Requirements for office space. Sanitary rules and regulations for office premises
Currently, tenants are placing increased demands on office space. Everything more companies wish to locate their office in a specially equipped building. Therefore, an increasing number of new or refurbished as a result of overhaul business centers specially designed for office rental in Moscow... These buildings are equipped modern systems life support. At the same time, heating, ventilation and air conditioning systems have automated control and weather-dependent regulation. Each tenant has the opportunity to set the desired parameters of the microclimate in the premises provided to him. Payment for energy resources must be made on a fact-of-use basis. For a modern office building, strict requirements are imposed on the energy efficiency of systems that ensure the maintenance of the permissible parameters of the internal environment, the consumption of thermal energy should not exceed 60 W / m2 of area. These requirements are met by a set of measures. The choice of materials for the building envelope ensures their thermal insulation characteristics... The cost of heating ventilation air in winter time using natural ventilation or unregulated separate supply and exhaust systems account for more than 50% of energy consumption for heating. To save energy resources for heating, ventilation systems with recuperation, as well as with controlled supply are used. fresh air... An increase in air exchange can be performed by a signal from the sensor for reaching the maximum permissible value of the carbon dioxide content or by a presence sensor.
Premises in buildings in which office rent in Moscow is provided must have a sufficient level of illumination of work surfaces according to sanitary standards - at least 400 lux. Natural light is provided during the day. At the same time, the location of 95% of the area of each of the working rooms from a source of natural light - windows - no more than 10 m. ceiling lamps, if necessary, local lighting is used. Window openings must be equipped with special sun protection devices that provide protection against direct sun rays but do not impede the penetration of natural light. For this are used design features buildings - canopies and ledges, and window blinds... Using curtains is less effective. For interior decoration walls and ceilings, it is advisable to use light colors.
 Special requirements apply to finishing materials... Widely used ceramic tiles, stone. These materials are durable, environmentally friendly, have low adsorption and are easily cleaned from contamination, therefore they provide a prestigious appearance and also make it easier to meet hygiene requirements.
Special requirements apply to finishing materials... Widely used ceramic tiles, stone. These materials are durable, environmentally friendly, have low adsorption and are easily cleaned from contamination, therefore they provide a prestigious appearance and also make it easier to meet hygiene requirements.
Proposed under rent office in Moscow must be provided with all types of communication: analog and digital telephone lines, Internet, as well as a digital integrated ISDN data transmission network inside the building. In addition, business centers may have a data center and a server room with the option of renting. A prerequisite is the systems fire safety and video surveillance. Typically, all digital building networks are integrated and have the ability to connect subscribers at organized workplaces.
The business center must operate own service management, cleaning services and maintenance of utility networks are provided.
A modern office is a place of joint work for groups of people, in connection with which such premises are subject to increased requirements for hygiene and sanitation. Otherwise, the spread of diseases caused by infections, high crowding, lack of ventilation, normal lighting, etc. among employees is possible. To avoid such consequences and organize acceptable conditions, sanitary standards have been developed for office space... They are regulated by the Labor Code of the Russian Federation, SanPiN, SNiP and many other legislative acts. The requirements for the sanitary condition of offices are numerous, so let's dwell on the main provisions in more detail.
Workplace. Sanitary rules and regulations in offices assume strictly fixed size workplace depending on the availability of equipment, employee health and other factors:
- with a PC and one LCD monitor - 4.5 sq. m (scanners, printers and other peripherals require additional space;
- in design bureaus, at least 6 square meters should be allocated per employee;
- for disabled employees, 5.65 sq. m per person, and for wheelchair users - 7.65 sq. m.
Modern workplace must be equipped with a personal computer, stationery, an ergonomic chair or chair, and a table. If the specifics of the enterprise require it, additional equipment must be installed in the office space - a copier, printers, scanners, etc. Cathode-ray tube monitors are being replaced today by LCD or plasma ones that do not have radiation harmful to the eyes.
