Control cabinet designation in the diagram. Conditional graphic and letter designations of electrical radioelements. Each diagram displays
When conducting electrical works each person, one way or another, is faced with the symbols that are in any electrical circuit. These diagrams are very diverse, with different functions, however, all graphic conventions are reduced to the same form and in all diagrams correspond to the same elements.
The main symbols in the electrical circuits of GOST are shown in the tables








Currently, not only domestic elements are used in electrical engineering and radio electronics, but also products manufactured by foreign firms. Imported electrical radioelements make up a huge assortment. They're in mandatory are displayed in all drawings as a legend. They determine not only the values of the main electrical parameters, but also a complete list of them included in a particular device, as well as the relationship between them.
To read and understand the contents of the wiring diagram
It is necessary to study well all the elements that make up its composition and the principle of operation of the device as a whole. Usually, all information is found either in reference books or in the specification attached to the schema. Positional designations characterize the relationship of the elements included in the device kit, with their designations on the diagram. In order to graphically designate one or another electrical radio element, standard geometric symbols are used, where each product is depicted separately, or in combination with others. The meaning of each individual image largely depends on the combination of symbols with each other.
Each diagram displays
Connections between separate elements and guides. In such cases, the standard designation of the same components and elements is of no small importance. For this, there are reference designations, where the types of elements, their design features and numerical values are displayed in literal expression. Elements used in general order, are indicated in the drawings as qualification, characterizing current and voltage, regulation methods, types of connections, pulse shapes, electronic communication, and others.
Built on the basis of the symbols of contacts: closing (Fig. 1, b), opening (c, d) and switching (d, f). Contacts that simultaneously close or open two circuits are designated, as shown in Fig. 1, (g, u and).
For the initial position of the closing contacts on electrical circuits ah, the open state of the switched electrical circuit is accepted, opening - closed, switching - the position in which one of the circuits is closed, the other is open (the exception is contact with the neutral position). UGO of all contacts is allowed to be depicted only in mirrored or rotated 90 ° positions.
The standardized UGO system provides for the reflection of such design features, as non-simultaneous actuation of one or more contacts in a group, their absence or presence in one of the positions.
So, if it is necessary to show that the contact closes or opens earlier than others, the symbol of its moving part is supplemented with a short stroke directed towards the actuation (Fig. 2, a, b), and if later, with a stroke directed to reverse side(Fig. 2, c, d).
The absence of fixation in a closed or open position (self-return) is denoted by a small triangle, the apex of which is directed towards the initial position of the movable part of the contact (Fig. 2, e, f), and fixation by a circle on the symbol of its stationary part (Fig. 2, g, and).
The last two UGOs on electrical circuits are used in cases where it is necessary to show a type of switching product, whose contacts usually do not possess these properties.
The conventional graphic designation of switches on electrical circuits (Fig. 3) is based on the symbols of the make and break contacts. This means that the contacts are fixed in both positions, that is, they do not have self-return.

Rice. 3.
The letter code of the products of this group is determined by the switched circuit and the design of the switch. If the latter is placed in a control, signaling, measurement circuit, it is designated Latin letter S, and if into the power circuit - with the letter Q. The control method is reflected in the second letter of the code: pushbutton switches and switches are designated with the letter B (SB), automatic - with the letter F (SF), all others - with the letter A (SA).
If there are several contacts in the switch, the symbols of their moving parts on electrical circuits are placed in parallel and connected with a mechanical connection line. As an example, Fig. 3 shows the conventional graphic designation of the SA2 circuit breaker, containing one NC and two NO contacts, and SA3, consisting of two NO contacts, one of which (in the figure - the right one) closes later than the other.
Switches Q1 and Q2 are used for switching power circuits. Contacts Q2 are mechanically connected to any control element, as evidenced by a segment of a dashed line. When displaying contacts in different sites circuits, their belonging to one switching product is traditionally reflected in (SA 4.1, SA4.2, SA4.3).
Rice. 4.
Similarly, based on the symbol of the switching contact, conditional graphic symbols two-position switches (fig. 4, SA1, SA4). If the switch is fixed not only in the extreme, but also in the middle (neutral) position, the symbol of the moving part of the contact is interfered with between the symbols of the fixed parts, the possibility of turning it in both directions is shown by a dot (SA2 in Fig. 4). The same is done if it is necessary to show on the diagram a switch that is fixed only in the middle position (see Fig. 4, SA3).
Distinctive feature of UGO pushbutton switches and switches - a button symbol connected to the designation of the moving part of the contact by a mechanical link (Fig. 5). In this case, if the conventional graphic designation is built on the basis of the main contact symbol (see Fig. 1), then this means that the switch (switch) is not fixed in the pressed position (when the button is released, it returns to its original position).

