters per shift, there are no other options for domestic production. If the sawlog is up to 300 mm (thinner), you can use disk logs for the thinner (“Vepr 700”).
Disc gang saws are a reliable and widespread solution for serious business. Their use requires a high degree of mechanization of the site, but the cost of a mechanized complete sawing line is quickly justified due to the high flow rate, low operating costs and high reliability of the equipment.
Artur Zaynutdinov, CEO TF ExpoForm LLC (www.expoform.ru):
Now the Russian market is dominated by a wide range of woodworking equipment, both from well-known and not so well-known manufacturers. When choosing it, first of all, you need to look at the service support of the purchased equipment. Often equipment is purchased with very favorable price or a complete set, and then problems with the supply of spare parts and service support begin. You should always choose as a supplier a well-known company in the market that supplies reliable equipment from a trusted manufacturer.
The second point worth paying attention to is the quality of assembly, materials and components used in the manufacture of specific equipment. Budget equipment has an advantage at the stage when production is just opening and funds are needed for promotion, but you want to equip production with everything as much as possible necessary equipment. But you must always remember that after some time the question of repairing or replacing equipment will arise.
It is no secret that most often we encounter poor quality when purchasing equipment from South-East Asia especially from China. There are also complaints about European manufacturers whose production or assembly sites are located in the above regions.
It is important to remember that good quality equipment is also valued in the secondary market and it is always easier and faster to sell it. Therefore, sometimes it is better to buy the right machine well-known manufacturer in the secondary market than to buy a new machine, painted bright colors, with shiny handles and a lot of dubious quality bells and whistles.