Microclimate. Sanitary standards for office work prescribe mandatory equipment office natural or forced ventilation for a constant supply of fresh air. In offices not exceeding 100 sq. meters, only vents and windows are allowed. In rooms of average and big size should be installed exhaust ventilation... The air temperature from the installed equipment is also taken into account - if it exceeds 26 degrees, then forced air exchange is required. Installed system ventilation must produce minimal noise, be manageable and consume little electricity.
 Hygiene of employees. Any office space should have a restroom. Their number is calculated from the number of employees working at a time (in one shift), as well as the presence of people with disabilities among them. So, if less than 10 healthy people work in a 3-storey building, then it is possible to equip 1 toilet on all floors, but if there is a disabled person in the staff, toilets should be available at each level. Personal hygiene booths for women are usually larger than for men, due to physiological characteristics.
Hygiene of employees. Any office space should have a restroom. Their number is calculated from the number of employees working at a time (in one shift), as well as the presence of people with disabilities among them. So, if less than 10 healthy people work in a 3-storey building, then it is possible to equip 1 toilet on all floors, but if there is a disabled person in the staff, toilets should be available at each level. Personal hygiene booths for women are usually larger than for men, due to physiological characteristics.
Sanitary norms and rules for office premises provide for the presence of natural and artificial lighting that is optimal for work and does not cause fatigue. Light intensity measured in lux (1 lumen / m2) depends on the type of office building and its purpose:
- office general purpose- 200-300 Lx;
- large office with free planning - 400 lux;
- office for drawing works - 500 lux;
- conference room - 200 Lx.
These figures are set by Russian office lighting regulations, while European regulations increase these figures by about 200 Lx. Also great importance assigned to the placement of fixtures. It is believed that the most optimal lighting is natural, therefore in modern offices envisaged big windows for day work, and powerful daylight sources for night shifts.
A comfortable workplace is a guarantee of high productivity of an employee. Of course, comfort is a broad concept that often depends on the focus of a person's work. Sanitary norms and rules provided for manufacturing enterprises and office space vary. However, both the first and the second are established by SanPiN 2.24.54896 under the title "Hygienic standards of the microclimate in production."
Basic conditions
Since the beginning of 2017, new Sanitary and Hygienic Requirements for production facilities have been introduced. They were approved by the Chief State sanitary doctor by its Resolution No. 81 on June 21 last year. The updated SanPiN standards set requirements for:
- Microclimate;
- The level of noise and vibration;
- Exposure to electro-, magnetic and electromagnetic fields.
These norms are the boundary-possible indicators of factors. Compliance with the requirements for production facilities can protect employees who are at the workplace eight hours a day (forty hours a week) from the development of pathologies or occupational diseases associated with the specifics of the performance of work duties.
The introduction of new hygienic requirements for the microclimate of industrial premises cancels the previously approved standards. For example SanPiN 2.2.41191-03 regarding the effect of electromagnetic fields.
The most important issues regulated by SanPiNs are the temperature and microclimate at the workplace of office employees.
Temperature regime in the office
Maintaining a normal temperature is an important condition for the normal functioning of a company. The temperature in the office affects not only the health indicators of employees, but also their productivity, as well as the normal functioning of the entire enterprise.
Temperature standards are regulated by SanPin 2.2.4 548 96. The fifth and sixth sections of the Rules are devoted to optimization and boundary temperature indicators depending on the season (warm or cold).
Office workers, whose work can be attributed to the intellectual, characterized by a low level physical activity, as well as a sedentary position, the Labor Code and SanPin places them in category Ia. For this category of employees, a temperature of twenty-three to twenty-five degrees (in summer) and twenty-two to twenty-four degrees (in winter) must be provided.
If the temperature in the room does not meet the specified standards, employees have the right to require the employer to reduce the duration of work shifts.
If the temperature indicators exceed the value of plus twenty-nine, the labor time is reduced to three to six hours (in accordance with the functions performed). If the temperature in the office exceeds thirty-two degrees, it is forbidden to work for more than one hour.
There are indicators for the cold season. At temperatures below nineteen degrees, the duration of the shift is reduced by an hour. At temperatures below thirteen degrees, the working day cannot exceed one hour.