Rice. 5.

Rice. 6.
If it is necessary to show fixation, use the symbols of contacts with fixation specially designed for this purpose (Fig. 6). The return to the initial position when another switch button is pressed is shown in this case with the sign of the locking mechanism, attaching it to the symbol of the moving part of the contact from the side opposite to the symbol of the button (see Fig. 6, SB1.1, SB 1.2). If the return occurs when the button is pressed again, the sign of the locking mechanism is depicted instead of the mechanical link (SB2).
(for example, biscuit) denote, as shown in Fig. 7. Here SA1 (for 6 positions and 1 direction) and SA2 (for 4 positions and 2 directions) are switches with outputs from moving contacts, SA3 (for 3 positions and 3 directions) - without outputs from them. The conventional graphic designation of individual contact groups is shown in the diagrams in the same position, belonging to the same switch is traditionally shown in the reference designation (see Fig. 7, SA1.1, SA1.2).
Rice. 7.

Rice. eight
To display multi-position switches with complex commutation, GOST provides several methods. Two of them are shown in Fig. 8. Switch SA1 - 5 positions (they are indicated by numbers; letters a-d introduced for clarification only). In position 1, chains a and b, d and e are connected to one another, in positions 2, 3, 4 - chains b and d, a and c, a and e, respectively, in position 5 - chains a and b, c and d ...
Switch SA2 - 4 positions. In the first of them, circuits a and b are closed (this is indicated by the points located under them), in the second - circuits c and d, in the third - c and d, in the fourth - b and d.
A. Yu. Zorin
Reading electrical diagrams is a necessary skill to represent the operation of electrical networks, nodes, as well as various equipment... Not a single specialist will begin to install the equipment until he or she reads the accompanying regulatory documents.
Schematic electrical diagrams allow the developer to convey a complete report on the product in a condensed form to the user, using conventionally graphic symbols (UGO). To avoid confusion and defects when assembling according to drawings, alphanumeric symbols are included in unified system design documentation (ESKD). Everything schematic diagrams are developed and applied in full compliance with GOSTs (21.614, 2.722-68, 2.763-68, 2.729-68, 2.755-87). The GOST describes the elements, provides a decoding of the values.
Reading drawings
The schematic diagram shows all the elements, parts and networks that make up the drawing, electrical and mechanical connections. Reveals the full functionality of the system. All elements of any electrical circuit correspond to the designations positioned in GOST.
A list of documents is attached to the drawing, in which all the elements and their parameters are prescribed. The components are listed in alphabetical order with numerical sorting. The list of documents (specification) is indicated on the drawing itself, or made out in separate sheets.
How to study drawings
First, the type of drawing is determined. According to GOST 2.702-75, each graphic document corresponds to an individual code. All electrical drawings have the letter designation "E" and the corresponding numerical value from 0 to 7. The electrical circuit diagram corresponds to the code "E3".
Reading the circuit diagram:
- Visually familiarize himself with the presented drawing, pay attention to the indicated notes and technical requirements.
- Find on the schematic image all the components indicated in the document list;
- Determine the power source of the system and the type of current (single-phase, three-phase);
- Find the main nodes, and determine their power supply;
- Get acquainted with the elements and protection devices;
- To study the control method indicated on the document, its tasks and the algorithm of actions. Understand the sequence of actions of the device when starting, stopping, short circuit;
- Analyze the work of each section of the chain, determine the main components, auxiliary elements, study the technical documentation of the listed details;
- Based on the studied data of the document, draw a conclusion about the processes occurring in each link of the chain shown in the drawing.
Knowing the sequence of actions, alphanumeric designations, you can read any electrical diagram.

Graphic symbols
The schematic diagram has two types - single-line and complete. On a single-line drawing only power wire with all elements, if the main network does not differ in individual additions from the standard one. Two or three slashes applied to the wire line denote a single-phase or three-phase network, respectively. The entire network is drawn in full and the generally accepted symbols in the electrical circuits are put down.
Single line electrical circuit, single phase network

Types and meaning of lines
- Thin and thick solid lines - in the drawings depicts lines of electrical, group communication, lines on the elements of the UGO.
- Dashed line - indicates the shielding of the wire or devices; denotes a mechanical link (motor-gearbox).
- Thin dash-dotted line - designed to highlight groups of several components that make up parts of the device, or a control system.
- A dash-dotted line with two dots is a disconnecting line. Shows a sweep important elements... Indicates an object remote from the device, connected to the system by mechanical or electrical communication.