The work of an organization whose management constantly disrupts temperature regime premises can be temporarily stopped for up to three months.
Requirements for the microclimate in the office
Sanitary rules stipulate requirements not only for the temperature regime, but also for the quality of air in the office. Therefore, the ventilation equipment of the organization is one of the most important criteria for the comfort of workplaces.
Office service involves long-term presence of workers in the building. Each employee has their own preferences and needs for improving performance indicators. Some prefer coolness, others are afraid of drafts and air conditioning.
To create a comfortable office microclimate requires a set of measures aimed at meeting the standards:
- Temperature regime;
- Air humidity level;
- Ventilation of air streams;
- Air speed;
- The presence of foreign particles in the air (dust).
These standards are provided for by SanPin, as well as GOST 30494 96 regarding the parameters of the microclimate of residential and non-residential premises... A comfortable office microclimate in the warm season provides for:
- Temperature regime within twenty two to twenty five degrees;
- Air humidity thirty to sixty percent;
- The air flow rate is not higher than 0.25 meters per second.
For the cold season, the indicators change:
- Temperature readings range from twenty to twenty-two degrees;
- Air humidity - from thirty to forty-five percent;
- Air movement 0.1 - 0.15 meters per second.
Permissible differences in temperature readings are one to two degrees.
The moisture level is an essential component of the comfortable work of office workers. What should be the humidity directly depends on the temperature conditions of the room. High humidity at normal temperature does not negative impact on the human body. A dry warm air can cause diseases of the mucous membranes, upper respiratory tract.
Light level
Office lighting is an important component that employers should not forget. Low light levels lead to rapid eye fatigue, and also reduces the overall performance of a person.
SanPin sets the lighting standards for an average office, which houses a computer, at five hundred lux. The permissible values of room illumination are from two hundred to three hundred lux.
What if there is not enough light? It will be necessary to install an additional light source at each workplace. When choosing light bulbs, preference should be given to energy-saving ones with “cold” white light. Such lamps do not heat up, which is important for the summer period.
Noise level
Background noise affects the productivity of office workers. The upper limit of the norm of such noise should not exceed fifty-five dB. Old computers, lamps, conversations on the street make noise.
New office equipment can cope with the problem of extraneous noise, metal-plastic windows, partitions with sound insulation.
Responsibility of the employer
Ensuring a comfortable working environment is the employer's responsibility, not a gesture of goodwill. Only by creating proper working conditions, the employer has the right to demand from employees to work on schedule. This rule is enshrined in article 163 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation. If the norms stipulated by the sanitary rules are violated, the employer takes immediate measures to eliminate them.
An employee has the right to apply to the State Labor Inspectorate for the protection of his rights.
The Sanitary and Epidemiological Service, upon a complaint by any worker, can inspect the enterprise. If violations are detected, a fine is imposed (from ten to twenty thousand rubles).
A person spends almost his entire conscious part of his life at the workplace. It is for this reason that the requirements that regulate the hygienic requirements of the microclimate in the premises where people work are natural. It is very important to comply with all these rules and regulations in office-type premises, where a person uses primarily mental activity. And this type of work is characterized by relative physical inactivity. This leads to the fact that the negative consequences of an incorrect working regime are further exacerbated.
The legislation provides for a number of laws regarding the temperature regime in office-type premises, as well as the liability of the owner (employer) for non-compliance and violation.

Temperature regime and microclimate very strongly affects the performance and well-being of a person. A low or high air temperature that has a long-term effect on a working person not only negatively affects human health, but also greatly reduces the productivity of his work. People working in office premises perform a wide variety of activities, most of which require being in one specific position for a long period. This is mainly a sedentary and sitting position:
- Making decisions.
- Communication with customers.
- Paperwork.
- Computer work and other similar professions.
Physical inactivity and mental work not very well coexist with the uncomfortable temperature regime of the air in an office-type room.
After conducting many experiments, the researchers found that even minor fluctuations in air temperature so strongly affect the efficiency of work in the office that, if it is impossible to provide the desired microclimate, it makes sense to shorten the working day.
It is very important to provide an appropriate temperature regime in the office. This is the obligation of the employer under the law, regardless of the level of subordination and the form of ownership of the organization.
Optimum or comfort
Everyone who works in the office wants to carry out their activities in conditions of maximum comfort... But this concept is highly subjective, since it is tied to the personal feelings of each individual individual. And these feelings, as you know, are different for everyone. What is an excellent option for one individual may simply be unacceptable to another. It is because of this that in regulations and office documents do not use such a concept as "comfortable conditions".
Instead of the subjective term “comfort”, a more definite and precise parameter “optimal conditions” is used in professional vocabulary. As for the optimal air temperature, this value is determined through complex calculations and physiological studies. The calculation takes into account the average human needs.
Optimal temperature requirements are legal. This is recorded in certain regulatory documents.
SanPiN on the protection of human health
 Into a special code Russian Federation all standards are collected. This code defines optimal health and hygiene standards for different spheres human activities, including for employment. These documents relate to the technical and medical fields. At the same time, it is also legislative, it is for this reason that it is necessary to fulfill all these norms.
Into a special code Russian Federation all standards are collected. This code defines optimal health and hygiene standards for different spheres human activities, including for employment. These documents relate to the technical and medical fields. At the same time, it is also legislative, it is for this reason that it is necessary to fulfill all these norms.
The abbreviation SanPiN stands for sanitary rules and norms. The document that regulates the workplace optimal conditions called SanPiN 2.2.4.548-96 and reads as follows: hygienic requirements for the microclimate in production premises... These SanPiN provide labor protection regulations for office workers and workers in production. These SanPiNs were adopted within the framework of Federal Law No. 52 of March 30, 1999 "On the Sanitary and Epidemiological Welfare of the Population."
Compliance with the requirements of SanPiN by the employer supported by articles Labor Code Of the Russian Federation No. 209 and 212. They talk about responsibility in case of non-compliance by the employer with the rules of labor and health protection, as well as about timely measures of rehabilitation, treatment and prevention, sanitation and other of a similar nature... Article 163 of the Labor Code of the Russian Federation prescribes that the employer must take a set of measures in order to ensure an optimal working microclimate.
What measures can be taken
The solution to this problem may be the following options:
- Equipment for the recreation of a special room.
- Transfer of a worker to another workplace.
- Earlier dissolution of houseworkers.
- Additional breaks.
If the employer refuses to comply with the requirements to ensure optimal performance, then he can be charged with two offenses at the same time.
- Violation of sanitary norms and rules (room temperature norms do not correspond to normative indicators).
- Ignoring labor legislation due to the fact that people work in inappropriate conditions.
If the boss in this situation is inactive and does not agree to provide employees with another workplace, then the time that he was in unfavorable conditions equates to a shift (daily work day) in duration. In other words, you can freely talk about employee overtime at the initiative of the boss with all the ensuing financial and legal consequences.
Seasonal requirements for air temperature in office premises
 In warm and cold seasons, the optimal room temperature conditions are achieved different ways... Based on this, we can conclude that the requirements for the indoor microclimate will differ. Accordingly, the measures that are provided for by SanPiN, in the event that it is impossible to ensure the optimal temperature regime or it is violated, will also have differences.
In warm and cold seasons, the optimal room temperature conditions are achieved different ways... Based on this, we can conclude that the requirements for the indoor microclimate will differ. Accordingly, the measures that are provided for by SanPiN, in the event that it is impossible to ensure the optimal temperature regime or it is violated, will also have differences.
To keep it not too hot
Prolonged stay in a room where the air temperature is very high is especially detrimental to health and performance. In a closed working room, this heat and stuffiness can be aggravated by a large crowd of people, the presence of working office equipment and adherence to a specially entered dress code.
It is because of this that the optimal temperature values and permissible maximum values for the hot season were established by law. For office workers with an air humidity of 40-60%, they are 23-25 degrees. A temperature rise of up to 28 degrees is permissible.
Excess air temperature in the office during the summer
If inside the office the thermometer deviates from the optimum by at least 2 degrees, then it becomes much more difficult to work. The employer will need to provide an air conditioner in the employees' premises and provide it Good work as well as timely service.