Network trunks are shown in full, but according to the standards, they are allowed to be cut if they interfere with the normal understanding of the circuit. The break is indicated by arrows, next to them indicate the main parameters and characteristics of electrical circuits.
The bold point on the lines indicates the connection, the soldering of the wires.
Electromechanical components
Schematic representation of electromechanical links and contacts

A - UGO coil of an electromechanical element (magnetic starter, relay)
B - thermal relay
С - device coil with mechanical interlock
D - closing contacts (1), opening (2), switching (3)
E - button
F - designation of the switch (knife switch) on the electrical diagram of the UGO of some measuring instruments. A complete list of these elements is given in GOST 2.729 68 and 2.730 73.
Elements of electrical circuits, devices

| Number in the picture | Description | Number in the picture | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Electricity meter | 8 | Electrolytic capacitor |
| 2 | Ammeter | 9 | Diode |
| 3 | Voltmeter | 10 | Light-emitting diode |
| 4 | temperature sensor | 11 | Diode optocoupler |
| 5 | Resistor | 12 | Npn transistor picture |
| 6 | Rheostat (variable resistor) | 13 | Fuse |
| 7 | Capacitor |
UGO time relays, buttons, switches, limit switches are often used in the development of electric drive circuits.

Schematic representation of a fuse. When reading the electrical diagram, you should carefully consider all the lines and parameters of the drawing so as not to confuse the purpose of the element. For example, the fuse and resistor are slightly different. In the diagrams, the power line is shown passing through the fuse, the resistor is drawn without internal elements.

Full diagram of a circuit breaker
Contact switching device. Serves automatic protection electrical network from accidents, short circuits. It can be powered mechanically or electrically.

Single line circuit breaker

The transformer is steel core with two windings. There is one and three-phase, step-up and step-down. It is also subdivided into dry and oil, depending on the cooling method. Power ranges from 0.1 MVA to 630 MVA (in Russia).
UGO transformers
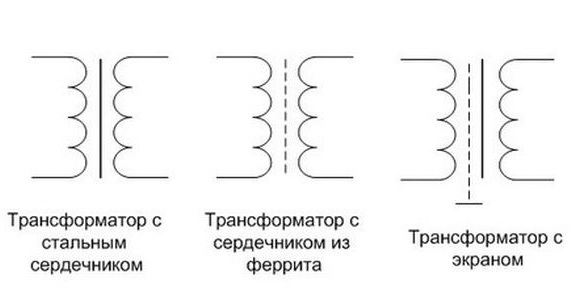
Designation of current transformers in the full (a) and single-line (c) diagrams

Graphic designation of electrical machines (EM)
Electric motors, depending on the type, are capable of not only consuming energy. When developing industrial systems, use motors that generate energy into the network when there is no load, thereby reducing costs.
A - Three-phase electric motors:
1 - Asynchronous with a squirrel-cage rotor
2 - Asynchronous with squirrel-cage rotor, two-speed
3 - Asynchronous with a phase rotor
4 - Synchronous electric motors; generators.
B - DC collector motors:
1 - with excitation of the winding from a permanent magnet
2 - Electric machine with an excitation coil
In conjunction with electric motors, the diagrams show magnetic starters, soft starters, a frequency converter... These devices are used to start electric motors, the smooth operation of the system. The last two elements protect the network from voltage “sag” in the network.
UGO magnetic starter on the diagram

Switches function as switching equipment. Disconnect and include in the work of certain sections of the network, as needed.
Graphical symbols in electrical diagrams of mechanical switches

Conditional graphic designations of sockets and switches in electrical circuits. Include in the developed drawings of electrification of houses, apartments, industries.