If suddenly for some reason this is not done, then the employee should not resignedly endure the unbearable heat, while still trying to meet everyone professional requirements... SanPiN allow with good reason to shorten the employee's standard eight-hour day, for which they were designed the following temperature requirements:
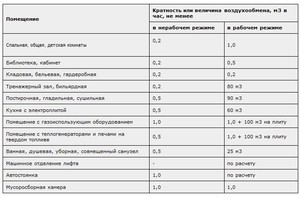
Many workers celebrate Negative influence air conditioner on your health, which is harmful compared to stuffiness and heat. According to the same requirements of SanPiN, along with humidity and temperature indicators, the speed of air movement in the room is limited, which should be in the range from 0.1 to 0.3 m / s. From these requirements of SanPiN it follows that an employee should not be under the jet of a blowing air conditioner.
Cold is the enemy of work
No work is good in a cold room, especially in an office, when the body cannot warm itself up with movement. There are categories of blue-collar occupations in which it is permissible for a short time to lower the temperature of the air to 15 degrees, but this does not apply to those people who work in the office.
Inside the office space, in cold weather, the temperature regime must be observed in the range from 22 to 24 degrees. The fluctuation of these values is possible, but not more than 2 degrees. For a short period of time, the thermometer may deviate from permissible norm maximum 4 degrees.
What to do if the office space is cold
Only if the air temperature does not drop below 20 degrees, the working personnel must be at the workplace for a full working day (8 hours). With each lowered degree, the working time is reduced:

Temperature measurements and their features
Accuracy of temperature measurements must be observed... This is due to the fact that each degree plays a special role in the duration of the working time.
If employees or the employer are unscrupulous, it may be tempting to understate or overestimate the true temperature values. It is possible that a mistake is made due to the fact that it is incorrectly placed or faulty device that you are measuring.
To avoid complications with the determination of air temperature indicators, SanPiN oblige to place the device at a distance of 1 meter above the floor level.
What is the responsibility of the employer if he does not comply with the requirements of the office microclimate
If for some reason the employer refuses to install an air conditioner (fan) in the summer and a heater in the winter, thereby maintaining the optimal temperature regime in the norm, then his subordinates should not tolerate it due to the fact that they can be fired. You can contact the Sanitary and Epidemiological Service. She will definitely come to your enterprise with a check. If during the check the complaint is confirmed, then the authorities cannot avoid responsibility for non-compliance with the requirements of SanPiN.
And also for non-compliance with the requirements, the employer faces a fine of about 12 thousand rubles. If, after a second check, the same violations are revealed again, then its activities will be suspended for 3 months in accordance with Article 6.3.
Workplace temperature: sanitary standards and regulations from 2016
From 1.01.2017 all employers and employees must comply with the new requirements of the sanitary and epidemiological service, which are related to physical factors in the workplace. This was approved by the decree of the chief sanitary state doctor of the Russian Federation dated June 21, 2016, Order No. 81. The updated sanitary standards and rules determine the impact on the human body and its activity of such indicators as:

It is customary to call the standards the maximum acceptable level of this or that factor, as well as its impact on a person who is at least 8 hours at the workplace, within the permissible limits. This impact should not lead to deviations in health or disease (SanPiN 2.2.4.3359-16 paragraph 1.4).
Due to the fact that new sanitary requirements were introduced, some of the old ones from January 2017 have ceased to apply. One of these is SanPiN 2.2.4.1191-03 o "Electromagnetic fields in industrial conditions".
To date, the question of what should be the temperature in the workplace for sanitary regulations is relevant for workers and employers.
Sanitary rules on air temperature in the workplace
Sanitary rules establish the optimal temperature readings in the workplace. These indicators include:
- Air speed.
- Relative humidity.
- Surface temperature.
- Air temperature.
 Normal sanitary indicators for cold and warm seasons are determined separately. The cold season is considered to be the period when the average daily outdoor air temperature has approached 10 degrees and below. If outside the window is more than this value, then this can be considered a warm season.