A bell on the electrical diagram according to UGO standards with a designated size

Dimensions of UGO in electrical circuits
On the diagrams, the parameters of the elements included in the drawing are applied. Full information about the element, capacitance, if it is a capacitor, rated voltage, resistance for the resistor are registered. This is done for convenience, so as not to make a mistake during installation, not to waste time on calculating and selecting the components of the device.
Sometimes the nominal data is not indicated, in this case the parameters of the element do not matter, you can select and install a link with a minimum value.
The accepted dimensions of the UGO are prescribed in the GOST standards of the ESKD standard.
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Dimensions in ESKD
The dimensions of graphic and letter images in the drawing, the thickness of the lines should not differ, but it is permissible to change them proportionally in the drawing. If in the symbols on various electrical circuits of GOST, there are elements that do not have information about the sizes, then these components are performed in sizes corresponding to the standard image of the UGO of the entire circuit.
UGO of the elements that make up the main product (device) can be drawn in a smaller size in comparison with other elements.
Along with UGO for more precise definition the names and purposes of the elements, the letter designation is applied to the diagrams. This designation is used for links in text documents and for drawing on an object. Using the letter designation, the name of the element is determined, if this is not clear from the drawing, technical specifications, number.
Additionally, one or more numbers are indicated with a letter designation, usually they explain the parameters. Additional letter code, indicating the denomination, model, additional data is prescribed in the accompanying documents, or is placed in a table in the drawing.
To learn how to read electrical circuits, it is not necessary to know all the letter designations by heart, graphic images various elements, it is enough to navigate in the corresponding GOST ESKD. The standard includes 64 GOST documents that disclose the main provisions, rules, requirements and designations.
The main symbols used in the diagrams according to the ESKD standard are shown in Tables 1 and 2.
Table 1
|
First letter of code (required) |
Element view group | Examples of element types |
| A | Devices | Amplifiers, telecontrol devices, lasers, masers |
| B | Loudspeakers, microphones, thermoelectric sensors, ionizing radiation detectors, pickups, selsyns | |
| C | Capacitors | |
| D | Integrated analog digital circuits, logic elements, memory devices, delay devices | |
| E | The elements are different | Lighting devices, heating devices |
| F | Discrete current and voltage protection elements, fuses, arresters | |
| G | Generators, power supplies, quartz oscillators | Batteries, accumulators, electrochemical and electrothermal sources |
| H | Indicating and signaling devices | Sound and light alarm devices, indicators |
| K | Relays, contactors, starters | Current and voltage relays, electric thermal relays, time relays, contactors, magnetic starters |
| L | Fluorescent light chokes | |
| M | Engines | DC and AC motors |
| P | Showing, registering and measuring instruments, counters, hours | |
| Q | Disconnectors, short-circuits, circuit breakers (power) | |
| R | Resistors | Variable resistors, potentiometers, varistors, thermistors |
| S | Switching devices in control, signaling and measuring circuits | Switches, switches, switches, triggered by various influences |
| T | Current and voltage transformers, stabilizers | |
| U | Converters of electrical quantities to electrical, communication devices | Modulators, demodulators, discriminators, inverters, frequency converters, rectifiers |
| V | Electronic tubes, diodes, transistors, thyristors, zener diodes | |
| W | Microwave lines and elements, antennas | Waveguides, dipoles, antennas |
| X | Contact connections | Pins, sockets, dismountable joints, collectors |
| Y | Electromagnetic clutches, brakes, chucks | |
| Z | Terminal devices, filters, limiters | Modeling lines, quartz filters |
The main two-letter designations are shown in Table 2
| First letter of code (required) | Element view group | Examples of element types | Two-letter code |
| A | Device (general designation) | ||
| B | Converters of non-electrical quantities to electrical quantities (excluding generators and power supplies) or vice versa analog or multi-digit converters or sensors for indicating or measuring | Speaker | BA |
| Magnetostrictive element | BB | ||
| Detector of ionizing elements | BD | ||
| Selsin - receiver | BE | ||
| Telephone (capsule) | Bf | ||
| Selsin - sensor | BC | ||
| Thermal sensor | BK | ||
| Photocell | BL | ||
| Microphone | BM | ||
| Pressure sensor | BP | ||
| Piezoelectric element | BQ | ||
| RPM sensor (tachogenerator) | BR | ||
| Pickup | BS | ||
| Speed sensor | BV | ||
| C | Capacitors | ||
| D | Integrated circuits, microassemblies | Analog integrated circuit | DA |
| Integrated circuit, digital, logic element | DD | ||
| Information storage device | DS | ||
| Delay device | DT | ||
| E | The elements are different | A heating element | EK |
| Lighting lamp | EL | ||
| Igniter | ET | ||
| F | Arresters, fuses, protective devices | Discrete instantaneous current protection element | FA |
| Discrete inertial current protection element | FP | ||
| Fuse fuse | FU | ||
| Discrete voltage protection element, arrester | FV | ||
| G | Generators, power supplies | Battery | GB |
| H | Indicator and signal elements | Sound alarm device | HA |
| Character indicator | HG | ||
| Light signaling device | HL | ||
| K | Relays, contactors, starters |
Relay current | KA |
| Indicator relay | KH | ||
| Electric thermal relay | KK | ||
| Contactor, magnetic starter | KM | ||
| Time relay | KT | ||
| Voltage relay | KV | ||
| L | Inductors, chokes | Fluorescent light choke | LL |
| M | Engines | - | - |
| P | Instruments, measuring equipment | Ammeter | PA |
| Pulse counter | PC | ||
| Frequency meter | PF | ||
| Note. The combination of PE is not allowed | Active energy meter | PI | |
| Reactive energy meter | PK | ||
| Ohmmeter | PR | ||
| Recording device | PS | ||
| Clock, action time meter | PT | ||
| Voltmeter | PV | ||
| Wattmeter | PW | ||
| Q | Switches and disconnectors in power circuits | Automatic switch | QF |
| Short-circuiter | QK | ||
| Disconnector | QS | ||
| R | Resistors | Thermistor | RK |
| Potentiometer | RP | ||
| Measuring shunt | Rs | ||
| Varistor | RU | ||
| S | Switching devices in control, signaling and measuring circuits. Note. The designation SF is used for devices without power circuit contacts. |
Switch or switch | SA |
| Push-button switch | SB | ||
| Automatic switch | SF | ||
| Switches triggered by various influences: - from the level |
SL | ||
| - from pressure | SP | ||
| - from position (track) | SQ | ||
| - from the frequency of rotation | SR | ||
| - from temperature | SK | ||
| T | Transformers, autotransformers | Current transformer | TA |
| Electromagnetic stabilizer | TS | ||
| Voltage transformer | TV | ||
| U | Communication devices. Converters of electrical quantities to electrical |
Modulator | UB |
| Demodulator | UR | ||
| Discriminator | UI | ||
| Frequency converter, inverter, frequency generator, rectifier | UZ | ||
| V | Electrovacuum and semiconductor devices | Diode, Zener diode | VD |
| Electrovacuum device | VL | ||
| Transistor | VT | ||
| Thyristor | VS | ||
| W | Microwave lines and elements Antennas | Coupler | WE |
| Short-circuiter | Wk | ||
| Valve | Ws | ||
| Transformer, discontinuity, phase shifter | WT | ||
| Attenuator | WU | ||
| Antenna | WA | ||
| X | Contact connections | Current collector, sliding contact | XA |
| Pin | XP | ||
| Nest | XS | ||
| Collapsible connection | XT | ||
| High frequency connector | XW | ||
| Y | Mechanical devices with electromagnetic drive | Electromagnet | Ya |
| Electromagnetic brake | YB | ||
| Electromagnetic clutch | YC | ||
| Electromagnetic chuck or plate | YH | ||
| Z | Terminal devices Filters. Limiters | Limiter | ZL |
| Quartz filter | ZQ |
Related Videos
An electrical diagram is a type of technical drawing that indicates various electrical elements in the form of symbols. Each element has its own designation.
All conventional (conventional-graphic) symbols on electrical circuits consist of simple geometric shapes and lines. These are circles, squares, rectangles, triangles, simple lines, dotted lines, etc. The designation of each electrical element consists of a graphic part and an alphanumeric part.
Thanks to the huge variety of electrical components, it becomes possible to create highly detailed electrical diagrams that are understandable to almost every electrician.
Each element in the electrical diagram must be carried out in accordance with GOST. Those. except for the correct display of the graphic image on the electrical diagram, all standard sizes each element, line thickness, etc.
There are several basic types of electrical circuits. This is a single-line, schematic, wiring diagram (connection diagram). There are also schemes general view- structural, functional. Each species has its own purpose. The same item on different schemes can be denoted in the same way or in different ways.
The main purpose of a single-line diagram is a graphical display of the power supply system (power supply to the facility, electrical wiring in the apartment, etc.). Simply put, a single-line diagram depicts the power section of an electrical installation. By the name, you can understand that the single-line diagram is executed in the form of a single line. Those. electrical power supply (both single-phase and three-phase) supplied to each consumer is indicated by a single line.
To indicate the number of phases, special serifs are used on the graphic line. One notch indicates that the power supply is single-phase, three notches indicate that the power is three-phase.
In addition to the single line, the designations of protective and switching devices are used. The first devices include high-voltage switches (oil, air, SF6, vacuum), circuit breakers, devices protective shutdown, differential circuit breakers, fuses, load break switches. The second includes disconnectors, contactors, magnetic starters.