Normal sanitary indicators for cold and warm seasons are determined separately. The cold season is considered to be the period when the average daily outdoor air temperature has approached 10 degrees and below. If outside the window is more than this value, then this can be considered a warm season.
Thermometer readings in an office building are slightly different in winter and summer. At any time man needs heat balance with the environment.
In addition to all this, depending on the energy consumption of a person, there are different indicators of the thermometer in various fields of activity.
Requirements for methods of measuring and organizing microclimate control in accordance with sanitary standards
Measurements of microclimatic indicators in order to control their compliance with sanitary standards should be held during the warm season- on those days when the outside air temperature differs from the maximum average temperature of the hottest month by no more than 5 degrees, and in cold weather - when the difference from the coldest month is no more than 5 degrees. The frequency of such measurements is determined by the functioning of the sanitary and technological equipment, as well as the stability of the production process.
When choosing the time and measurement sites, it is worth considering all the factors that affect the microclimate of the workplace (the functioning of heating and ventilation systems, phases technological process and others). It is worth measuring microclimatic indicators at least 3 times per shift. If the indicators associated with technological and other reasons fluctuate, then additional measurements should be taken at the lowest and highest values of the thermal load on the employee.
Measurements should be taken at the workplace. If your place of work is several production sites, then the indicators should be measured at each separately.
 If there is a source of local moisture release, cooling or heat release ( outdoor baths, heated units, gates, doorways, windows and others like them), then the indicators need to be measured at points that maximally and minimally distant from the thermal source of influence.
If there is a source of local moisture release, cooling or heat release ( outdoor baths, heated units, gates, doorways, windows and others like them), then the indicators need to be measured at points that maximally and minimally distant from the thermal source of influence.
In those rooms where there is a high density of workplaces, but there are no sources of moisture release, cooling and heat release, the places for measuring microclimatic indicators, relative to the speed of movement and air humidity, should be evenly distributed over the area of the room according to the following principle:
- Room area up to 100 square meters - the number of measured areas is 4.
- From 100 to 400 meters - 8.
- More than 400 - the distance between sites should not be more than 10 meters.
Sedentary work movement speed and temperature indicators should be measured at heights of 0.1 and 1 meter from the floor, and relative air humidity - 1 meter from the working platform or floor. In standing operation, the driving speed and temperature are measured at heights of 1 and 1.5 meters, and the relative humidity is 1.5 meters.
If there is a radiant heat source, then at the workplace the thermal radiation is measured from each source, perpendicularly positioning the device to the incident flow. These measurements are taken at heights of 0.5, 1 and 1.5 meters from the working platform or floor.
The temperature on the surfaces is measured in cases where the place of work is at a distance of no more than 2 meters from them.
Relative humidity and air temperature in the presence of sources of air flows and heat radiation at workplaces measured by aspiration psychrometers... If there are no such sources, then the relative humidity and temperature regime of the air can be measured with psychrometers, which are not protected from the effects of the speed of movement and thermal radiation of the air. You can also use those devices that separately measure indicators of humidity and air temperature.
Air speed is measured by rotary anemometers (cup, vane and others). Small values of air speed (less than 0.5 meters per second), especially if there are multidirectional flows, are measured by thermoelectric anemometers, as well as spherical and cylindrical catathermometers, if they are protected from thermal radiation.
Surface temperatures measured by remote (pyrometers) or contact (electrothermometer) devices.
The intensity of thermal radiation is measured with devices that provide the sensor's viewing angle as close as possible to the hemisphere (not less than 160 degrees), sensitive in the visible and infrared spectral regions (radiometers, actinometers, and others).
The permissible error of the measuring instruments and the measuring range must meet the following criteria:

Based on the results of the study, a protocol is drawn up which reflects general information about a production facility, placement of sanitary and technological equipment, sources of moisture release, cooling, heat release; all diagrams for the placement of measurement sites for all the necessary parameters of the microclimate and other data are given.
Ultimately, at the end of the protocol, the results of the measurements performed should be assessed in accordance with regulatory sanitary requirements.
Didn't receive an answer to your question? Suggest a topic to the authors.