High voltage circuit breakers in single line diagrams are depicted as small squares. As for automatic switches, RCDs, differential circuit breakers, contactors, starters and other protective and switching equipment, they are depicted in the form of a contact and some explanatory graphic additions, depending on the device.
Wiring diagram (connection diagram, connection, location) is used for direct production electrical works... Those. these are working drawings, using which the installation and connection of electrical equipment is carried out. Also, according to the wiring diagrams, separate electrical devices(electrical cabinets, electrical panels, control panels, etc.).


The wiring diagrams depict all wiring connections both between individual devices (circuit breakers, starters, etc.), and between different kinds electrical equipment (electrical cabinets, shields, etc.). For correct connection wired connections on wiring diagram depicts electrical terminal blocks, conclusions electrical apparatus, brand and section electrical cables, numbering and lettering of individual wires.
Electrical schematic diagram - the most complete scheme with all electrical elements, connections, letter designations, technical characteristics of apparatus and equipment. According to the schematic diagram, other electrical circuits are performed (installation, single-line, equipment layout, etc.). The schematic diagram shows both the control circuits and the power section.

Control circuits (operational circuits) are buttons, fuses, coils of starters or contactors, contacts of intermediate and other relays, contacts of starters and contactors, phase (voltage) control relays, as well as connections between these and other elements.
The power section depicts circuit breakers, power contacts of starters and contactors, electric motors, etc.
In addition to the graphic image itself, each element of the circuit is supplied with an alphanumeric designation. For example, a circuit breaker in a power circuit is designated QF. If there are several machines, each is assigned its own number: QF1, QF2, QF3 etc. The coil (winding) of the starter and contactor is designated KM. If there are several of them, the numbering is similar to the numbering of the machines: KM1, KM2, KM3 etc.

In each circuit diagram, if there is any relay, then at least one blocking contact of this relay is necessarily used. If the circuit contains an intermediate relay KL1, two contacts of which are used in the operational circuits, then each contact receives its own number. The number always starts with the number of the relay itself, and then comes the serial number of the contact. In this case, it turns out KL1.1 and KL1.2. The designations of auxiliary contacts of other relays, starters, contactors, automatic machines, etc. are carried out in the same way.
In electrical schematic diagrams, in addition to electrical elements, electronic designations are very often used. These are resistors, capacitors, diodes, LEDs, transistors, thyristors and other elements. Each electronic element on the diagram also has its own letter and number designation. For example, a resistor is R (R1, R2, R3 ...). Capacitor - C (C1, C2, C3 ...) and so on for each element.
In addition to graphic and alphanumeric designations on some electrical components indicated specifications... For example, for a circuit breaker, this is the rated current in amperes, the cut-off trip current is also in amperes. For an electric motor, the power is indicated in kilowatts.
For the correct and correct drawing up of electrical circuits of any kind, it is necessary to know the designations of the elements used, state standards, the rules for registration of documentation.
If for an ordinary person the perception of information occurs when reading words and letters, then for locksmiths and assemblers they are replaced by alphabetic, digital or graphic designations. The difficulty is that while the electrician finishes his studies, gets a job, learns something in practice, how new SNiPs and GOSTs appear, according to which adjustments are made. Therefore, you should not try to learn all the documentation right away. It is enough to gain basic knowledge, and add actual data in the course of working days.
For circuit designers, instrumentation locksmiths, electricians, the ability to read wiring diagrams is a key quality and an indicator of qualifications. Without special knowledge, it is impossible to immediately understand the intricacies of designing devices, circuits and methods of connecting electrical nodes.
Types and types of electrical circuits
Before you start studying the existing designations of electrical equipment and its connections, you need to understand the typology of the diagrams. On the territory of our country, standardization has been introduced in accordance with GOST 2.701-2008 dated 1.07.2009, according to “ESKD. Schemes. Types and types. General requirements».
Based on this standard, all schemes are divided into 8 types:
- United.
- Located.
- General.
- Connections.
- Installation connections.
- Complete principled.
- Functional.
- Structural.
Among the existing 10 types indicated in this document, there are:
- Combined.
- Divisions.
- Energy.
- Optical.
- Vacuum.
- Kinematic.
- Gas.
- Pneumatic.
- Hydraulic.
- Electrical.
For electricians, it is of the greatest interest among all the above types and types of circuits, as well as the most demanded and often used in work - an electrical circuit.
The last GOST, which came out, was supplemented with many new designations, which is relevant today with the cipher 2.702-2011 dated 1.01.2012. The document is called “ESKD. Rules for the implementation of electrical circuits ", refers to other GOSTs, including the one mentioned above.
The text of the regulation sets out clear requirements in detail for all types of wiring diagrams. Therefore, be guided by installation works with electrical diagrams follows exactly this document. The definition of the concept of an electrical circuit, according to GOST 2.702-2011, is as follows:
"An electrical circuit should be understood as a document containing conventional designations of parts of the product and / or individual parts with a description of the relationship between them, the principles of operation from electrical energy."
Once defined, the document contains the rules for the implementation on paper and in software environments for designations of contact connections, wire markings, letter designations and a graphic representation of electrical elements.
It should be noted that more often in home practice, only three types of electrical circuits are used:
- Mounting- the device displays printed circuit board with the arrangement of elements with a clear indication of the place, value, principle of attachment and connection to other parts. The wiring diagrams for residential premises indicate the number, location, rating, connection method and other precise instructions for installing wires, switches, lamps, sockets, etc.
- Principal- they indicate in detail the connections, contacts and characteristics of each element for networks or devices. Distinguish between complete and linear concepts. In the first case, control, control of elements and the power circuit itself are depicted; in a linear scheme, they are limited only to the circuit with the image of the remaining elements on separate sheets.
- Functional- here, without detailing the physical dimensions and other parameters, the main nodes of the device or circuit are indicated. Any detail can be shown as a block with a letter designation, supplemented by links with other elements of the device.
Graphic symbols in electrical circuits
The documentation, which indicates the rules and methods of graphical designation of circuit elements, is represented by three GOSTs:
- 2.755-87 - graphic symbols of contact and switching connections.
- 2.721-74 - graphic symbols of parts and assemblies of general use.
- 2.709-89 - graphic symbols in wiring diagrams of sections of circuits, equipment, contact connections of wires, electrical elements.
In the standard with the code 2.755-87, it is used for single-line electrical switchboard circuits, conditional graphic images (UGO) of thermal relays, contactors, circuit breakers, circuit breakers, and other switching equipment. There is no designation in the standards for difavtomats and RCDs.
On the pages of GOST 2.702-2011, it is allowed to display these elements in an arbitrary order, with explanations, decoding of the UGO and the circuit itself of difavtomats and RCDs.
GOST 2.721-74 contains UGOs used for secondary electrical circuits.
IMPORTANT: To designate switching equipment, there are:
4 basic images of UGO
9 functional signs of UGO
| UGO | Name |
| Arc extinguishing | |
| Without self-return | |
| Self-return | |
| Limit or travel switch | |
| With automatic triggering | |
| Switch disconnector | |
| Disconnector | |
| Switch | |
| Contactor |
IMPORTANT: Designations 1 - 3 and 6 - 9 are applied to fixed contacts, 4 and 5 - are placed on movable contacts.
Basic UGO for single-line circuits of electrical panels
| UGO | Name |
| Thermal relay | |
| Contactor contact | |
| Switch - load switch | |
| Automatic - circuit breaker | |
| Fuse | |
| Differential circuit breaker | |
| RCD | |
| Voltage transformer | |
| Current transformer | |
| Switch (load switch) with fuse | |
| Motor protective circuit breaker (with built-in thermal relay) | |
| A frequency converter | |
| Electricity meter | |
| Closing contact with "reset" button or other push button switch, with return and opening by means of a special drive of the control element | |
| N / O contact with push button switch, with return and opening by pulling in the control button | |
| N / O contact with push-button switch, with return and opening by pressing the button of the control element again | |
| Closing contact with push-button switch, with return and opening automatically of the control element | |
| Closing contact with delayed action, which is initiated on return and trip | |
| Closing contact with delayed action, which is only triggered when triggered | |
| Closing contact with delayed action, which is activated upon return and trip | |
| Closing contact with delayed action, which only picks up on return | |
| Closing contact with delayed action, which only turns on when triggered | |
| Time relay coil | |
| Photo relay coil | |
| Pulse relay coil | |
| General designation of a relay coil or contactor coil | |
| Indicator lamp (light), lighting | |
| Motor drive | |
| Terminal (dismountable connection) | |
| Varistor, surge arrester (surge suppressor) | |
| Arrester | |
Socket (plug connection):
|
|
| A heating element |
Designation of measuring electrical devices for characterizing circuit parameters
GOST 2.271-74, the following designations are adopted in electrical panels for buses and wires:

Letter designations in electrical diagrams
The standards for the letter designation of elements on electrical circuits are described in the standard GOST 2.710-81 with the name of the text “ESKD. Alphanumeric designations in electrical circuits ". The mark for difavtomats and RCDs is not indicated here, which is prescribed in clause 2.2.12 of this standard as a designation with multi-letter codes. For the main elements of electrical panels, the following letter coding is adopted:
| Name | Designation |
| Automatic switch in the power circuit | QF |
| Automatic switch in the control circuit | SF |
| Circuit breaker with differential protection or difavtomat | QFD |
| Switch or load switch | QS |
| RCD (residual current device) | QSD |
| Contactor | KM |
| Thermal relay | F, KK |
| Time relay | KT |
| Voltage relay | KV |
| Impulse relay | KI |
| Photo relay | KL |
| Surge arrester, arrester | FV |
| Fuse fuse | FU |
| Voltage transformer | TV |
| Current transformer | TA |
| A frequency converter | UZ |
| Ammeter | PA |
| Wattmeter | PW |
| Frequency counter | PF |
| Voltmeter | PV |
| Energy meter active | PI |
| Reactive energy meter | PK |
| Heating element | EK |
| Photocell | BL |
| Lighting lamp | EL |
| Light bulb or indicator light | HL |
| Plug or socket | XS |
| Switch or switch in control circuits | SA |
| Pushbutton switch in control circuits | SB |
| Terminals | XT |
The image of electrical equipment on the plans
Despite the fact that GOST 2.702-2011 and GOST 2.701-2008 take into account such a type of wiring diagram as a "layout" for the design of structures and buildings, it is necessary to be guided by the standards GOST 21.210-2014, which indicate "SPDS.
Images on the plans of conditional graphic wiring and electrical equipment ". The document established UGO on the plans for laying electrical networks for electrical equipment (lamps, switches, sockets, electrical panels, transformers), cable lines, busbars, tires.
The use of these symbols is used for drawing up drawings of electrical lighting, power electrical equipment, power supply and other plans. The use of these designations is also used in basic single-line diagrams of electrical panels.
Conditional graphic images of electrical equipment, electrical devices and electrical receivers
The contours of all depicted devices, depending on the information richness and complexity of the configuration, are taken in accordance with GOST 2.302 on the scale of the drawing according to the actual dimensions.

Conditional graphic symbols of lines of wires and conductors

Conditional graphic images of buses and busbars

IMPORTANT: The design position of the busbar trunking must exactly match on the diagram with the place of its attachment.
Conditional graphic images of boxes, cabinets, boards and consoles

Conventional graphic designations of switches, switches
On the pages of the GOST 21.210-2014 documentation, there is no separate designation for pushbutton switches, dimmers (dimmers). In some schemes, in accordance with clause 4.7. normative act arbitrary designations are used.
 Graphical symbols for socket outlets
Graphical symbols for socket outlets
 Conventional graphic symbols of lamps and projectors
Conventional graphic symbols of lamps and projectors
The updated version of GOST contains images of luminaires with fluorescent and LED lamps.

Conventional graphic designations of monitoring and control devices

Conclusion
The given graphic and letter images of electrical parts and electrical circuits are not complete list, since the regulations contain many special characters and ciphers, which are practically not used in everyday life. To read electrical diagrams, you will need to take into account many factors, first of all - the country of the manufacturer of the device or electrical equipment, wiring and cables. There is a difference in labeling and symbol on the diagrams, which can be pretty confusing.
Secondly, you should carefully consider areas such as the intersection or absence of a common network for wires located with a patch. On foreign diagrams, if the bus or cable does not have a common power supply with crossing objects, a semicircular continuation is drawn at the point of contact. This is not used in domestic circuits.
If the diagram is depicted without observing established by GOST standards, then it is called a sketch. But for this category, there are also certain requirements, according to which, according to the given sketch, an approximate understanding of the future wiring or design of the device should be drawn up. Figures can be used to draw up more accurate drawings and diagrams based on them, with the necessary designations, marking and compliance with scales.